Governor Newsom Extends Key Provision to Continue Fast-tracking Wildfire Projects

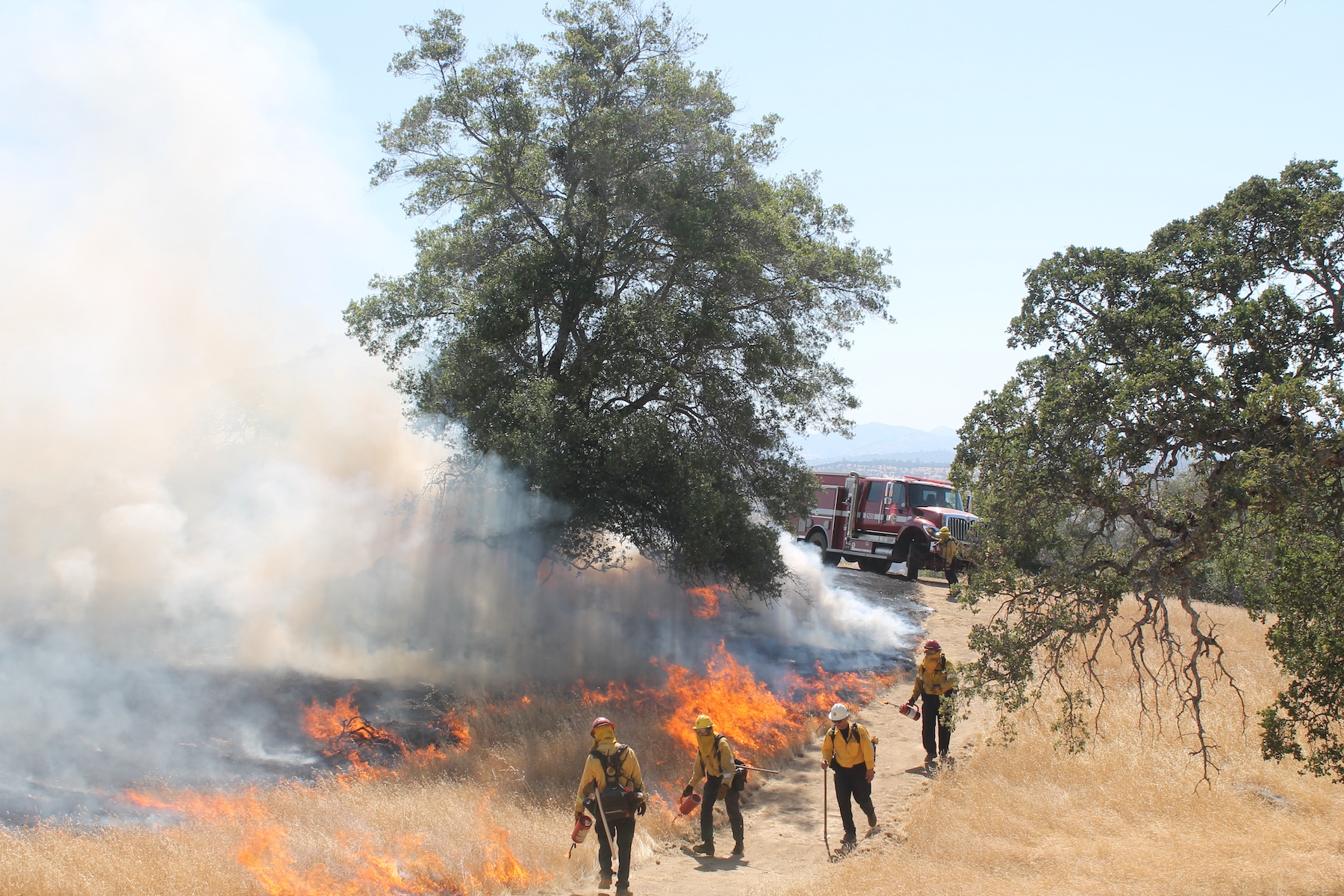
Governor Newsom Extends Key Provision to Continue Fast-tracking Wildfire Projects
December 31, 2025 – Governor Newsom announced the extension of a key provision of the March 2025 Emergency Proclamation on wildfire that will enable California to continue moving faster than ever to reduce catastrophic wildfire risk through a streamlined permitting process for wildfire prevention projects. Previously, qualifying projects had to be “initiated” in the calendar year 2025. Now, eligible projects can be initiated through May 1, 2026. Through this fast-track process, projects are now being approved in as little as 30 days, saving a year or more of review time for more complex projects. To date, nearly 240 projects covering more than 40,000 acres have been approved statewide and half are already underway or have been completed.
California Unveils First-ever Statewide LiDAR Maps
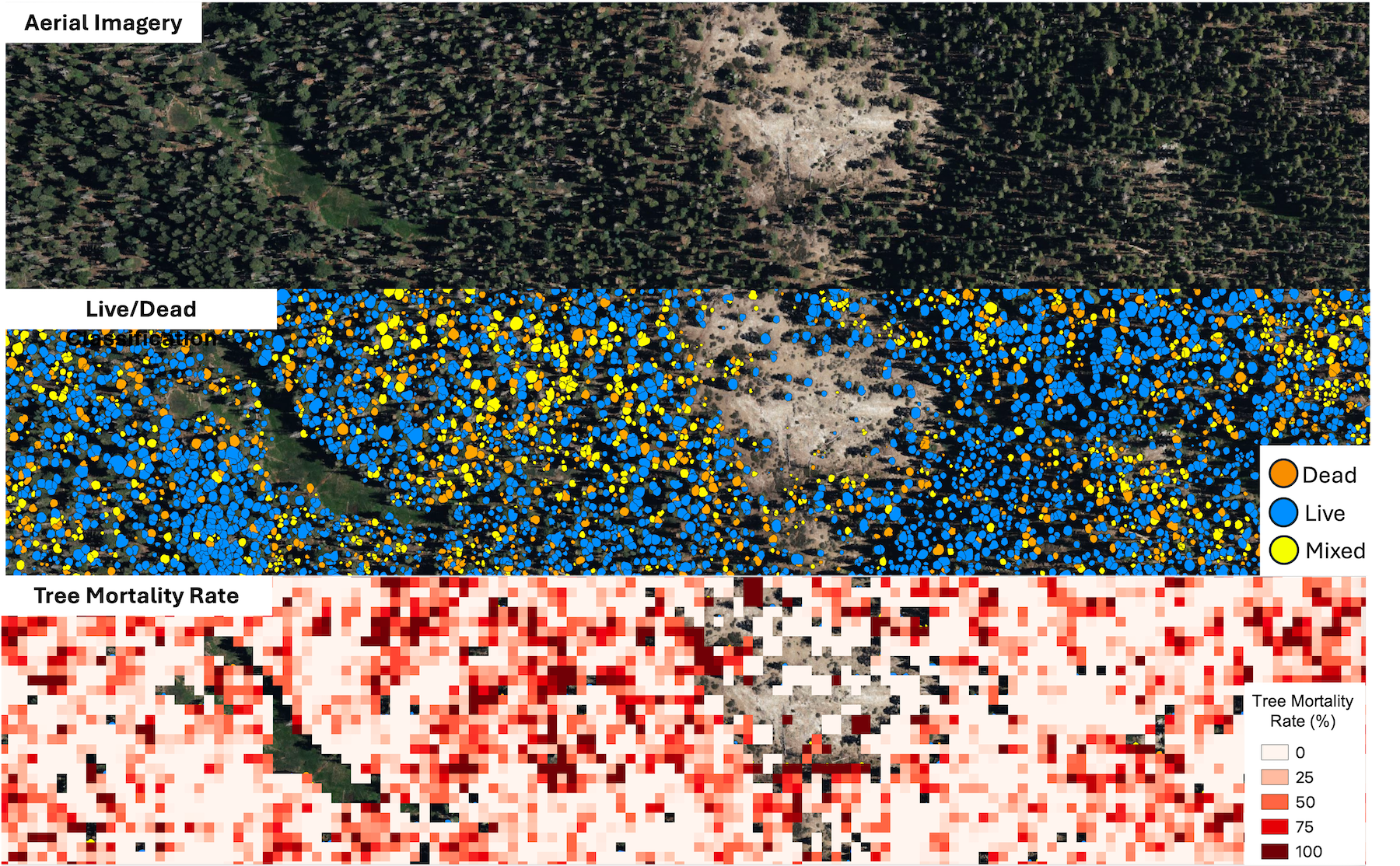
California Unveils First-ever Statewide LiDAR Maps
December 12, 2025 – The California Natural Resources Agency (CNRA), in partnership with the California Air Resources Board (CARB), NASA Ames Research Center, and the Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force announced the public release of consistent, statewide datasets on forest and vegetation conditions built from LiDAR, the gold standard for forest and vegetation information. This release is powered by the Wildfire, Ecosystem Resilience, and Risk Assessment Initiative (WERK) which has processed more than 100 million acres of LiDAR data across California. That total includes 40 million acres collected through CNRA’s use of $30M dedicated by the State Legislature for wildland remote sensing. For the first time, California has a single wall-to-wall picture of forest and vegetation conditions that is the highest resolution available and consistent across the entire state. Agencies, tribes, researchers, land managers, and community partners can begin incorporating the released products into their own tools, models, and planning processes immediately.
LiDAR (light detection and ranging) creates detailed three-dimensional maps of the landscape. Using LiDAR, the WERK initiative provides information on where trees and shrubs are, how tall and dense they are, where ladder fuels can carry fire into the canopy, and how much carbon is stored in vegetation. The statewide release includes 10-meter and 30-meter resolutions datasets that cover all of California. In addition, 1-meter datasets are already available in select areas, with statewide access to ultra-high resolution data launching in early 2026.
The WERK datasets are being hosted in partnership with the Wildfire Science & Technology Commons at the San Diego Supercomputer Center, supported by the National Science Foundation. These products will also be incorporated into the Task Force’s California Landscape Metrics beginning with the next data refresh.
Governor Newsom Signs Executive Order to Expand Beneficial Fire Use

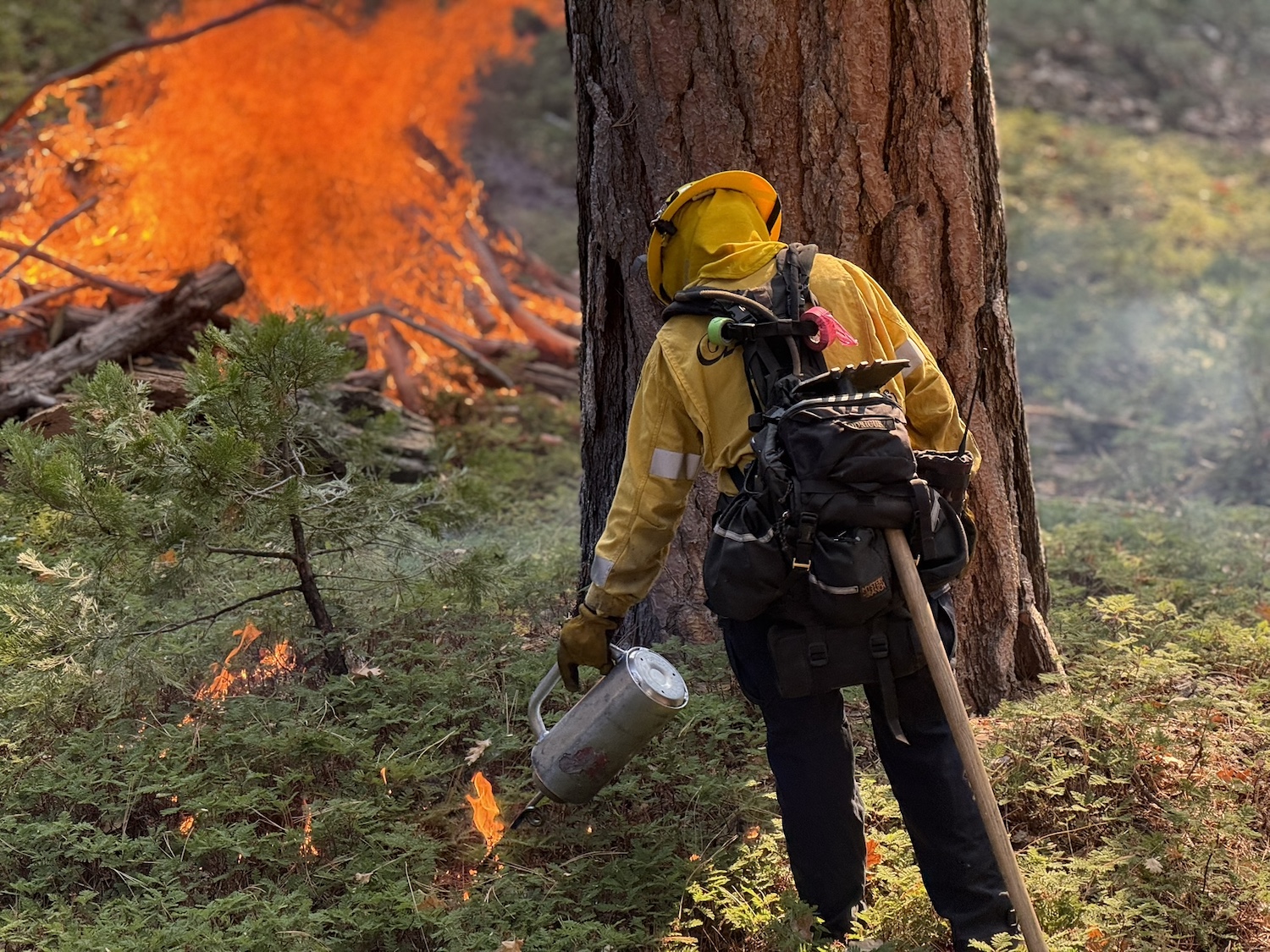
Governor Newsom Signs Executive Order to Expand Beneficial Fire Use
October 29, 2025 – Governor Newsom signed an executive order directing state agencies to reduce red tape and expand tools to safely deploy beneficial fire projects. The order directs a suite of actions to fast-track critical work in the coming months with a key focus on directing state agencies to provide immediate on-the-ground support to local governments and fire practitioners to maximize use of beneficial fire, helping ensure that California does not miss the critical fall weather window to conduct prescribed and cultural burns. The order supports collaborative efforts to update beneficial fire permitting, address air quality concerns associated with smoke and enable resource conservation districts and other entities to carry out beneficial fire projects.
The executive order helps strengthen and build on California’s wildfire prevention strategy by:
- Accelerating funding and projects: Distributes funding to resource conservation districts and other eligible government agencies in advance of beneficial fire work, as well as creates more simplified grant funding processes.
- Expanding local participation: Removes policies and regulatory roadblocks that would make it more difficult for local agencies to engage in this work, including suspending the state law that prohibits resource conservation districts and volunteer fire departments from participating in the Prescribed Fire Liability Claims Fund Pilot Program.
- Working with tribal communities: Directs state agencies to continue prioritizing tribal consultation, access, collaboration, and co-management—so we can work together to expand and support cultural burning and other forms of tribal stewardship.
- Increasing education and data: Directs the California Air Resources Board (CARB) to create new modeling and related technologies, such as the Prescribed Fire Information Reporting System (PFIRS) and make this technology available to support air districts’ efforts to promote fast, efficient and low-cost permitting, and expands training opportunities for beneficial fire practitioners.
- Mitigating air quality risks: Increases collaboration and creates new best practices that provide beneficial fire practitioners consistent permitting and smoke management plan guidance while protecting public health and communicating potential smoke impacts to the public and create guidance for local communities.
Building on nation-leading progress
The executive order builds on unprecedented progress already made by state, federal, tribal, local, and nonprofit partners to increase the pace and scale of beneficial fire implementation across the state. Key advancements include:
- The Task Force issued California’s Strategic Plan for Expanding the Use of Beneficial Fire (2022), a comprehensive roadmap to coordinate the efforts of state, federal, and tribal partners to treat up to 400,000 acres with beneficial fire annually by 2025.
- Prescribed fire treatments in California nearly doubled between 2021 and 2023. Federal, state, and local agencies completed 260,000 acres of prescribed fire treatments in 2023.
- In May, CAL FIRE, for the first time ever, met and exceeded its 50,000-acre goal for beneficial fire as outlined as a goal within the California Strategic Plan for Expanding the Use of Beneficial Fire. This was accomplished even with the Park Fire in late 2024 and the January 2025 fires in Los Angeles.
- As of June, CARB, in close coordination with the California Air Pollution Control Officers Association, has held over 20 prescribed fire training sessions for stakeholders to discuss smoke management, public information, and tools and technology related to prescribed fire.
- In 2021, CARB released California Smoke Spotter — a critical tool to inform the public of air quality impacts from wildfire and prescribed fire smoke.
- The Governor and Legislature established a first-in-the-nation Prescribed Fire Liability Claims Fund in 2022 backed with $20 million in state funding, to accelerate beneficial fire on private lands by covering losses in the rare instance that a prescribed or cultural burn escapes control.
- In September 2024, Governor Newsom signed SB 310, which reduces barriers for California Native American tribes to conduct cultural burns in their ancestral territories. The Karuk Tribe and the California Natural Resources Agency (CNRA) entered into the landmark SB 310 Cultural Fire agreement in February 2025. Out of this effort, the Tribe and CNRA have developed a template agreement for other tribes to utilize educational materials to support government-to-government collaboration in advancing cultural fire.
- In September 2024, Governor Newsom signed SB 1101, which streamlines CAL FIRE’s contracting and procurement process to support beneficial fire.
- In August 2023, the Governor’s Wildfire and Task Force launched an Interagency Treatment Dashboard that provides transparency on the location of completed beneficial fire projects.
- CAL FIRE’s Prescribed Fire Monitoring Program released the first version of a manual outlining field monitoring protocols in 2023 to assist land managers with unit selection, data collection, tools and technologies, data storage, and analysis procedures.
Governor Newsom Unveils California’s Updated Climate Adaptation Strategy

Governor Newsom Unveils California’s Updated Climate Adaptation Strategy
September 4, 2025 – Governor Newsom unveiled California’s updated Climate Adaptation Strategy — the state’s overarching framework to better protect communities and nature from dangerous climate impacts. California last updated the Strategy in 2021. The updated strategy sets strategic direction through six priorities:
- Protecting communities most vulnerable to climate change
- Improving public health and safety to protect against increasing climate risk
- Building a climate-resilient economy
- Expanding nature-based climate solutions and strengthening the resilience of natural systems
- Making decisions based on best available climate science
- Partnering and collaborating to leverage resources
These priorities are supported by cross-cutting climate resilience actions, each with associated success metrics. The strategy aligns with and builds on the goals set forth by California’s Wildfire and Forest Resilience Action Plan and includes the following actions specific to wildfire resilience:
- Prioritize actions that reduce wildfire risks to California Native American tribes and climate vulnerable communities.
- Support wildfire-prone communities by increasing the capacity of local and regional partnerships to build and maintain a pipeline of forest health and fire prevention projects.
- Invest Community Development Block Grant Disaster Recovery funds in long-term disaster recovery and resilience building that targets the unmet housing recovery needs of low and moderate-income households in a way that mitigates disaster risk and reduces future losses among vulnerable communities.
- Reduce health impacts of wildfire and prescribed fire smoke.
- Reduce the risk of energy infrastructure-related ignitions that lead to catastrophic wildfire.
- Bring to scale a thriving forest and wood products market in California that leverages public investments by energizing private capital for sustainable forest management, regional economic recovery, and climate resilience.
- Increase the pace and scale of wildfire resilience and forest health projects.
- Reduce risks of wildfire through increased use of fuel breaks and fuels reduction.
- Assist the federal government in scaling up forest treatments by supporting collaborative forest management and encouraging landscape level planning.
- Coordinate and guide prescribed fire and cultural fire activities and address the key barriers to its widespread use in California.
- Expedite permitting processes for wildfire and forest resilience projects using exemptions or the California Vegetation Treatment program.
- Invest in science-based management focused on climate resilience of California’s fire adapted landscapes.
- Improve wildfire smoke guidance for schools, children, and other vulnerable populations. Develop outreach materials for health care providers and the public on wildfire smoke health effects and ways to decrease exposure.
- Collaborate with federal, state, tribal, and private partners to increase pace and scale of restoration of fire-adapted lands and maximize the climate resilience benefits of these treatments.
- Leverage federal funding to support fire-hardening roads and communities.
California Extends Timeline for Some On-the-ground Fuel Reduction Work Eligible for Streamlining

California Extends Timeline for Some On-the-ground Fuel Reduction Work Eligible for Streamlining
Following Governor Newsom’s Emergency Proclamation on wildfire, the California Natural Resources Agency (CNRA) and the California Environmental Protection Agency (CalEPA) have approved over 100 critical fuels reduction projects spanning tens of thousands of acres across the state, moving at record pace while also ensuring environmental protections are being upheld.
Recognizing that reducing wildfire risk to landscapes and communities may require multiple stages of treatments, California recently extended regulatory suspensions to allow qualifying long-term fuels reduction projects up to five years from commencement to complete on-the-ground work. Typically, projects must be completed within two years of initiating work on-the-ground. However, extensions may be allowed for up to five years from the commencement of on-the-ground work for fuels reduction projects that have been awarded funding from the following state grant programs:
- CAL FIRE Wildfire Prevention Grants
- CAL FIRE Forest Health Grants
- California Forest Improvement Program within the Coastal Zone (projects must have fuels reduction as a key objective)
- Climate Bond early action funding (Prop 4)
- Other programs funded through Wildfire Resilience Packages since 2020-2021
Projects that receive extensions must submit progress reports that are required under their grant agreements to the suspension review teams at CNRA and CalEPA. Additionally, state agencies within CNRA (e.g. CAL FIRE, State Parks, CDFW, State Lands Commission, State Conservancies) are eligible to apply for extensions of up to five years from the commencement of on-the-ground work for projects that they lead and directly implement.
For eligibility criteria, requirements for environmental protections, FAQs, support resources for project assistance, a map of approved projects, and the application link, visit the Task Force webpage. The deadline to submit suspension requests for projects is December 31, 2025.
California Signs Cultural Burning Agreement with Karuk Tribe
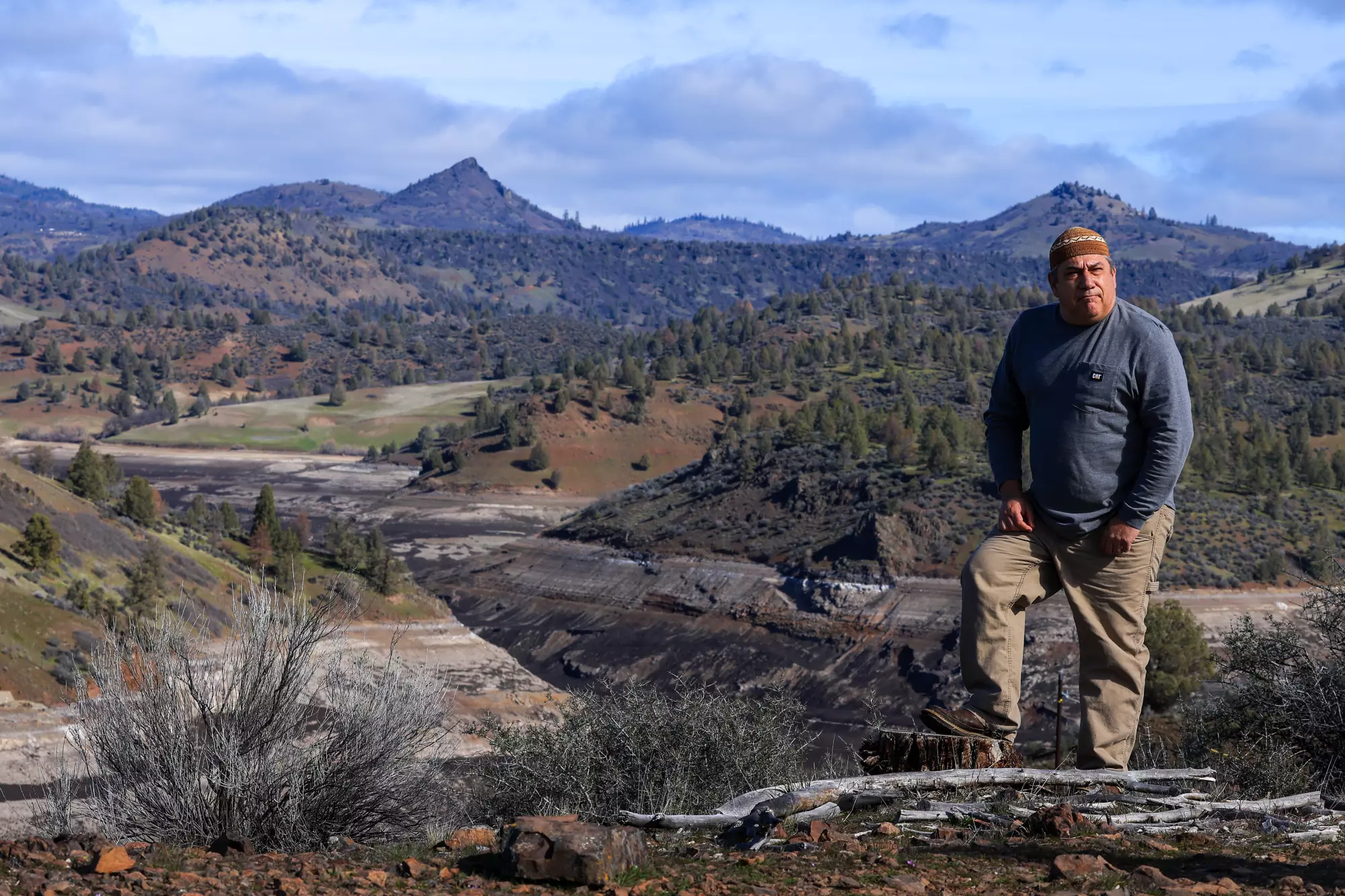

California Advances Wildfire Resilience and Honors Tribal Sovereignty Through Cultural Burning Agreement with the Karuk Tribe
March 7, 2025 – The Karuk Tribe and the California Natural Resources Agency (CNRA) have entered into a historic agreement as part of CNRA and CalEPA’s announcement that SB 310 is now in effect. This legislation and agreement acknowledges tribal sovereignty and addresses historical injustices while contributing to the mitigation of catastrophic wildfire by enabling CNRA and local air districts to enter into agreements with federally recognized California Native American tribes to support them in conducting cultural burns in their ancestral territories. For more information, read the FAQ on SB 310.
CNRA will be hosting a webinar about the landmark cultural burn agreement with the Karuk Tribe and SB 310 on April 1, 2025 at 1pm.
New Web Resources Help Californians Find Relief from Smoke and Prepare for Wildfires
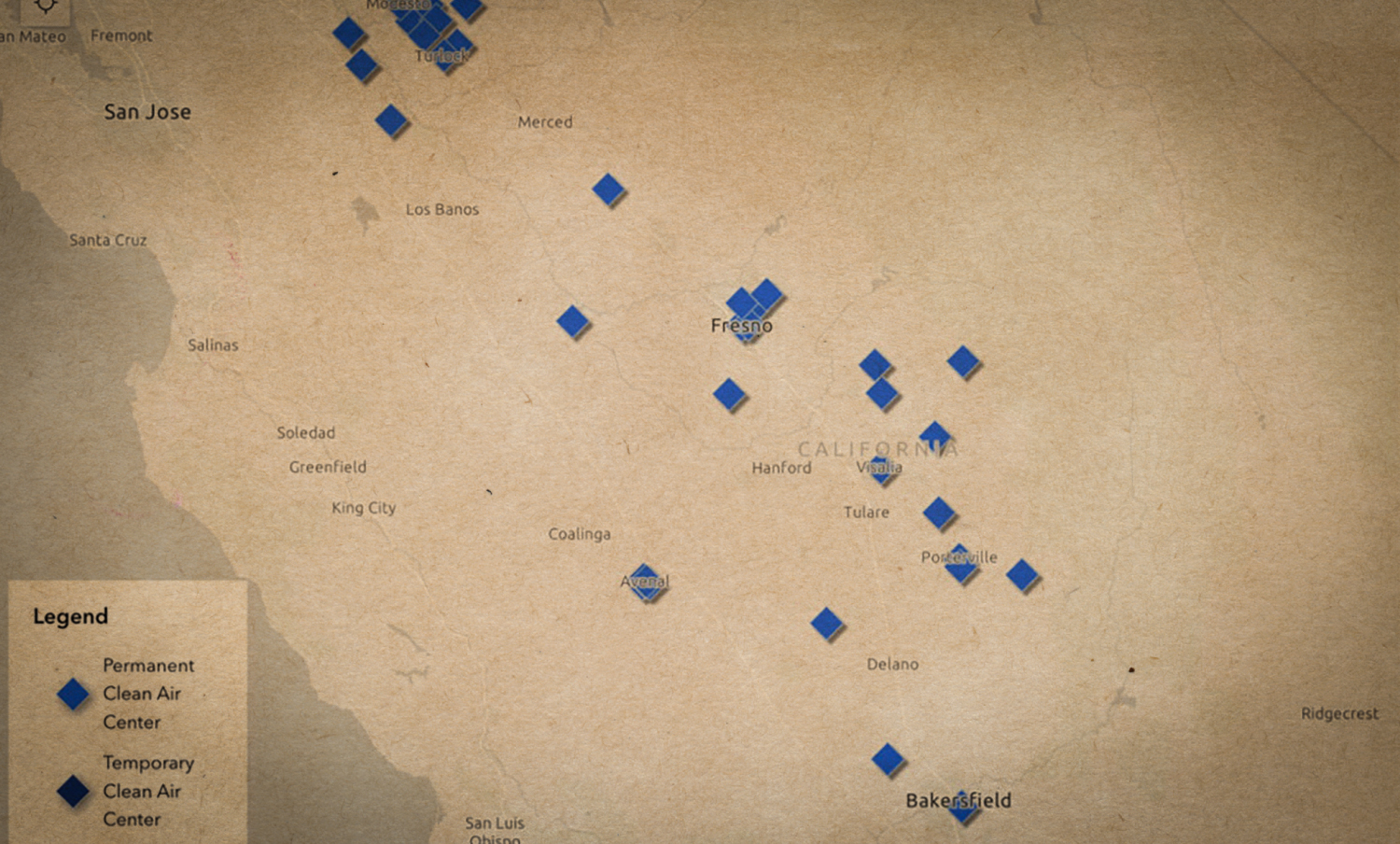
New Web Resources Help Californians Find Relief from Smoke and Prepare for Wildfires
June 24, 2024 – Clean Air Centers Maps Shows Where to Find Relief from Wildfire Smoke: The California Air Resources Board announced the launch of an interactive, statewide map that offers a one-stop-shop for information about the location and services available at Clean Air Centers. Clean Air Centers will offer Californians who don’t have access to adequate air filtration a safe place to go during periods of heavy smoke. Built in collaboration with local air quality control districts, the online map makes it possible to see where Clean Air Centers are located and provides easy-to-access information, including operating hours, contact information and on-site resources like free Wi-Fi.
CAL FIRE Updates Wildfire Preparedness Website: In preparation for the fire year, CAL FIRE has updated the ReadyForWildfire.org site. This one-stop-shop provides advice and guidance on everything from home hardening and defensible space, to what to pack for evacuation, to what California is doing to enhance and protect forest health.
CAL FIRE Invests $47M in School Greening
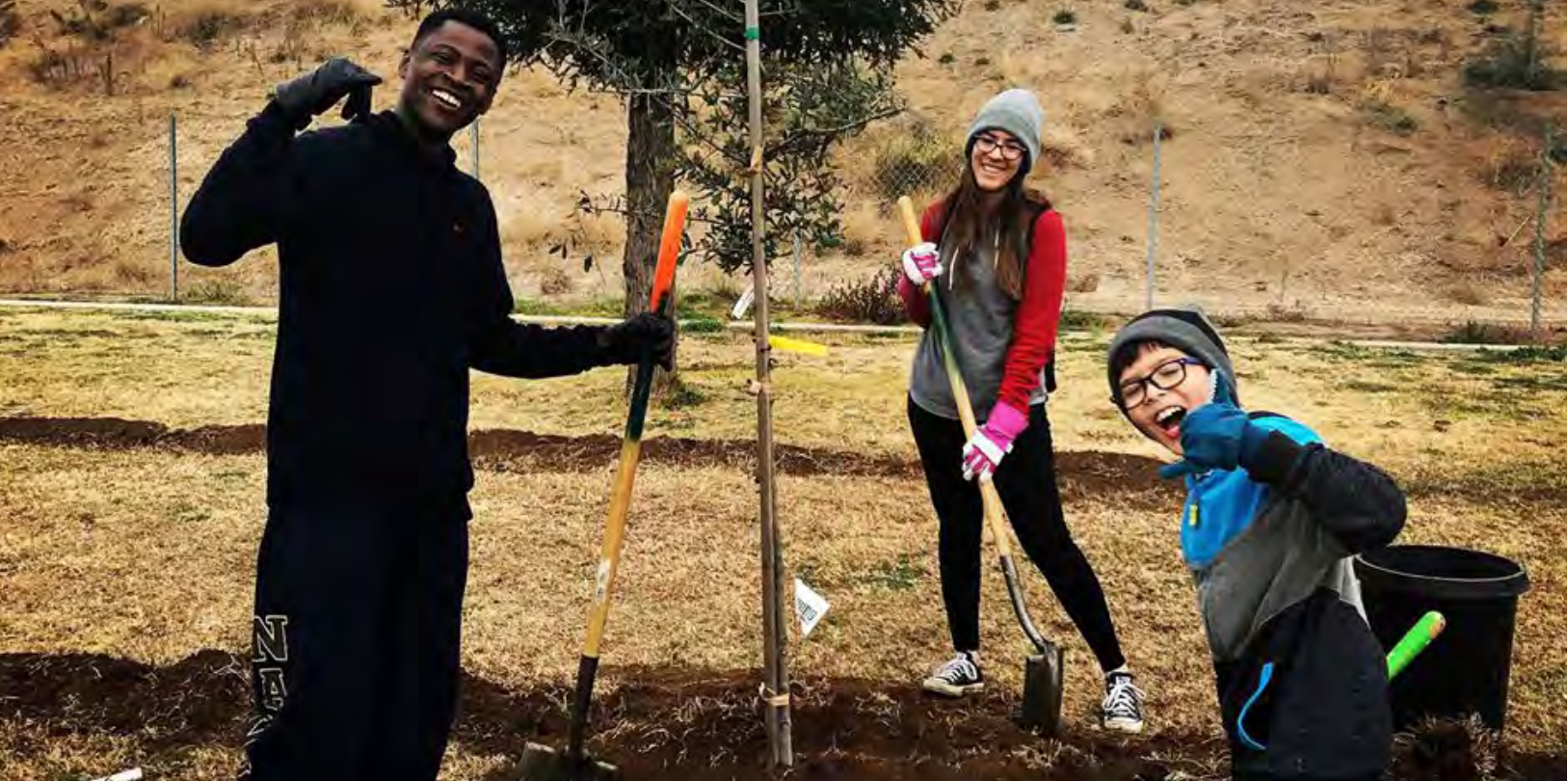

CAL FIRE Invests $47M in School Greening
More shade is on the way! On July 13, Governor Newsom announced CAL FIRE’s $47 million investment to help schools convert pavement to green spaces and plant trees and other vegetation. This first round of CAL FIRE’s $117 million Green Schoolyard Grant program will support 6 implementation projects and 9 planning projects on 100 schoolyards statewide. The program is part of the Governor’s Extreme Heat Action Plan, which is backed by the $52.3 billion California Climate Commitment budget. This program supports the goal of to expanding urban canopy, as laid out in the Task Force Action Plan.
CARB Releases Final 2022 Scoping Plan

CARB Releases Final 2022 Scoping Plan
On November 16, the California Air Resources Board (CARB) released the 2022 Scoping Plan for Achieving Carbon Neutrality (2022 Scoping Plan), which will be presented to the CARB Board on December 15, 2022. The 2022 Scoping Plan lays out a path to achieve targets for carbon neutrality and reduce anthropogenic greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 85 percent below 1990 levels no later than 2045. Significant reductions in fossil fuel combustion will be achieved by deploying clean technologies and fuels, requiring further reductions in short-lived climate pollutants, supporting sustainable development, employing technology to capture and store carbon, and taking increased action on natural and working lands to reduce emissions and sequester carbon.

