See Progress on Protecting People and Communities from Wildfire

From day 1, Governor Newsom declared California’s firefighters and wildfire resilience as a top priority of his administration. And California and partners continue to deliver nation-leading results. Since taking office, the Governor has committed more resources and investments than ever before to significantly boost wildfire response capabilities while tackling root causes of the wildfire crisis head-on.
Here are the top 5 things to know about California’s progress on protecting people and communities from wildfire:
1. Historic Investments Making Big Impacts Statewide

• Invested $2.5 billion: California has invested more than $2.5 billion in wildfire resilience since 2021 and the Governor is committing to invest an additional $1.5 billion from the 2024 voter-approved climate bond (known as Proposition 4).
• Doubled CAL FIRE resources: To support more effective wildfire response, CAL FIRE nearly doubled its fire protection staff since 2019 from 5,829 to 10,741 positions, and nearly doubled its fire protection budget from $2 billion to $3.8 billion.
• Added 2,400 firefighters: The Governor’s proposed investments will add 2,400 new firefighters to CAL FIRE’s firefighting force over the next five years.
• Boosted Cal OES: Since 2019, the budget of the California Office of Emergency Services (Cal OES), a key agency in responding to and rebuilding after fires, increased from $1.8 billion to $3.1 billion, and its staffing grew from 1,139 to 1,879 positions.
2. On the Ground in California's Wildlands: Unprecedented Results in Record Time
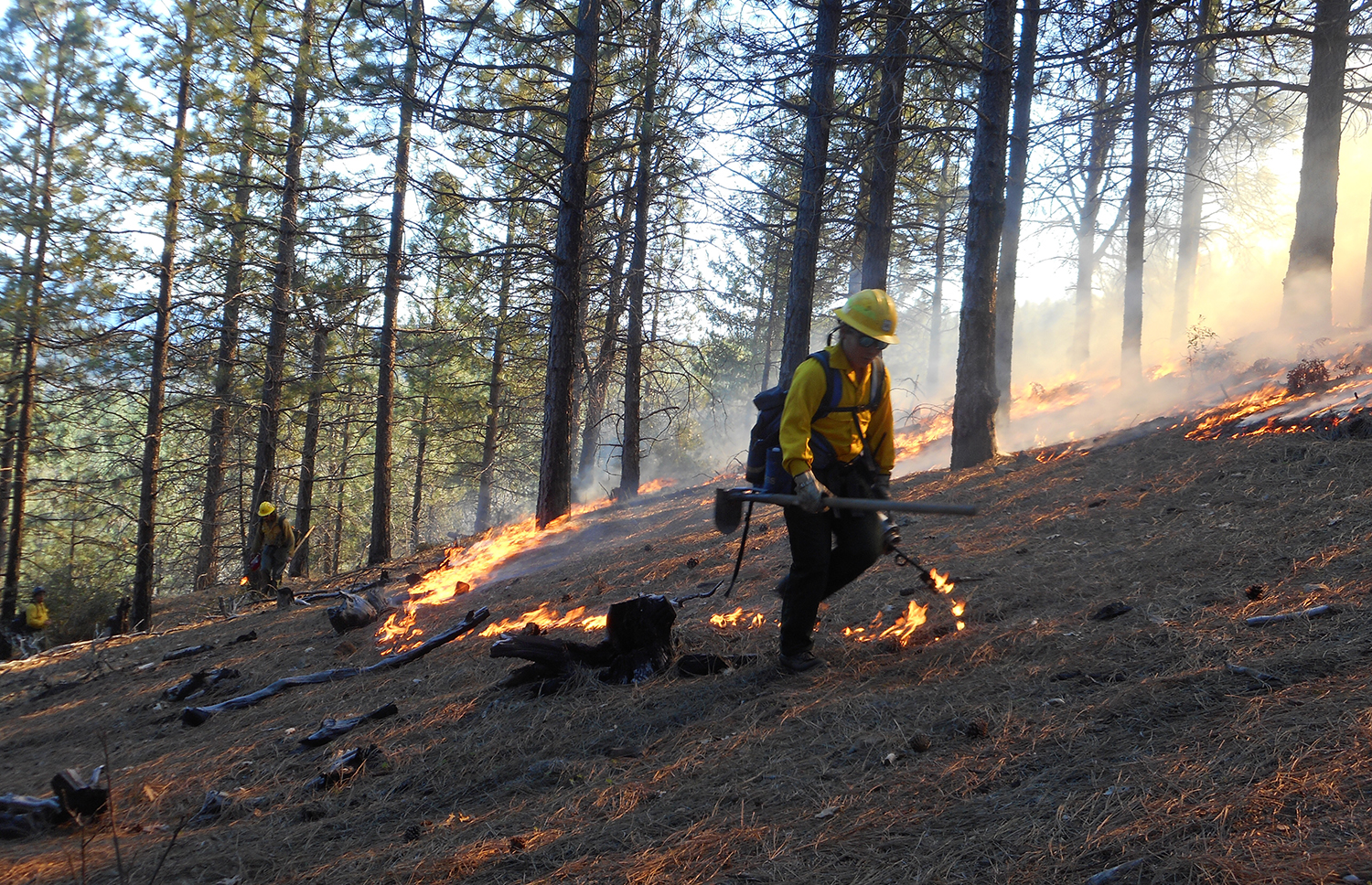

• Launched 2,200 projects: These historic investments continue to pay off. More than 2,200 landscape health and fire prevention projects are underway, and from 2021-2023, the state and its partners treated nearly 1.9 million acres, including nearly 730,000 acres in 2023.
• Nearly doubled prescribed fire: Prescribed fire treatments nearly doubled between 2021 and 2023. Federal, state, and local agencies completed 260,000 acres of prescribed fire treatments in 2023.
• Created emergency teams: State and federal partners have established 15 Emergency Forest Restoration Teams (EFRTs) across the state to rapidly restore private forestlands after fires.
• Awarded $500 million to forest health: Since 2021, CAL FIRE has committed more than $500 million in support of 150 wildfire and forest resilience projects through its Forest Health Grant Program
• Built local capacity: The Department of Conservations’s Regional Forest and Fire Capacity (RFFC) program has awarded more than $140 million to communities across the state to create fire adapted communities and landscapes.
• Promoted tribal projects: CAL FIRE awarded $25.7 million in 2023 and 2024 for 18 projects to help California Native American tribes manage ancestral lands and promote wildfire resilience.
3. New Tools Increase Transparency and Show Progress in Action

• Innovative tools for tracking progress: The Governor’s Task Force launched an Interagency Treatment Dashboard to display completed federal, state, local, and private vegetation management projects across the state. The Dashboard, launched in 2023, provides transparency, tracks progress, facilitates planning, and informs firefighting efforts.
• Documenting effectiveness: See for yourself. CAL FIRE’s Fuels Treatment Effectiveness Dashboard spotlights and documents how recent wildfire resilience projects are protecting communities and landscapes when wildfire strikes. Examples of effective resilience projects include the Loafer Creek LLC Vegetation Management Project, where prescribed fires and forest health treatments slowed the 2024 Park Fire and the Starchman Fuel Break Project that reduced the rate of spread of the 2024 French Fire, enabling fire crews to extinguish it.
4. Protecting Neighborhoods and Empowering Communities to Join the Movement
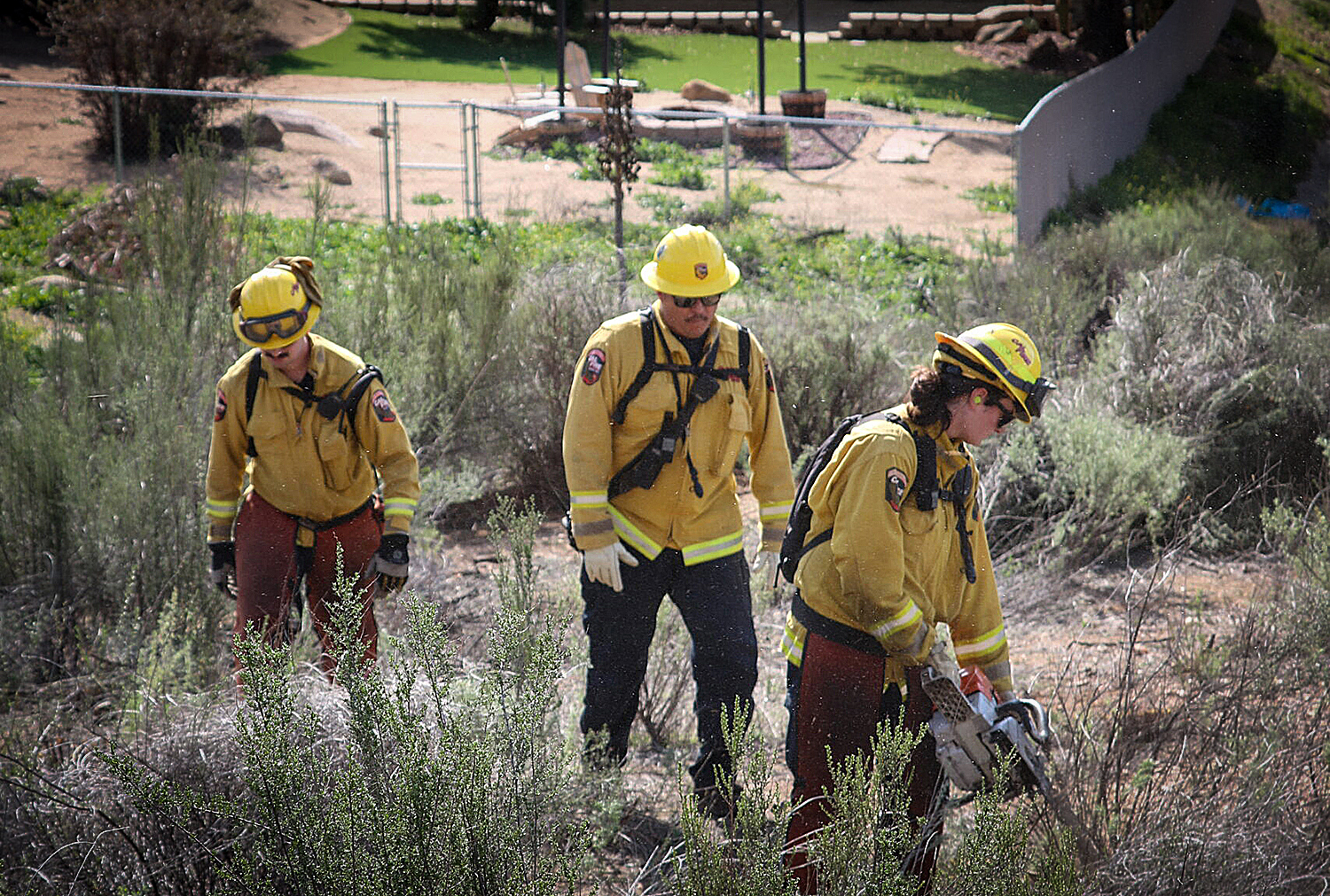

• Awarded $450 million for wildfire prevention: Since 2019, CAL FIRE has awarded more than $450 million for 450 wildfire prevention projects across the state, and conducts Defensible Space Inspections on more than 250,000 homes each year.
• Protecting homes: CAL FIRE established a new California Wildfire Mitigation Assistance Program to coordinate regional and local efforts with state policies, strategies, and programs for community wildfire mitigation, including a home hardening initiative that will provide funding for defensible space and ignition resistant retrofits to approximately 2,400 homes.
• Providing smoke updates: CARB’s California Smoke Spotter mobile app and Prescribed Fire Information Reporting System provide real-time information on smoke impacts from wildfires and prescribed burns.
5. Leading the Future of Fire: Expanding Capacity and Leveraging Technology to Tackle Wildfire
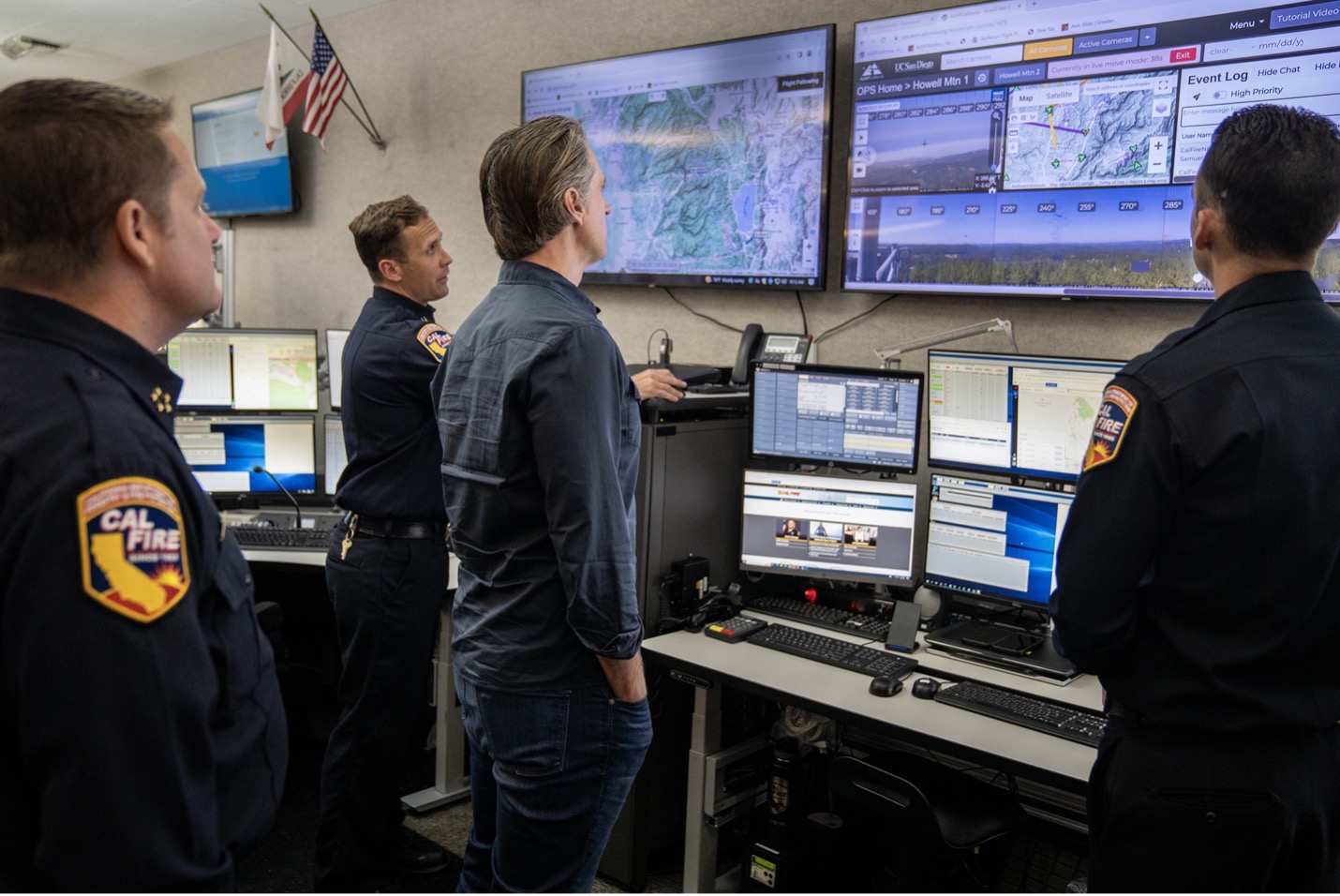

In addition to ramping up state work to increase landscape and community resilience, the Governor has substantially increased funding and staffing levels at CAL FIRE and Cal OES to improve the state’s ability to track, fight, and recover from fires.
• Increased firefighting capacity: CAL FIRE has enhanced its firefighting capabilities with 16 state of the art helicopters (FireHawks) and 7 C-130 tankers. And since 2019, CAL FIRE has added 55 type III engines, for a total of 398. Cal OES has added 106 engines to its fleet, for a total of 261.
• Utilizing AI to detect fires: CAL FIRE partnered with UC San Diego to support the development of ALERTCalifornia which utilizes AI to identify and monitor wildfires. ALERTCalifornia was named one of TIME’s Best Inventions of 2023.
• Integrated fire forecasting: In 2021, Cal OES and CAL FIRE established the Wildfire Forecast and Threat Intelligence Integration Center, in collaboration with the California Military Department and California Public Utilities Commission, to serve as the state’s central organizing hub for wildfire forecasting and coordination of wildfire threat intelligence and data sharing.
• Leveraging technology for fire response: CAL FIRE and Cal OES have also invested heavily in drones, satellite technology for advanced mapping, and AI-powered tools to spot fires quicker, and a Fire Integrated Real-Time Intelligence System (FIRIS) to provide real-time mapping of wildfires.
California Passes Proposition 4 — Providing $1.5 Billion for Wildfire Resilience

California Passes Proposition 4 — Providing $1.5 Billion for Wildfire Resilience
November 5, 2024 – Californians passed Proposition 4, the first-ever climate bond to go before California voters. The proposition provides $10 billion in bond funds for critical wildfire, flood protection, and other climate resilience projects around the state, including $1.5 billion for wildfire resilience. This funding will enable agencies to improve landscape health and resilience and protect communities from wildfire risks through programs such as the Regional Forest and Fire Capacity Program. The funding also includes $50 million for long-term capital infrastructure projects that utilize wildfire mitigation waste for non-combustible uses.
In addition to funding wildfire resilience, $1.2 billion will be used to protect natural lands and preserve biodiversity, with $870 million directed to the Wildlife Conservation Board to help the state to meet its goal to protect 30% of lands by 2030. The approval of Proposition 4 is a major advancement for California’s efforts to increase the pace and scale of wildfire and landscape resilience treatments, adapt to a changing climate, and reach goals set in the California’s Wildfire and Forest Resilience Action Plan.
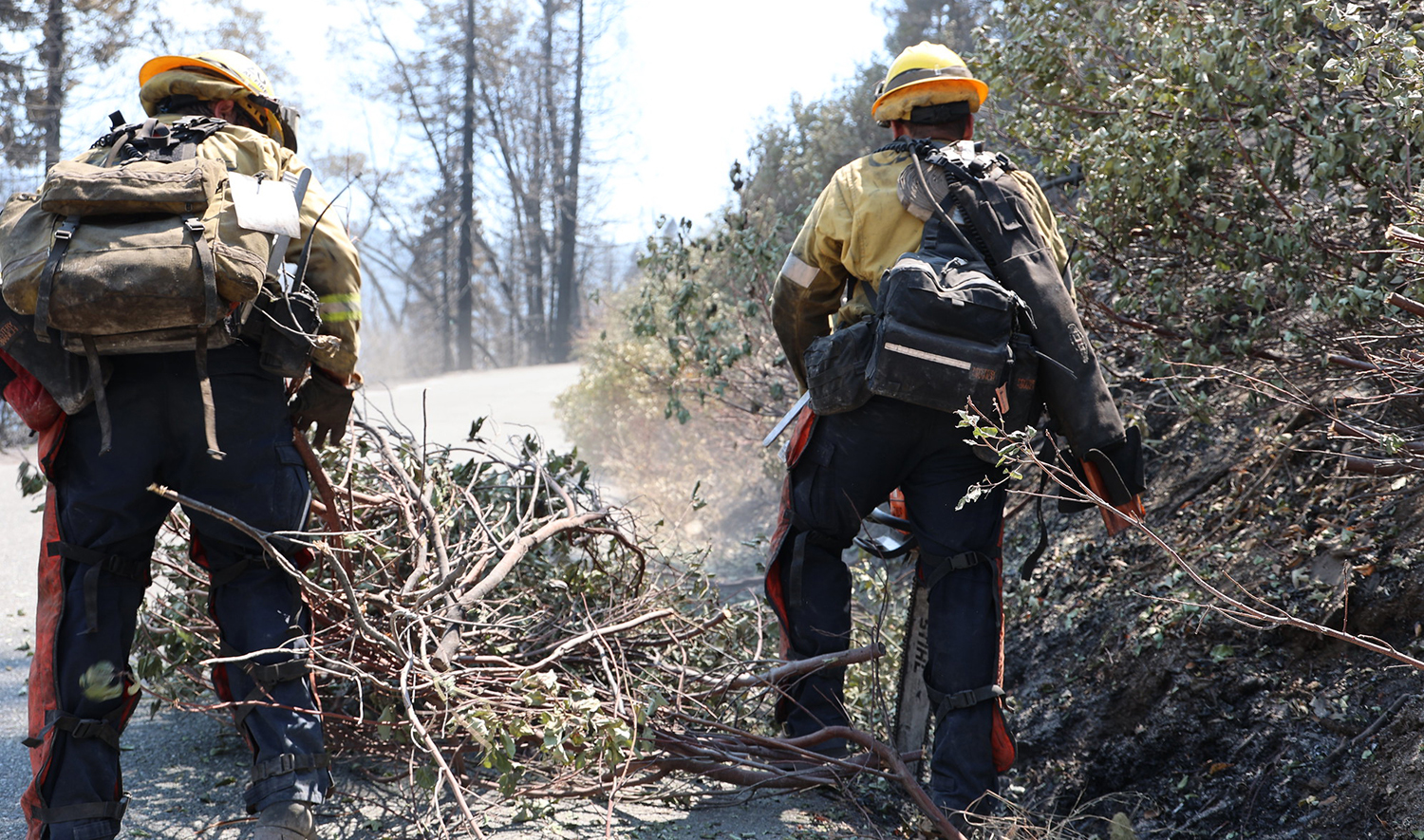
CA State Parks and Partners Treat Over 900 Acres with Beneficial Fire
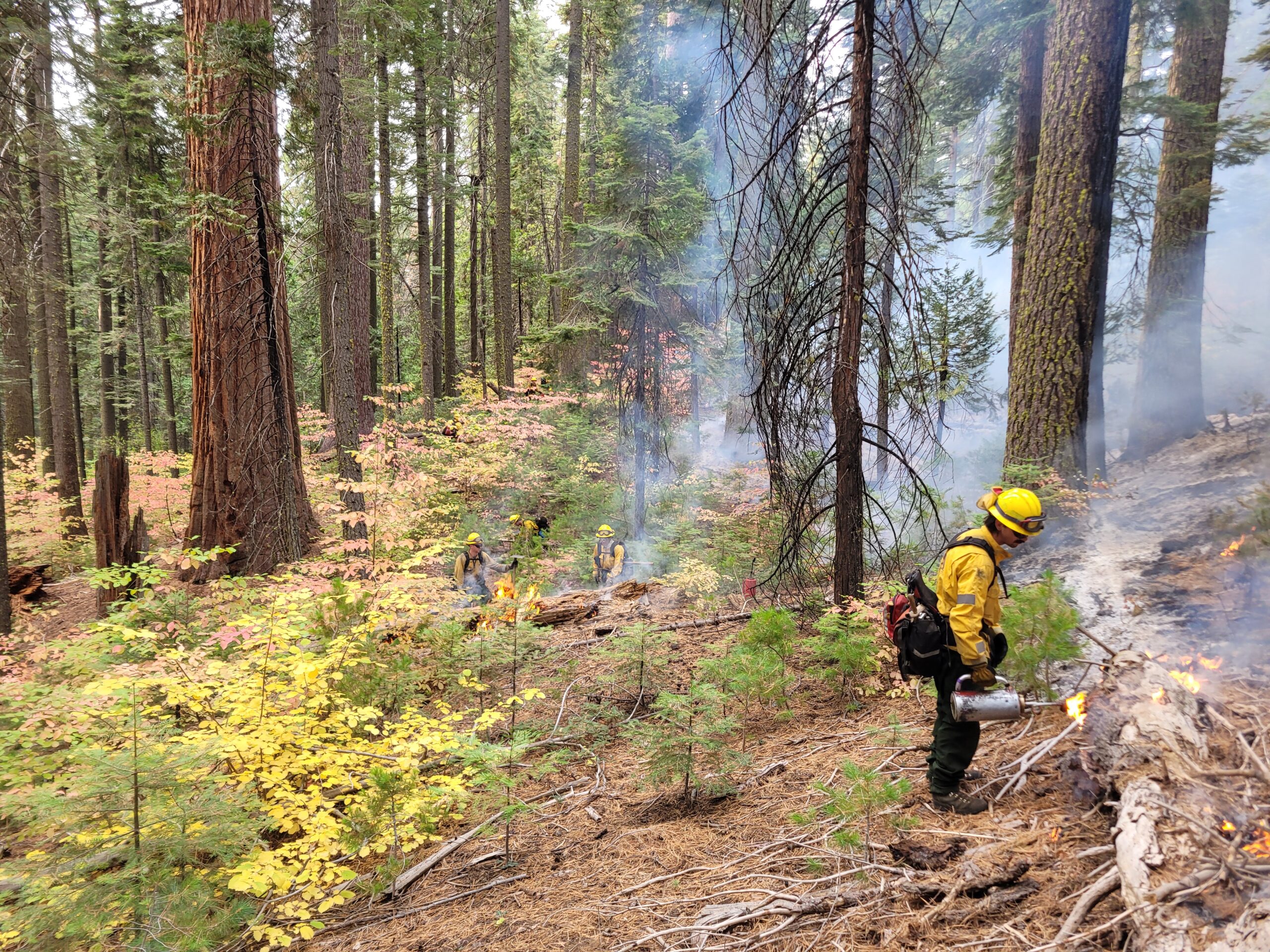

photo by: Richard Rappaport
CA State Parks and Partners Treat Over 900 Acres with Beneficial Fire
From October 29 to November 1, California State Parks with the assistance of CAL FIRE and the USFS treated 914 acres in the South Grove Natural Preserve at Calaveras Big Trees State Park with prescribed fire.
State Parks, CAL FIRE, USFS and contractors spent years organizing interagency collaboration and preparing the perimeter along with the giant sequoia trees for beneficial fire. Preparation included using mechanical treatments appropriate for State Parks Natural Preserves to remove large fuels from the surrounding fire road and using hand tools to remove large material from the base of over 700 mature giant sequoias.
The entire South Grove Natural Preserve is over 1,300 acres. Critical to giant sequoia stewardship and regeneration, State Parks will continue to be prepared to treat the remaining acres and bring fire back to the entire landscape in regular intervals. This project restores and maintains a complex forest community, promotes giant sequoia regeneration and wildfire resilience, reduces hazardous fuel loads, improves wildlife habitat, and protects park infrastructure.
Meeting Showcases California's Momentum Toward Wildfire Resilience
Meeting Showcases California's Momentum Toward Wildfire Resilience
October 10, 2024
At the Task Force’s most well-attended meeting to-date, nearly 500 people gathered in South Lake Tahoe (and over 300 joined online) for the Sierra Nevada Regional Meeting. Hosted by the California Tahoe Conservancy and Tahoe Fund, the meeting featured several new tools that will revolutionize how California tracks and communicates progress toward improving wildfire and landscape resilience. Other topics covered included progress being made in the Tahoe Basin and the benefits of landscape fuels treatments to vibrant ecosystems and economically thriving communities.
REGIONAL MEETING AGENDA HIGHLIGHTS
• Director’s Report: Director Wright provided an update on recent accomplishments and investments in the Sierra Nevada and a preview of the 2025 Action Plan.
• Statewide Progress on Wildfire Resilience Efforts
– Interagency Treatment Dashboard
– Core Reporting Metrics
– Treatment Effectiveness.
• State & Regional Presentations
– Protecting & Restoring Tahoe: Tahoe partners shared their progress and priorities for advancing state, regional, and local goals through the Environmental Improvement Program.
– Focus on Wildlife – A Vision for Vibrant Ecosystems: A panel of state and regional leaders discussed next steps for evolving large-landscape projects to promote comprehensive climate, watershed, and wildlife benefits.
– Focus on Recreation – A Vision for Thriving Communities: A panel of regional leaders discussed how Sierra partners are broadening planning and implementation to promote recreation and rural economies.
Welcome & Opening Remarks
• Wade Crowfoot, CA Natural Resources Agency
• Kara Chadwick, US Forest Service
• Serra Smokey, Washoe Tribe of NV & CA
• James Settelmeyer, NV Dept. Conservation & Natural Resources
• Joe Tyler, CAL FIRE
Director's Report
• Patrick Wright, Task Force
Statewide Progress on Wildfire Resilience Efforts
Moderator: John Battles, UC Berkeley
• Alan Talhelm and Emily Brodie, CAL FIRE
• MV Eitzel, UC Davis
• Frank Bigelow, CAL FIRE
Tools:
• Monitoring, Reporting & Assessment Page
• Interagency Treatment Dashboard
• CAL FIRE’s Fuels Treatment Effectiveness Reports
Protecting & Restoring Tahoe
• Kacey KC, Nevada Division of Forestry
• Jason Vasques, Tahoe Conservancy
• Julie Regan, Tahoe Reg. Planning Agency
Focus on Wildlife – A Vision for Vibrant Ecosystems
Moderator: Erin Ernst, Tahoe Conservancy
• Stephanie Coppeto, US Forest Service
• Rachel Henry, US Fish & Wildlife Service
• Rich Adams, CA State Parks
• Rhiana Jones, Washoe Tribe of NV & CA
• Meghan Hertel, CA Natural Resources Agency
Focus on Recreation – A Vision for Thriving Communities
Moderator: Danna Stroud, GoBiz
• Amy Berry, Tahoe Fund
• Stew McMorrow, CAL FIRE
• Luke Hunt, Sierra Nevada Conservancy
• Michelle Abramson, Sierra Buttes Trails
• John Wentworth, MLTPA
Closing Remarks
• Task Force Co-Chairs
Sierra Nevada Regional Meeting

Sierra Nevada Regional Meeting
Register early to reserve your seat at the next meeting of the California Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force, October 10 at the Tahoe Blue Event Center in South Lake Tahoe, hosted by the California Tahoe Conservancy and the Tahoe Fund.
The Task Force and CAL FIRE will unveil several new tools that will revolutionize how California tracks and communicates progress toward improving wildfire and landscape resilience at its seventh regional meeting on October 10th in South Lake Tahoe:
Interagency Treatment Dashboard: One year after its beta release with 2022 data, CAL FIRE will present three years (2021-2023) of treatment data from a more complete range of federal, state, local, tribal, and private entities through its expanded and improved Interagency Treatment Dashboard.
Draft Metrics: Task Force Science Advisory Panel staff will present a subset of initial proposed metrics to document the outcomes of recent projects on wildfire hazard, watershed health, and wildlife habitat.
Fuel Treatment Effectiveness Dashboard: CAL FIRE will demonstrate its prototype dashboard to document the benefits of fuels treatments in reducing the impacts of recent fires, including the Park Fire in Butte and Tehama County.
CAL FIRE Director Joe Tyler will also provide a report on the current fire season, and three panels of federal, state, tribal, and regional leaders will discuss their efforts to create vibrant forest ecosystems and thriving communities through landscape-scale wildfire resilience projects.
On October 9 and 11, Task Force Partners will host field tours offering immersive opportunities to better understand the critical landscape health and wildfire resilience work being done in the Sierra Nevada region.
The $28 registration fee for the October 10 meeting offsets the cost of breakfast, refreshments, and lunch. If this fee poses a hardship, contact ForestTaskForce@fire.ca.gov.
Registration closes October 3. No registrations will be allowed after this date.
EVENT SCHEDULE

OCTOBER 10 TENTATIVE MEETING SCHEDULE
Resource Fair
8:30 – 10:00 a.m.
Morning Session
10:00 a.m. – 12:15 p.m.
Lunch
12:30 – 2 p.m.
Afternoon Session
2 p.m. – 4:30 p.m.
Reception at the Tahoe Blue Event Center
(Meeting registration is required.)
4:30 p.m. – 6:30 p.m.
hotel information
field tours
FIELD TOURS WILL BE OFFERED ON OCT 9 & 11
All tours will be accessed by bus. Parking/meet up locations TBD.
Lunch will not be served.
Tahoe Forest Products Mill
See the first new industrial-scale sawmill built in Sierra Nevada in several decades.
Destination: Tahoe Forest Products worked in partnership with the Washoe Development Corporation an affiliate of the Washoe Tribe of Nevada & California to construct the first new industrial-scale sawmill in the Sierra Nevada in several decades. The mill provides employment opportunities for local citizens and tribal members while supporting forest health and wildfire restoration efforts throughout the Central Sierra. Visit the mill and learn about both the innovative partnerships and engineering that made this long-envisioned opportunity a reality.
Three Tours: start times will be 12:30, 1:00 and 1:30 pm.
Tour lasts approximately 2.5 hours.
Caldor Fire Preparation, Response, and Recovery
Learn what happened before, during, and after one of 2021’s largest wildfires.
Destination: This tour will showcase projects and treatments implemented prior to the 2021 Caldor Fire, successes and lessons learned during initial response to the fire, as well as the significant efforts that have helped the impacted ecosystems recover and accelerated access to recreational opportunities in this post-fire landscape. Tour stops will include Echo Summit, Christmas Valley, Pioneer Trail, and Fountain Place.
Start/End Time: 9am – 1pm
West Shore Prescribed Fire and Indigenous Stewardship
See impacts of long-term prescribed burn projects and multi-benefit ecosystem restoration.
Destination: This tour will visit the renowned Sugar Pine Point State Park to view the effects of a decades-long prescribed fire program. The tour will then explore Máyala Wáta at Meeks Meadow to learn how the Washoe Tribe is partnering with diverse groups to restore ecosystems and habitat by addressing the detrimental impacts of historical cattle grazing, logging, and fire suppression.
Start/End Time: 9am – 1pm
East Shore Shared-Use Trail and Recreation Management
Recreate on a scenic shoreline trail and learn about managing forests in high-visitation areas.
Experience by foot one of Tahoe’s most scenic and historic shoreline trails. Participants will have the opportunity to walk all or part of this spectacular 3-mile pave path while gaining insights on the challenges and solutions for managing forests in high-visitation areas.
TIME: 9am – 1pm
Questions? Please contact foresttaskforce@fire.ca.gov
Thank You to our Hosts


Thank You to our Sponsors















U.S. Forest Service Announces Funding to Reduce Wildfire Risk
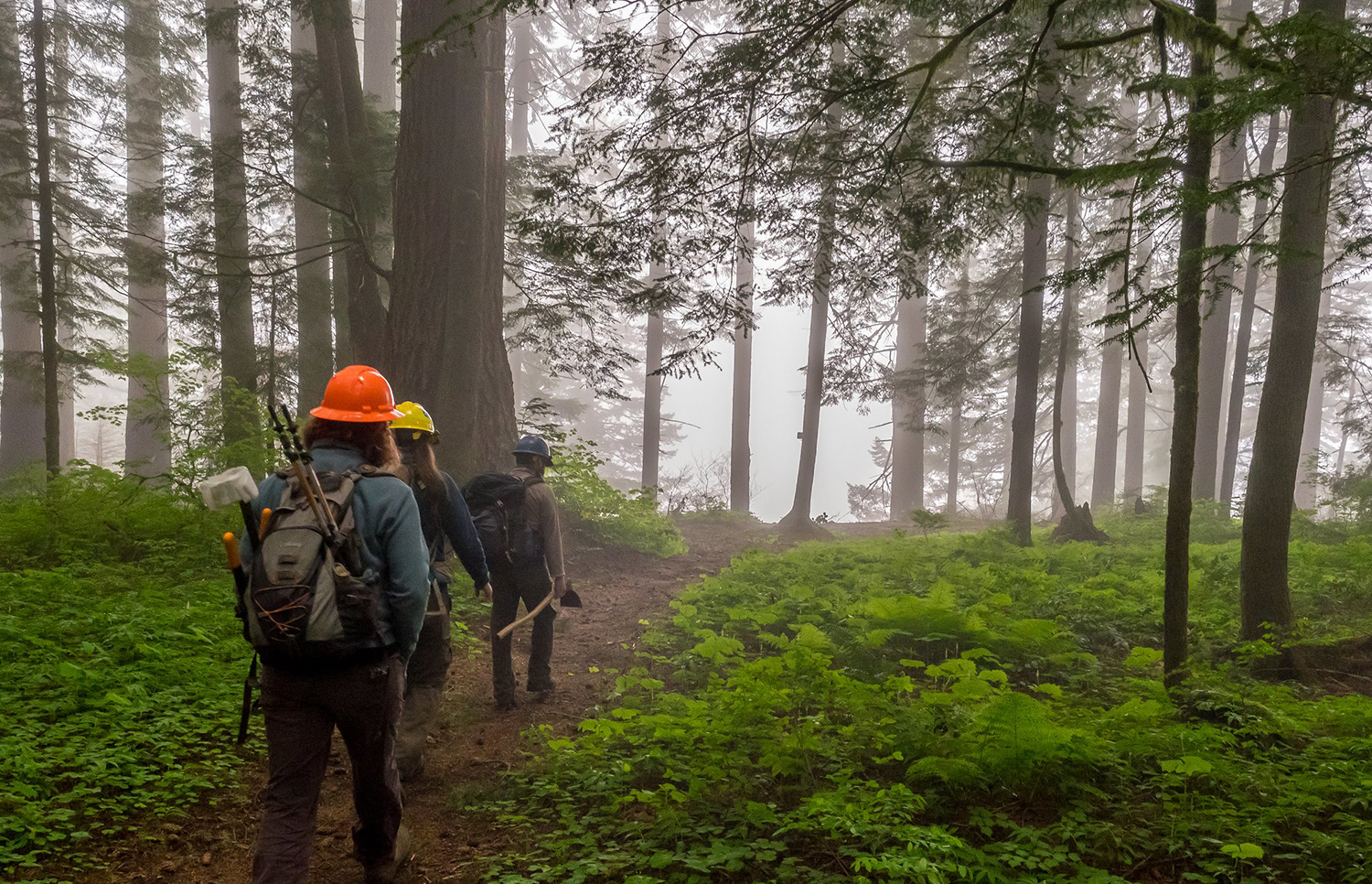

U.S. Forest Service Announces Funding to Local Businesses and Underserved Populations to Reduce Wildfire Risk
$25M Funding Opportunity to Reduce Wildfire Risk
August 6, 2024 – The U.S. Forest Service announced a funding opportunity through the Hazardous Fuels Transportation Assistance program to reduce wildfire risk, increase market opportunities, and support local jobs.
The program is available to local businesses that remove hazardous fuels from national forests and transport the material to be processed for wood products or services. Transporting the materials out of the national forest prevents them from being burned in the forests or left in place where they are subject to insects and diseases that increase the risk for wildfire.
The funding focuses on the removal of hazardous fuels with little commercial value, creating economic opportunities while improving overall forest health and resilience.
$15M to Help Underserved and Small-Acreage Landowners Access Climate Markets
August 28, 2024 – The U.S. Forest Service announced it is investing $15 million to connect underserved and small-acreage forest landowners with emerging climate markets. These investments will expand access to markets that were previously out-of-reach for underserved and small-acreage landowners to access new economic opportunities to maintain healthy working forests as pressures increase to convert forests to other uses. In California, nearly $2 million will go to the Shelterwood Collective, a 900-acre Indigenous, Black, Disabled, and Queer-led community forest and collective of land protectors and cultural changemakers.
New Conservation Strategy to Protect Montane Forests in Southern California
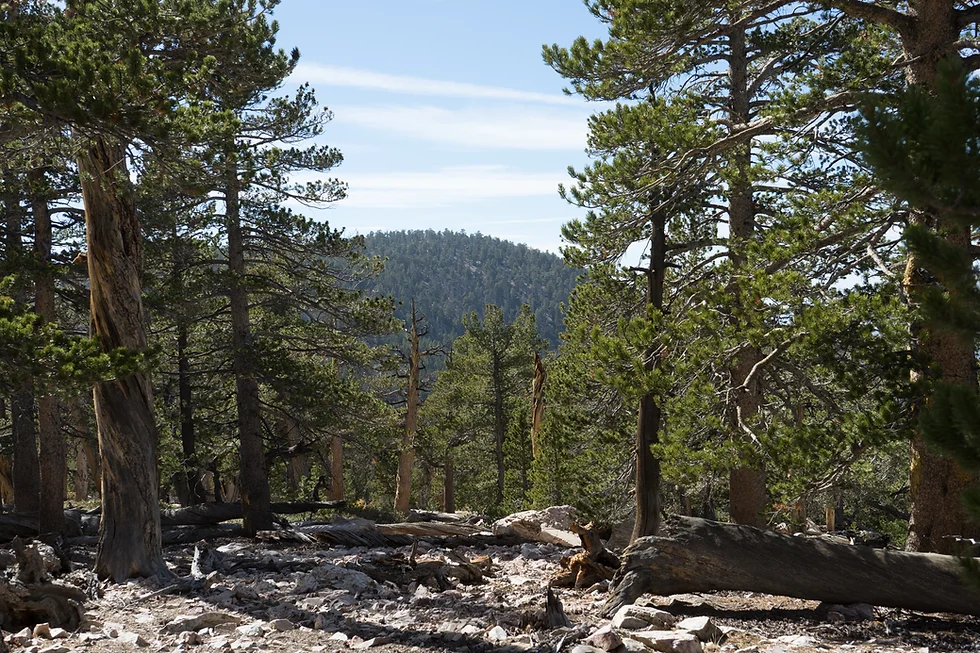

New Conservation Strategy to Protect Montane Forests in Southern California
July 30, 2024 – The Southern Montane Forest Project released its Climate-Adapted Conservation Strategy, an initiative that will bolster the resilience of montane (i.e. higher-elevation forests) to confront threats from wildfires, droughts, pollution, and invasive species.
The strategy takes an all-lands approach, calling for state, federal, academic, and non-profit efforts to work in concert within the USFS’s Southern California Wildfire Crisis Landscape.
Southern California’s montane forests are a key Task Force priority because they protect watersheds that supply about 40% of downstream water for drinking and agriculture. They capture carbon, prevent soil erosion, and serve as critical habitats for threatened and endangered wildlife. They also supply Indigenous communities with food, fiber, and medicine while providing recreational opportunities to over 24 million people.
New Web Resources Help Californians Find Relief from Smoke and Prepare for Wildfires
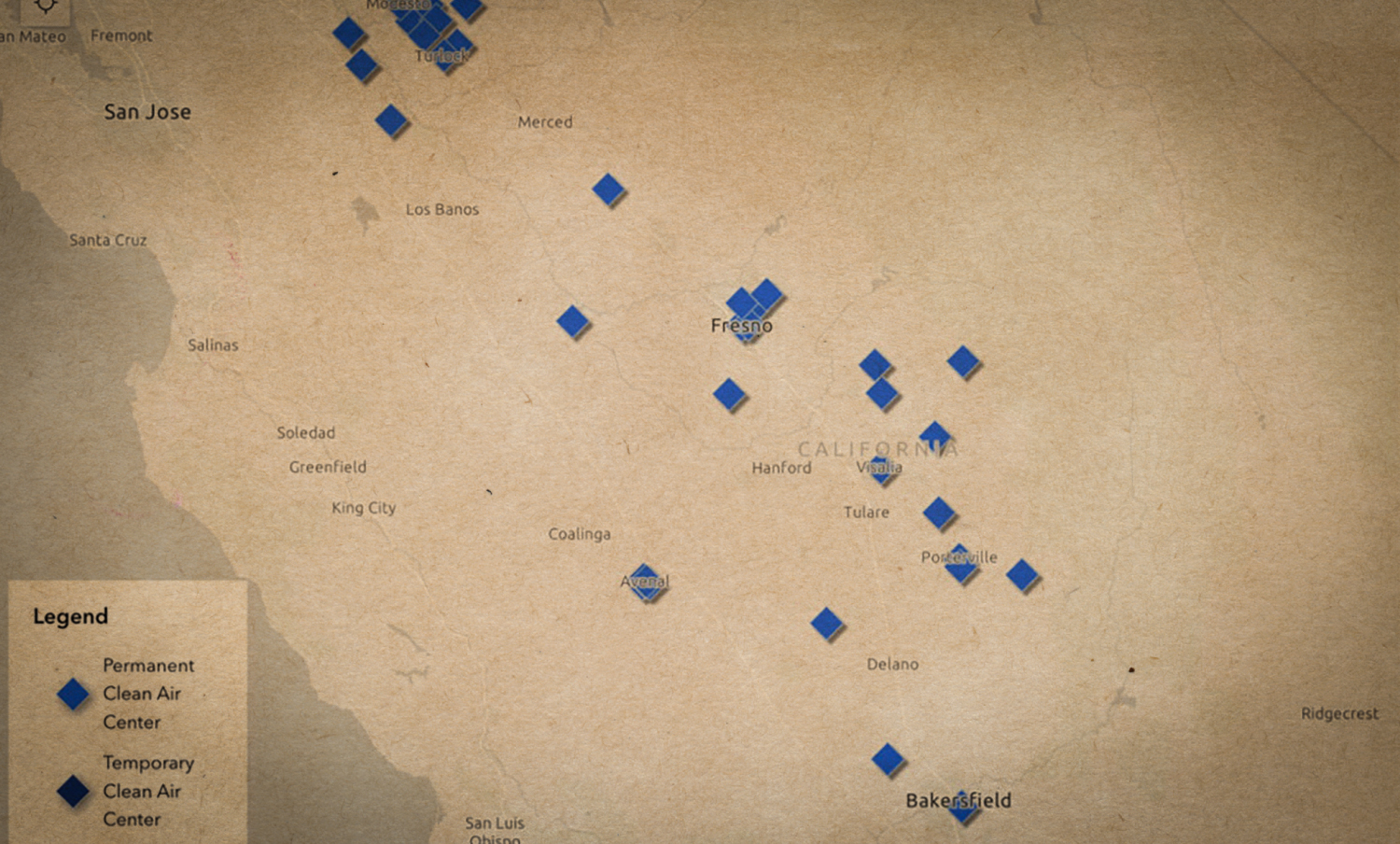
New Web Resources Help Californians Find Relief from Smoke and Prepare for Wildfires
June 24, 2024 – Clean Air Centers Maps Shows Where to Find Relief from Wildfire Smoke: The California Air Resources Board announced the launch of an interactive, statewide map that offers a one-stop-shop for information about the location and services available at Clean Air Centers. Clean Air Centers will offer Californians who don’t have access to adequate air filtration a safe place to go during periods of heavy smoke. Built in collaboration with local air quality control districts, the online map makes it possible to see where Clean Air Centers are located and provides easy-to-access information, including operating hours, contact information and on-site resources like free Wi-Fi.
CAL FIRE Updates Wildfire Preparedness Website: In preparation for the fire year, CAL FIRE has updated the ReadyForWildfire.org site. This one-stop-shop provides advice and guidance on everything from home hardening and defensible space, to what to pack for evacuation, to what California is doing to enhance and protect forest health.
California National Forests Complete Record Number of Prescribed Fire Acres
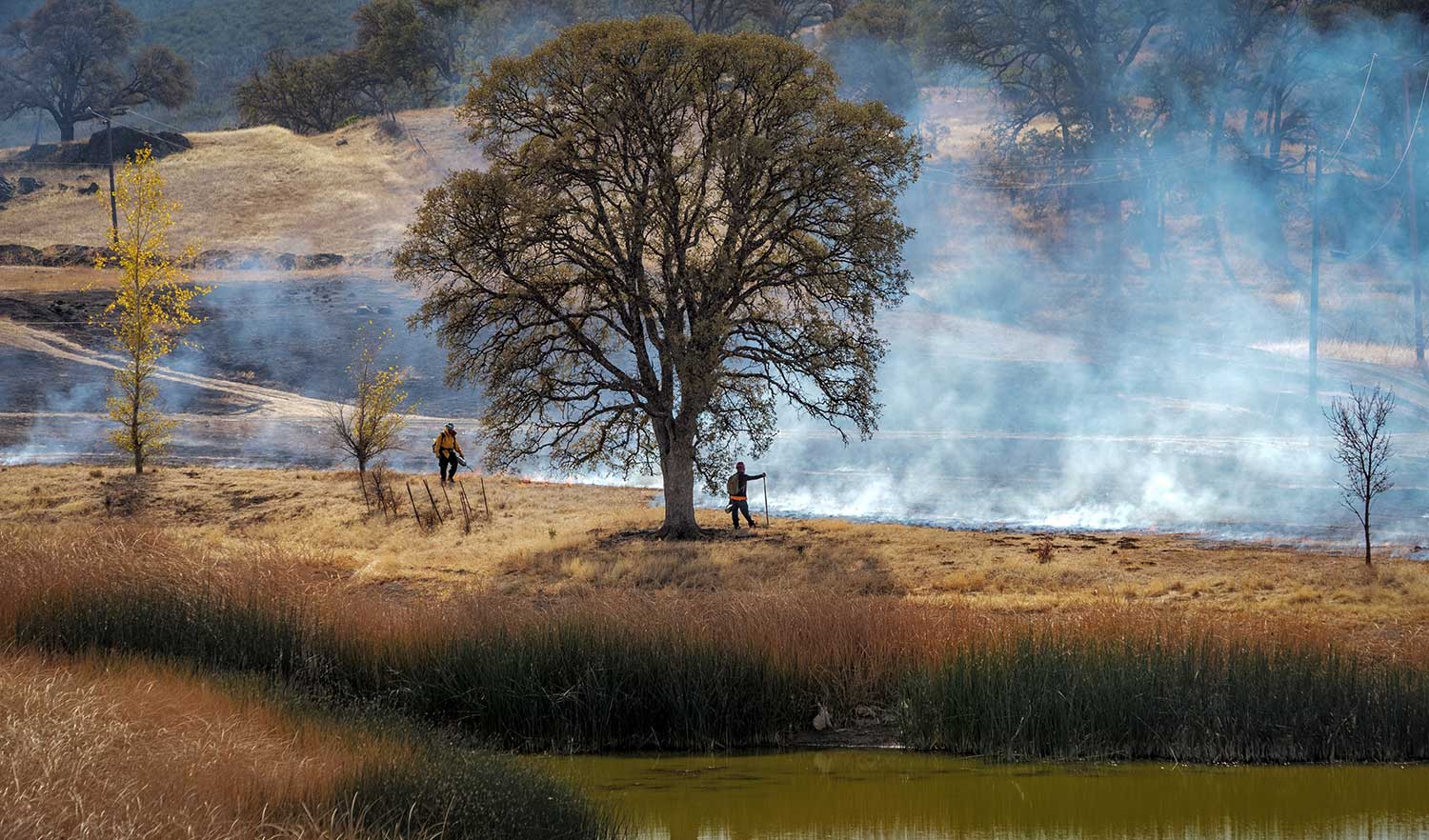

California National Forests Complete Record Number of Prescribed Fire Acres
As of June 24, the USFS has treated 63,878 acres with prescribed fire on national forests in California. The previous record was set in 2018 when 63,711 acres were treated. USFS fire managers are using prescribed fire to reduce hazardous fuels and reduce threats to communities from extreme fires. Reintroducing fire also minimizes the spread of pest insects and disease, recycles nutrients back to the soil, and improves natural conditions for native flora and fauna.
Federal Climate Financial Report Demonstrates Need for Proactive Action on Wildfire Resilience
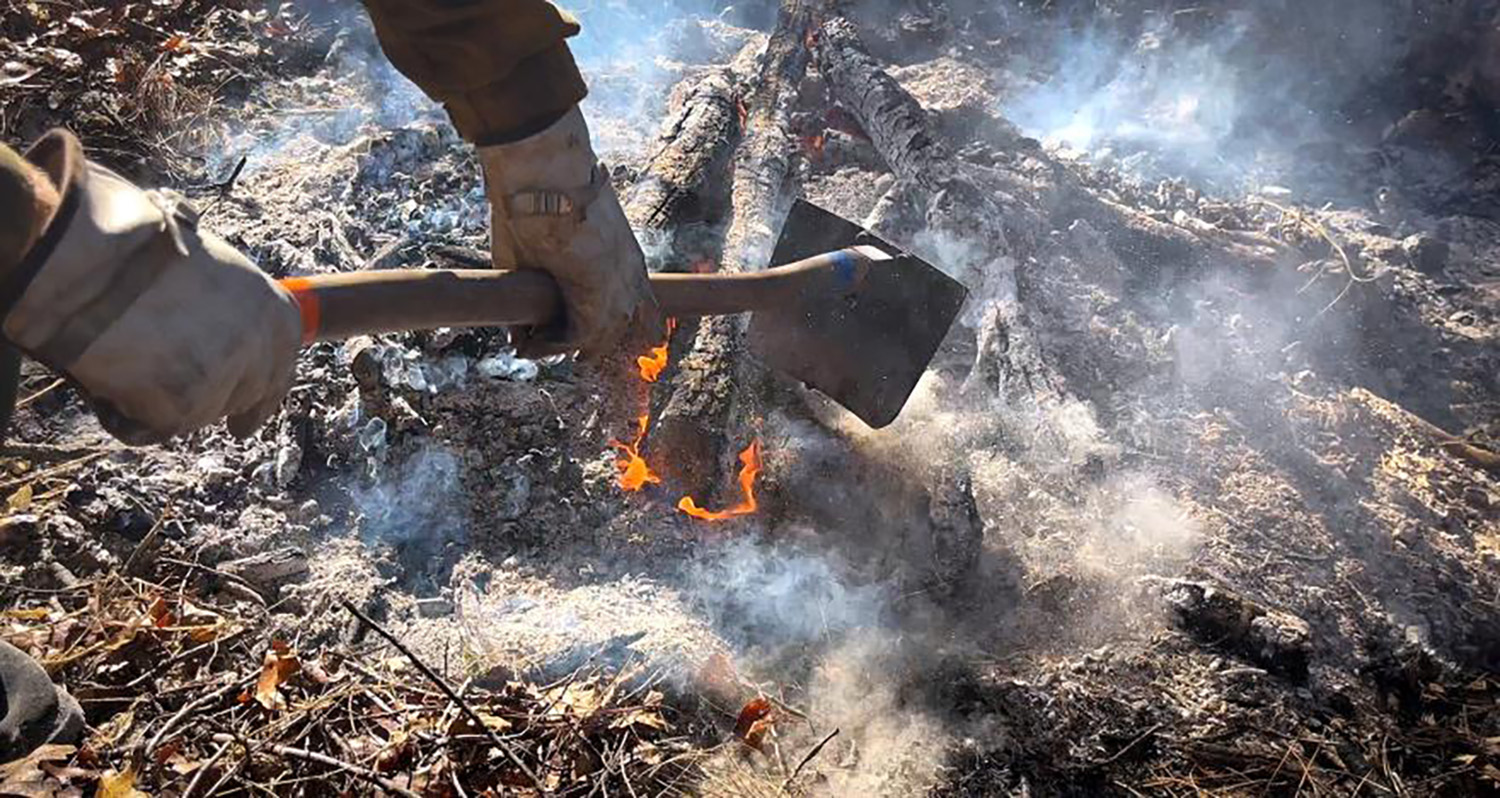

Federal Climate Financial Report Demonstrates Need for Proactive Action on Wildfire Resilience
Over the last decade, suppression has cost the USFS and the Department of the Interior an average of more than $3 billion per year. The Climate Financial Risk report provides estimates for 10 future climate scenarios and a wide range of projections for fire extent and fire suppression spending. A central estimate across the 10 future climate scenarios shows that lands in the National Forest System would experience a near doubling of the area burned by mid-century (2041-2059) and a 42% increase in costs by 2050, to $3.9 billion. Anticipated increased costs of fire suppression due to climate change brings additional urgency to the need for proactive wildfire risk reduction treatments and efforts to protect and prepare communities ahead of wildfires.





