June 6 Sacramento Meeting Recap
SACRAMENTO TASK FORCE MEETING RECAP
June 6, 2025
The Task Force quarterly meeting at the California Natural Resources Agency in Sacramento brought together regional leaders for a provocative conversation about how we can most efficiently expend state dollars to meet the state’s wildfire needs.
Thanks to the Governor and the Legislature more than $1.5 billion is available to spend on wildfire resilience projects throughout the state. At the Task Force meeting, a panel of regional leaders offered their insights on how to most efficiently and effectively expend those funds to meet their priorities, along with how they are organizing to align with state goals and drive rapid wildfire resilience work on the ground.
A second panel of agency leaders discussed how they’re coordinating across programs and funding sources, including Prop 4, to support regional partners and accelerate on-the-ground wildfire resilience.
Welcome & Executive Remarks
Co-chairs
- Wade Crowfoot, California Natural Resources Agency
- Chris Feutrier, U.S. Forest Service
Task Force Executive Committee
- Anale Burlew, CAL FIRE
- Joe Stout, Bureau of Land Management
- Katy Landau, California Environmental Protection Agency
- Don Hankins, Indigenous Stewardship Network
- Abby Edwards, Office of Land Use and Climate Innovation
- Doug Teeter, Rural County Representatives of California
Director’s Report
Director’s Report
Patrick Wright, Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force
Regional Progress in Planning & Priority Setting
Regional Progress in Planning & Priority Setting
Moderator: Angie Lottes, CA State Parks
Southern California: Jeff Heys, U.S. Forest Service
Sierra Nevada: Sarah Campe, Sierra Nevada Conservancy – Paul Ringold, Giant Sequoia Lands Coalition
Northern California: Karen Gaffney, North Coast Resource Partnership – Alison Blodorn, Inner Coast Collaborative
Central Coast: Kostoula Vallianos, CA Coastal Conservancy – Timothy Federal, San Mateo RCD
Agency Preparations for Regional Funding
Moderator: Nick Goulette, Watershed Center
Lisa Lien-Mager, CA Natural Resources Agency
Shanna Atherton, Department of Conservation
Alan Talhelm, CAL FIRE
Angie Avery, Sierra Nevada Conservancy
Evyan Borgnis Sloane, CA Coastal Conservancy
Rebecca Fris, Wildlife Conservation Board
Closing Remarks
Task Force Executive Committee
Leading Scientists Shared Latest Findings on Wildfire Resilience at December 13 Meeting. Recap Now Available.
SACRAMENTO TASK FORCE MEETING RECAP
December 13, 2024
The Task Force quarterly meeting at the California Natural Resources Agency in Sacramento featured leading scientists discussing their findings on what is working and what we need to improve on to address California’s wildfire crisis.
The lively and candid conversations challenged California’s climate leaders to take a hard look at existing priorities and ensure the latest science is being used to inform the state’s policies to reduce the risks of catastrophic wildfire and restore healthy natural landscapes in the face of climate change. Findings shared at the meeting were part of a Science Synthesis that will help inform the Task Force’s 2025 Action Plan.
Highlights Include:
Forest & Rangeland Assessment: Jamie Lydersen from CAL FIRE provided a preview on the upcoming release of an updated FRAP report that informs leaders and land managers at a statewide level using data-based indicators to show current state and recent trends on California forests and rangelands.
Synthesis of Science
Through a series of panel discussions, members of the Task Force’s Science Advisory Panel provided highlights from a synthesis of scientific findings since 2021 on issues related to wildfire and landscape resilience that will help inform the Task Force’s 2025 Action Plan. Topics covered included:
- How did we get here and why does it matter?
- What have we learned about what works and where we go from here?
- Part 1: Landscape Resilience & Community Protection
- Part 2: Post-Fire Considerations
Welcome & Executive Remarks
Co-chairs
- Wade Crowfoot, California Natural Resources Agency
- Jennifer Eberlien, U.S. Forest Service
Task Force Executive Committee
- Anale Burlew, CAL FIRE
- Joe Stout, Bureau of Land Management
- Katy Landau, California Environmental Protection Agency
- Don Hankins, Indigenous Stewardship Network
- Abby Edwards, Office of Land Use and Climate Innovation
- Doug Teeter, Rural County Representatives of California
Director’s Report
Director’s Report
Patrick Wright, Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force
Forest and Rangeland Assessment
Forest and Rangeland Assessment
Jamie Lydersen, CAL FIRE
Science Synthesis: How did we get here and why does it matter?
Science Synthesis: How did we get here and why does it matter?
Moderator: Steve Ostoja, USDA Climate Hub
Chris Fettig, U.S. Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Research Station
Lenya Quinn-Davidson, U.C. Agriculture & Natural Resources
Science Synthesis: What have we learned about what works and where we go from here?
Part 1: Landscape Resilience & Community Protection
Moderator: Steve Ostoja, USDA Climate Hub
Emily Schlickman, U.C. Davis
Scott Stephens, U.C. Berkeley
Malcolm North, U.S. Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Research Station
Science Synthesis: What have we learned about what works and where we go from here?
Part 2: Post-Fire Considerations
Moderator: Malcolm North, U.S. Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Research Station
Brandon Collins, U.S. Forest Service
Dana Walsh, U.S. Forest Service
Don Lindsay, California Department of Conservation
Closing Remarks
Task Force Executive Committee
State and Federal Investments Conserve Forestlands in Perpetuity

State and Federal Investments Conserve Forestlands in Perpetuity
October 29, 2024 – CAL FIRE and the U.S. Forest Service have announced grant awards to protect forestlands threatened with conversion to non-forest uses. Together, these investments improve forest health and reduce wildfire risk throughout the state.
CAL FIRE awarded $8.5 million through California Forest Legacy to four projects that ensure long-term land stewardship on properties that will continue to provide, in perpetuity, such benefits as sustainable timber production, wildlife habitat, recreation opportunities, carbon sequestration, watershed protection, and open space. One funded project will enable the Colfax-Todds Valley Consolidated Tribe to acquire the Owl Creek property in Placer County; while Placer Land Trust will hold a conservation easement to ensure protection of the property, the Tribe will manage the land using Indigenous management practices.
The USFS awarded more than $265 million to 21 projects nationwide through the federal Forest Legacy program to conserve nearly 335,000 acres of private forestlands. In California, a $1.5 million grant will conserve 94 acres of unique montane mixed-conifer forest in the recreation destination of Lake Arrowhead, east of Los Angeles. The property provides habitat for 7 federal and 4 state species of concern.
Interagency Treatment Dashboard Shows Progress Toward Resilience

FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
October 10, 2024
California Unveils First-of-Their-Kind Dashboards Mapping Out Fire-Prevention Work to Protect Communities
New tools created by CAL FIRE and Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force simplify data, boost transparency, and help inform wildfire planning and response – adding to the suite of tools the state has created
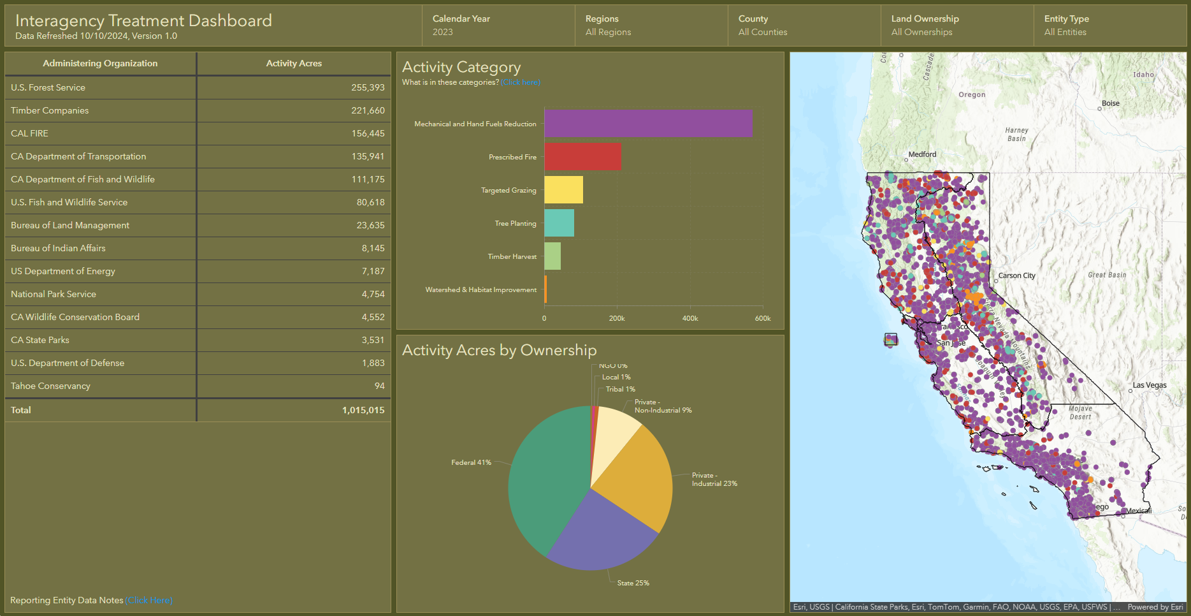
(South Lake Tahoe, CA) – The Governor’s Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force and the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (CAL FIRE) unveiled several new tools today to help California track and communicate the state’s significant progress in improving wildfire and landscape resilience.
Key takeaways from the Task Force’s Sierra Nevada Regional Meeting in South Lake Tahoe include:
• Interagency Treatment Dashboard updated to show 2021, 2022 and 2023 data.
• Over one million acres of treatments were conducted on about 700,000 footprint acres in 2023.
• Prescribed fire treatments more than doubled between 2021 and 2023.
• CAL FIRE Fuel Treatment Effectiveness Dashboard is showing the impact of treatments impacted by recent wildfires.
“Thousands of wildfire resilience projects have been completed across California to protect our communities and landscapes from catastrophic wildfire in recent years, and more are underway,” said Wade Crowfoot, Secretary of the California Natural Resources Agency and co-chair of the Task Force. “Thanks to historic investments from our state and federal leaders, dozens of local agencies and hundreds of organizations are delivering these projects. Now for the first time, we have a dashboard that tracks all these diverse projects in one place and on one map. This enables us to measure our overall progress toward building wildfire resilience across the state and provides regional leaders valuable information to plan future projects.”
Interagency Treatment Dashboard
The updated version of the Interagency Treatment Dashboard shows wildfire resilience work (or “treatments”) for three calendar years (2021, 2022 and 2023). The data, which was sourced from federal, state, local, tribal, and private entities, is now available in a single hub that allows Californians to easily see where treatments (such as prescribed fire, mechanical thinning, and tree planting) have been completed. This information is used to inform firefighting efforts, ensure transparency to the public, and track progress toward statewide goals.
The Task Force released a Beta version of the Dashboard last year with 2022 data. This updated version now includes data for 2021, revised data for 2022, and new data for 2023.
Over 1 million acres worth of treatment work on 700,000 acres of land
The Dashboard shows significant progress on multiple fronts to bolster wildfire resilience in California. In 2023, more than one million acres of treatments were conducted on about 700,000 acres, with many acres receiving multiple treatments such as thinning, prescribed fire, or other practices to improve forest health and community resilience. The Task Force is tracking both “activity acres” – which reflect the level of effort conducted through various state, federal, and private programs – and “footprint acres” – which show the total geographic area treated in a calendar year.
The 2023 data shows a significant increase in acres treated since 2021. The increase is largely due to a significant expansion of prescribed fire treatments, which more than doubled since 2021. These efforts have put the state on a solid path toward meeting its joint commitment with the U.S. Forest Service to complete treatments on more than a million acres by the end of 2025.
The Task Force is committed to increasing the pace and scale of statewide actions to address California’s wildfire crisis. The Dashboard is part of a larger strategy to connect the various statewide entities committed to this monumental task.
Fuel Treatment Effectiveness Dashboard
CAL FIRE also launched a Fuel Treatment Effectiveness Dashboard, which shows how wildfire prevention projects are helping protect communities and landscapes when wildfire strikes. “Utilizing technology, we can now track in real time when wildfires hit areas where fuel treatments have been conducted. We can then go into an area and see how those treatments affected fire behavior, evacuation routes, firefighting efforts and more,” said CAL FIRE Chief/Director Joe Tyler. “This new dashboard is a tool for the public to see how fuels treatments had a positive impact on the firefight and how this work is making a difference.”
“No other state in the country is tackling wildfire resilience at this scale or with this level of innovation,” added U.S. Forest Service Deputy Regional Forester Kara Chadwick, who co-chaired today’s meeting. “From groundbreaking prescribed fire projects to comprehensive data tracking systems, we’re setting the standard for what it means to protect our landscapes and communities.”
The meeting is supplemented by field tours on October 8 and 11, to showcase wildfire resilience projects in the Tahoe Basin. Tour highlights include recovery efforts following the 2021 Caldor Fire, long-term prescribed burn projects in Sugar Pine Point State Park, meadow restoration at Máyala Wát undertaken by the Washoe Tribe of Nevada and California, and the first new industrial-scale sawmill built in Sierra Nevada in several decades.
“Today’s meeting is a major milestone in our efforts to better document and share our collective progress,” said Task Force Director Patrick Wright. “We will continue to build on our collective momentum to make California more resilient to wildfire.”
The next Task Force meeting will take place in Sacramento on December 13 and will provide a synthesis of the latest scientific findings that are informing California’s approach to address wildfire risks in a changing climate. These findings will be incorporated into the Task Force’s 2025 Action Plan Update.
Sky Biblin, Communications Coordinator
Governor’s Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force
916-502-6527
California IBank Invests $25M in Wildfire Innovation Fund

California IBank Invests $25M in Wildfire Innovation Fund
September 3, 2024 – California’s Infrastructure and Economic Development Bank (IBank) announced $25 million from the Climate Catalyst Revolving Loan Fund will be invested in the California Wildfire Innovation Fund to reduce wildfire risk. Funds will be used to restore California forests, improve forest health, and put new biomass technologies to work.
The California Wildfire Innovation Fund is managed by Blue Forest, a conservation finance non-profit that supports entrepreneurs and companies working toward forest restoration and economic revitalization.
The fund offers flexible, low-cost financial support for emerging opportunities across California’s forest restoration and wood utilization sectors.
CAL FIRE Funds 94 Wildfire Projects

CAL FIRE Funds 94 Wildfire Projects to Build Climate and Community Resilience
August 20, 2024 – CAL FIRE announced grants with $90.8 million in funding for 94 local wildfire prevention projects across California. Wildfire Prevention Grant projects include hazardous fuels reduction and wildfire prevention planning and education, with an emphasis on improving public health and safety while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Over two-thirds of the projects will go to communities that are low-income and disadvantaged. These grants bring CAL FIRE’s Wildfire Prevention Grants Program total funding to $450 million that have supported over 450 projects across the state which have collectively accelerated progress toward the goals of California’s Wildfire and Forest Resilience Action Plan.
New Website Offers a Deep Dive into Intentional Fire
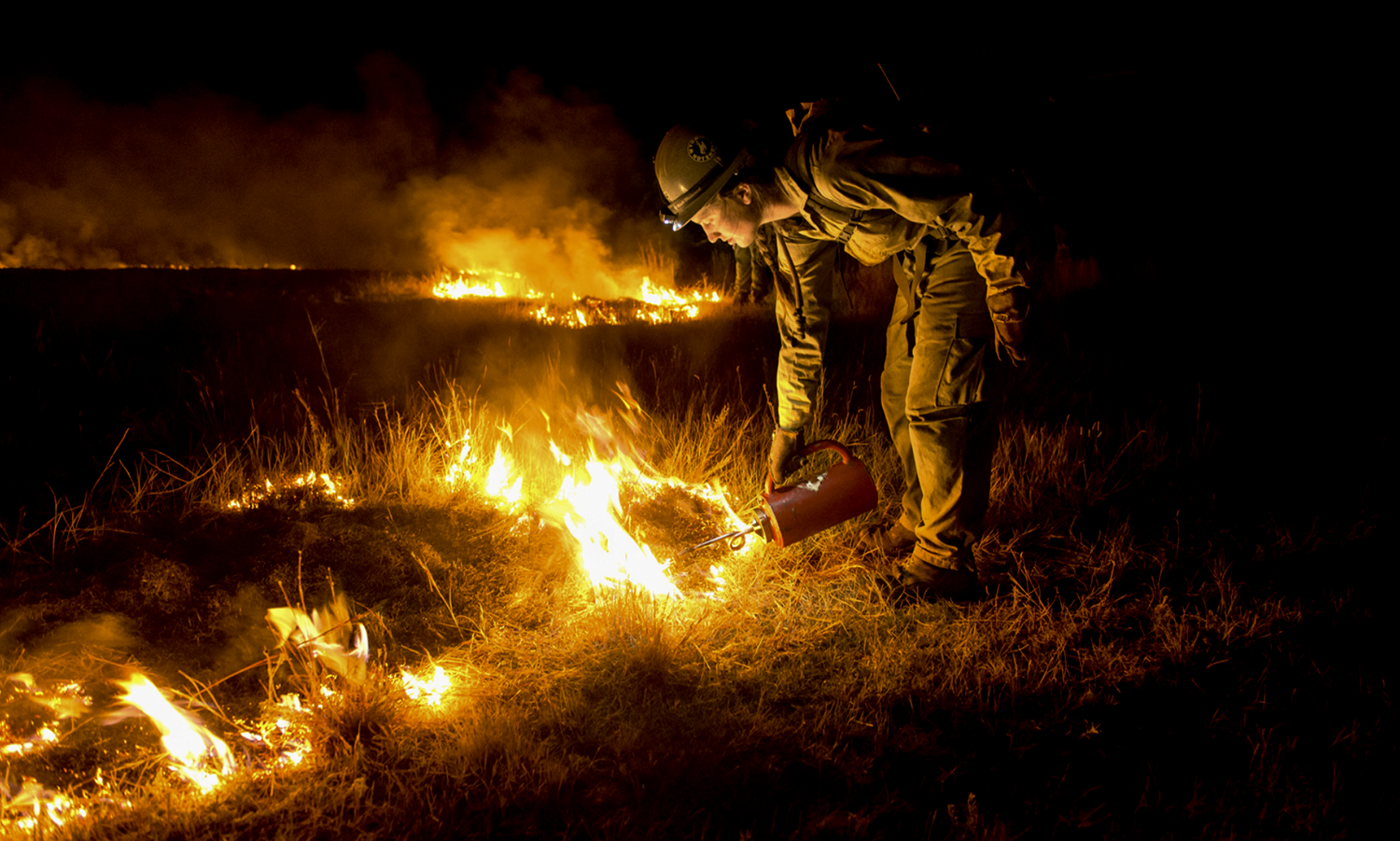

New Website Offers a Deep Dive into Intentional Fire
July 25, 2024 – Intentionalfire.org, a new educational website from the Climate & Wildfire Institute, offers an immersive, interactive view into the use of intentional fire, including prescribed fire and cultural fire. The website provides concise and easy to understand information about the benefits and importance of intentional fire. It also features engaging audio and video clips, project case studies, and actionable steps for people to help advance intentional fire in their communities. Increased use of intentional fire is a critical component of California’s Strategic Plan for Expanding the Use of Beneficial Fire.
CNRA Webinar on the State of Wildfire in California

CNRA Webinar on the State of Wildfire in California
August 8, 2024 – California Natural Resources (CNRA) Secretary Wade Crowfoot hosted a webinar on the state of wildfire in California as part of the Secretary Speaker Series.
Secretary Crowfoot was joined by representatives from the Task Force, CAL FIRE, U.S. Forest Service, the Karuk Tribe, and others for a conversation on current efforts to protect California from dangerous wildfires and restore the health of our landscapes.
Recap of Sacramento 7/12 Task Force Meeting
SACRAMENTO TASK FORCE MEETING RECAP
July 12, 2024
The Task Force held its quarterly meeting at the California Natural Resources Agency in Sacramento and live on Zoom. CAL FIRE Director Joe Tyler provided an update on the current fire season and Task Force Director Patrick Wright reported on state and federal budget allocations. Then several panels of statewide and regional leaders discussed challenges and next steps for aligning and coordinating state, federal, and private funding to better support regional priority needs and increase program sustainability.
Moderated by Forest Schafer, State Coordinator with the Task Force, panels focused on three key areas related to Aligning Regional Investments:
- State & Federal Frameworks
- Expanding Partnerships
- Regional Approaches
Welcome & Executive Remarks
Co-chairs
- Wade Crowfoot, CA Natural Resources Agency
- Jennifer Eberlien, U.S. Forest Service
Task Force Executive Committee
- Patrick Wright, Wildfire & Forest Resilience Task Force
- Joe Tyler, CAL FIRE
- Valerie Hipkins, USFS Pacific Southwest Research Station
- Sam Assefa, Governor’s Office of Planning and Research
- Ed Valenzuela, California State Association of Counties
- Katy Landau, CalEPA
Director’s Report
- Patrick Wright, Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force
Aligning Regional Investments
State & Federal Frameworks
- Liz Berger, U.S. Forest Service
- Trevor McConchie, Washington State Department of Natural Resources
- Mary McDonnell, California Department of Conservation
- Shannon Johnson, CAL FIRE
Expanding Partnerships
- Chris Morrill, National Fish & Wildlife Foundation
- Michelle Wolfgang, Eldorado National Forest
- Sashi Sabaratnam, PG&E
- Eric Tsai, California Department of Water Resources
Regional Approaches
• Brittany Covich, Sierra Nevada Conservancy
• Karen Gaffney, North Coast Resource Partnership
• Heather Marlow, RCD of Greater San Diego
Closing Remarks
- Task Force Executive Committee
The Next Task Force Meeting is this Friday, July 12th

The Next Task Force Meeting is this Friday, July 12th
Join us in person in Sacramento (no registration needed) or remotely via Zoom. The agenda will include an update on the current fire season from CAL FIRE Director Joe Tyler, a report on state and federal budget allocations from Task Force Director Patrick Wright, and a session on aligning and coordinating state, federal and private funding to better support regional priorities.
Friday, July 12, 2024 – 9:00 AM to 12:15 PM
In person: CA Natural Resources Agency Auditorium, 715 P St., Sacramento, CA
Online: Register for Zoom




