Introduction
The California Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force (Task Force) was established in 2021 to advance a holistic, integrated approach toward creating landscape and community resilience. The Task Force’s purpose is to deliver on the key commitments in the California Wildfire and Forest Resilience Action Plan (Action Plan) – a comprehensive framework for establishing healthy and resilient landscapes and communities that can withstand and adapt to wildfire, drought and a changing climate.
Senate Bill (SB) 456 requires the Task Force to submit a report annually on progress made in achieving the goals and key actions identified in the Action Plan.
To meet the requirements of SB 456, this report includes:
> II. Task Force Progress
a. Progress on Key Actions
b. Progress on Joint Strategies
c. Progress on Treatment Goals
I. Highlights from 2023
This report covers progress made by the Task Force and its interagency partners from January 2023 through December of 2023.
Progress highlights are summarized under the four multi-jurisdictional goals of the Action Plan:
Goal 1: Increase The Pace and Scale of Forest Health Projects
- USFS and Department of Interior published Reforestation Goals and Assessments, and a Climate-Informed Plan to Increase Federal Seed and Nursery Capacity which includes an agency-specific target to reforest over 2.3 million acres nationwide by 2030. The report also includes an opportunity assessment of voluntary reforestation through federal programs and partnerships. (April 2023)
- Bureau of Land Management launched a Statewide WUI Environmental Assessment Statewide Wildland-Urban Interface (WUI) Fuels Treatment Programmatic Environmental Assessment (EA) to streamline plans to protect communities, reduce wildfire risk, and improve forest health. Under the EA, fuels treatment projects will be coordinated across land ownerships to create a landscape-level network of strategic fuels treatments and breaks within the WUI. (August 8, 2023)
- CAL FIRE and Bureau of Land Management entered into a statewide agreement through the Good Neighbor Authority and a contract worth approximately $4.5 million was made available to CAL FIRE as part of the agreement. The primary objective of this contract is to mitigate the potential devastation caused by wildfires specifically on BLM lands. (August 10, 2023)
- The Federal Wildland Fire Mitigation and Management Commission, co-chaired by the U.S. Departments of Agriculture and Interior and the Federal Emergency Management Agency, released a final report submitted to Congress that reflects a comprehensive review of the federal wildfire system and makes 148 recommendations. (September 27, 2023)
- The Task Force with American Forests developed a Reforestation Pipeline Report which outlines strategies to ensure California has the capacity to actively reforest lands impacted by wildfires, drought, and pests by offering solutions to address critical supply gaps through a Reforestation Pipeline Partnership. The report will be integrated into the 2025 Action Plan. (December 31, 2023)
Goal 2: Strengthen Protection of Communities
- UCSD’s ALERTCalifornia and CAL FIRE embarked on an innovative Artificial Intelligence (AI) implementation trial. ALERTCalifornia deployed 1,032 high-definition, pan-tilt-zoom cameras as a 24-hour surveillance network for efficient monitoring of active wildfires and other disasters. The pilot will enlist AI to identify abnormalities in the camera feeds and promptly notify emergency command centers. (May 3, 2023)
- California Department of Public Health published California Wildfire Smoke and Air Pollution Health Burden Mapping Dashboard that displays the health burden (excess emergency room visits) related to air pollution and wildfire smoke. The Dashboard allows users to visualize the burden in any zip code of interest, as well as how the burden is distributed among races and ages, and proximity to medical facilities, schools, historical wildfires and air quality readings (May 2023).
- CAL FIRE rolled out a first-of-its-kind approach to curbing the state’s catastrophic wildfire problem by providing new protections for prescribed fire and cultural burn practitioners. The $20 million allocated for the Prescribed Fire Liability Claims Fund Pilot will cover losses in the rare instance that a prescribed or cultural burn escapes control. (June 2023)
- Cal OES and CAL FIRE piloted a home hardening initiative that provides funding for defensible space and ignition resistant retrofits to approximately 2,400 homes in six counties over the next three years. (September 21, 2023)
- CAL FIRE Office of State Fire Marshal established a Defensible Space Assessment Training Program to increase defensible space and home hardening assessments within the State Responsibility Area. The training helps to educate property owners about wildfire safety improvements that may be undertaken to harden a structure and make it more resistant to wildfire. (September 25, 2023)
- The Office of Energy Infrastructure Safety adopted its 2025 Wildfire Mitigation Plan (WMP) Update Guidelinesto assist California’s electrical corporations in meeting a statutory requirement to submit three-year WMPs to Energy Safety on an annual basis for review and approval (September 2023).
- The Task Force with the Resources Legacy Fund, CAL FIRE, and Ascent Environmental initiated the Fire Adapted Communities Roadmap and Dashboard Project – a strategic statewide initiative focused on fire-adapted and resilient communities, expanding, and building upon other ongoing California wildfire resilience initiatives. (December 2023)
- CAL FIRE completed more than 250,000 Defensible Space inspections for calendar year 2023.
- CAL FIRE’s Office of State Fire Marshal and National Fire Protection Association Recognized the 785thFirewise USA® community in CA.
Goal 3: Manage Landscapes to Achieve State Economic & Environmental Goals
- CAL FIRE initiated Green Schoolyards Grants to improve tree canopy cover on California K-12 public school campuses and nonprofit childcare facilities. (March 22, 2023)
- CNRA published an annual progress report on the 30×30 Initiative showing that California added approximately 631,000 acres of conserved land since April 2022, bringing the statewide total to 24.4 percent of lands and 16.2 percent of coastal waters protected. (May 2023)
- Governor Newsom signed Senate Bill 337, codifying into law the statewide goal to conserve at least 30 percent of California’s land and coastal waters by 2030 (30×30). The three primary objectives of 30×30 are to conserve and restore biodiversity, expand access to nature, and mitigate and build resilience to climate change. (October 7, 2023)
- CNRA released the Outdoors for All Strategy which provides a blueprint to increase access to the outdoors for all Californians. Outdoors for All is focused on expanding parks and outdoor spaces in underserved communities, supporting programs to connect people who lack access, and fostering a sense of belonging for all Californians in the outdoors. (November 15, 2023)
Goal 4: Drive Innovation and Measure Progress
- CAL FIRE posted the first version of a manual outlining field monitoring protocols for the California Prescribed Fire Monitoring Program and outcome monitoring of completed Forest Health grants. The protocols include project and unit selection; data collection instructions for various project types; use of tools and technologies by field personnel; and data storage, handling and analysis procedures. (March 14, 2023)
- Task Force launched the beta version of a first-of-its kind Interagency Treatment Dashboard that displays the size and location of state and federal forest and landscape resilience projects in California. The dashboard offers a one-stop-shop to access data, provide transparency, and align the efforts of more than a dozen agencies to build resilient landscapes and communities in California. (August 29, 2023)
- Task Force published Regional Profiles and Regional Resource Kits for all four regions of California. The kits bring together the scientific data needed to help regional entities plan, prioritize, and monitor projects. (October 4, 2023)
- Task Force partners collaborating on Planscape continued to add functionalityand discuss future plans for the free decision support tool. The Planscape tool was developed to assist regional planners in prioritizing landscape treatments to mitigate fire risk, maximize ecological benefits, and help California’s landscapes adapt to climate change. Planscape is a collaborative effort by the California Natural Resources Agency, the USFS, University of California, and Spatial Informatics Group (SIG) with support from Google.org.
II. Task Force Progress
Progress on Key Actions
The 2021 California Wildfire and Forest Resilience Action Plan comprises 99 Key Actions organized under the four multi-jurisdictional goals. Each of the Key Actions are assigned to a lead agency (or agencies) and a work group. Since April of 2021, the Task Force has tracked progress on the 99 Key Actions. Each quarter, the work groups update their progress on Key Actions and the Task Force summarizes these updates on its Progress on the Key Actions webpage.

Key Action Status as of December 31, 2023:
37 – Complete
37 – Remain On-Going Support Efforts
9 – Near Completion
16 – In Progress
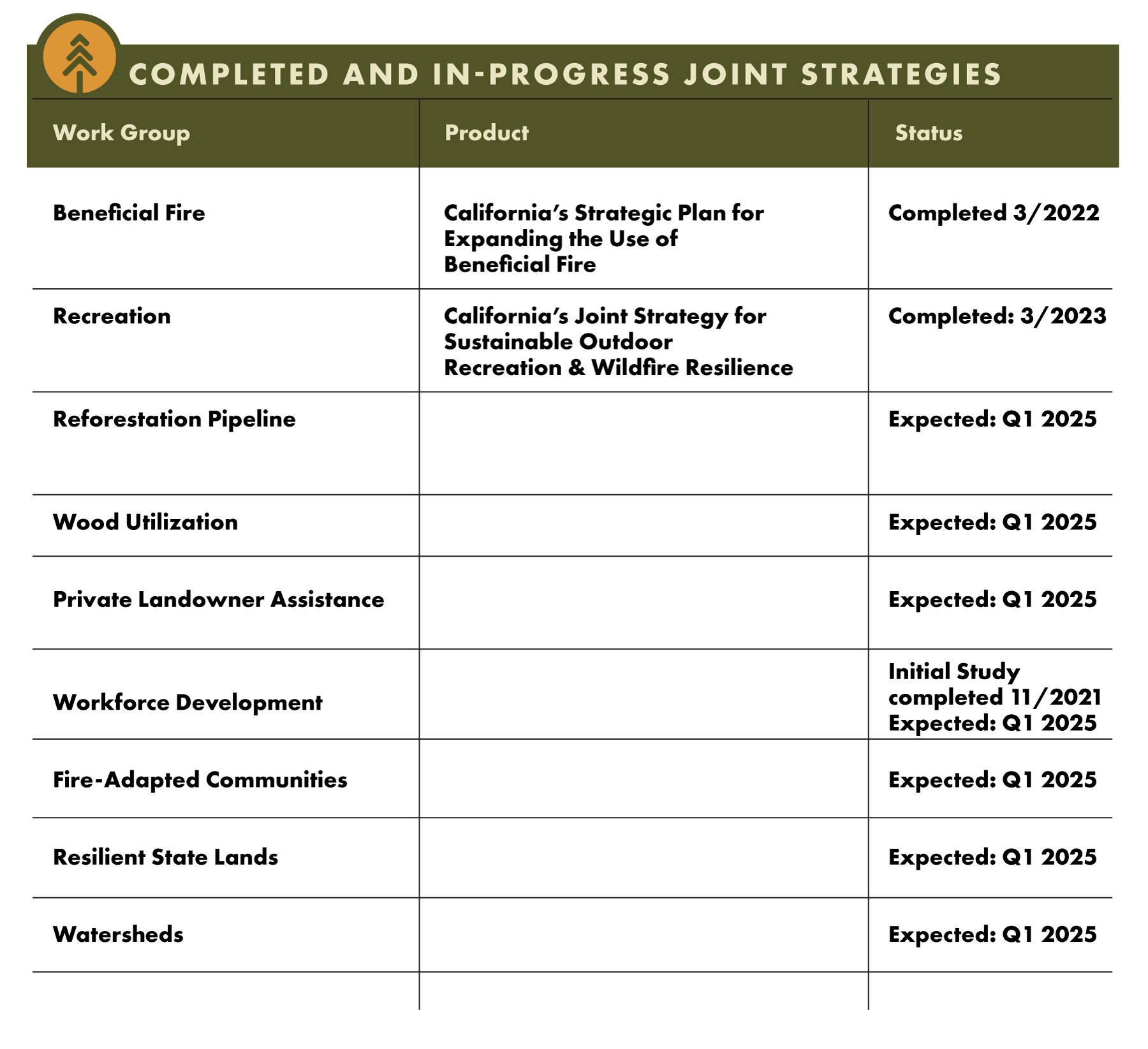
Progress on Joint Strategies
Task Force work groups continued developing joint strategies in 2023 that set aggressive yet achievable targets for critical components of the Action Plan. The strategies highlight logistical barriers and policy issues and identify solutions for aligning efforts and achieving resilience. Upon completing a joint strategy, a work group will begin to implement their identified solutions.
Progress on Treatment Goals
Key Action 4.8 of the Action Plan calls for the development of consistent reporting tools. As such, the Task Force has developed an Interagency Treatment Tracking System and Dashboard which catalogs, summarizes, and makes available spatial and non-spatial data and information on vegetation treatments conducted by state, federal and local agencies, and others to advance the State’s goals to increase landscape management efforts to reduce wildfire risks and improve ecosystem health and resilience. The associated Dashboard is a highly interactive online tool, currently in Beta form, by which users can sort treatments by region, county, land ownership, and more.
Vegetation treatment data is being counted and displayed in two ways:
- Footprint acres are calculated through spatial analysis to ensure an acre that experienced one or more treatments is only counted once annually.
- Activity acres track every treatment action, including those that occurred in sequence on the same acre over time. For example, a thinning project may have been conducted on an acre prior to a prescribed burn.
The Task Force is measuring progress toward acreage targets based on “footprint acres” because this metric best captures the geographic areas that were treated during the year.
Approximately 60 different activities are displayed in the Dashboard, grouped into the categories of:
- Mechanical and hand fuels reduction
- Timber harvest
- Tree planting
- Prescribed Fire
- Targeted grazing
III. Measuring the Impact of Our Work
To comprehensively understand and communicate the impacts of projects implemented, acres treated, and funding invested, it is important to evaluate and measure the benefits of treatments at both the landscape and regional scale and track progress toward multiple landscape and socio-economic objectives.
A. Core Reporting Metrics
The Task Force is developing a honed set of Core Reporting Metrics that will help us understand and track progress toward multiple objectives – including reducing fire risk to communities, restoring landscape resilience, and enhancing biodiversity, carbon storage, water security, air quality, and social and economic health. A candidate set of metrics was recommended by the Task Force’s Science Advisory Panel and was presented for public review and feedback in February 2024.
Using a set of core metrics will help facilitate a more nuanced discussion with the public and decision makers on the impacts work is having beyond number of acres treated and help inform adaptive management. Core Reporting Metrics will evolve over time as new data becomes available and our scientific understanding of our ecosystems and climate change grow.
B. Programmatic Monitoring and Evaluation Efforts
Using data collected directly from the field and from remote sensing technology, various State and federal agencies are monitoring ecosystem conditions over time. They aim to answer important questions like how ecosystems are changing, how these changes impact public safety, and how management practices affect these changes. These complementary monitoring efforts range from project-level to statewide. They use the Task Force’s Regional Resource Kits, along with data from the Interagency Tracking System and Dashboard, to gather and analyze information.
IV. A Regional Framework
The Task Force recognizes that central to achieving the goals of the Action Plan is the need to mobilize regional approaches to landscape health and resilience.
The Task Force’s Regional Framework provides a structure for assessing landscape conditions, setting objectives, planning, funding and implementing projects, and measuring progress towards social-ecological resilience. The Regional Frameworks include the following key components:
A. Engaging the Regions
Hosting Regional Meetings has proved invaluable for the Task Force to gain a deeper understanding of each region’s unique physical and socio-economic landscapes, establish relationships with the organizations and individuals that are making a difference on the ground, and better understand the unique challenges and opportunities each region faces. In 2023, the Task Force hosted meetings in three of the four Task Force Regions:
- Southern California: February 2, 2023, at King Gillette Ranch in Calabasas, sponsored by Santa Monica Mountains Conservancy and Mountains Recreation and Conservation Authority
- Central Coast: May 11, 2023, in Santa Cruz hosted by the California State Coastal Conservancy and San Mateo Resource Conservation District.
- Northern California: October 5, 2023, in Redding hosted by Shasta College, North Coast Resource Partnership, and Napa and Tehama RCDs.
B. Regional Profiles
The Task Force Science Advisory Panel developed a series of Regional Profiles to summarize the social and ecological context relating to community and ecosystem resilience to wildfire in each of the state’s regions. Each Regional Profile includes stakeholder input gathered via an anonymous survey about priority areas of investment for achieving resilience, as well as more focused interviews with regional experts and leaders about key issues, barriers, and opportunities for increasing resilience to wildfire.
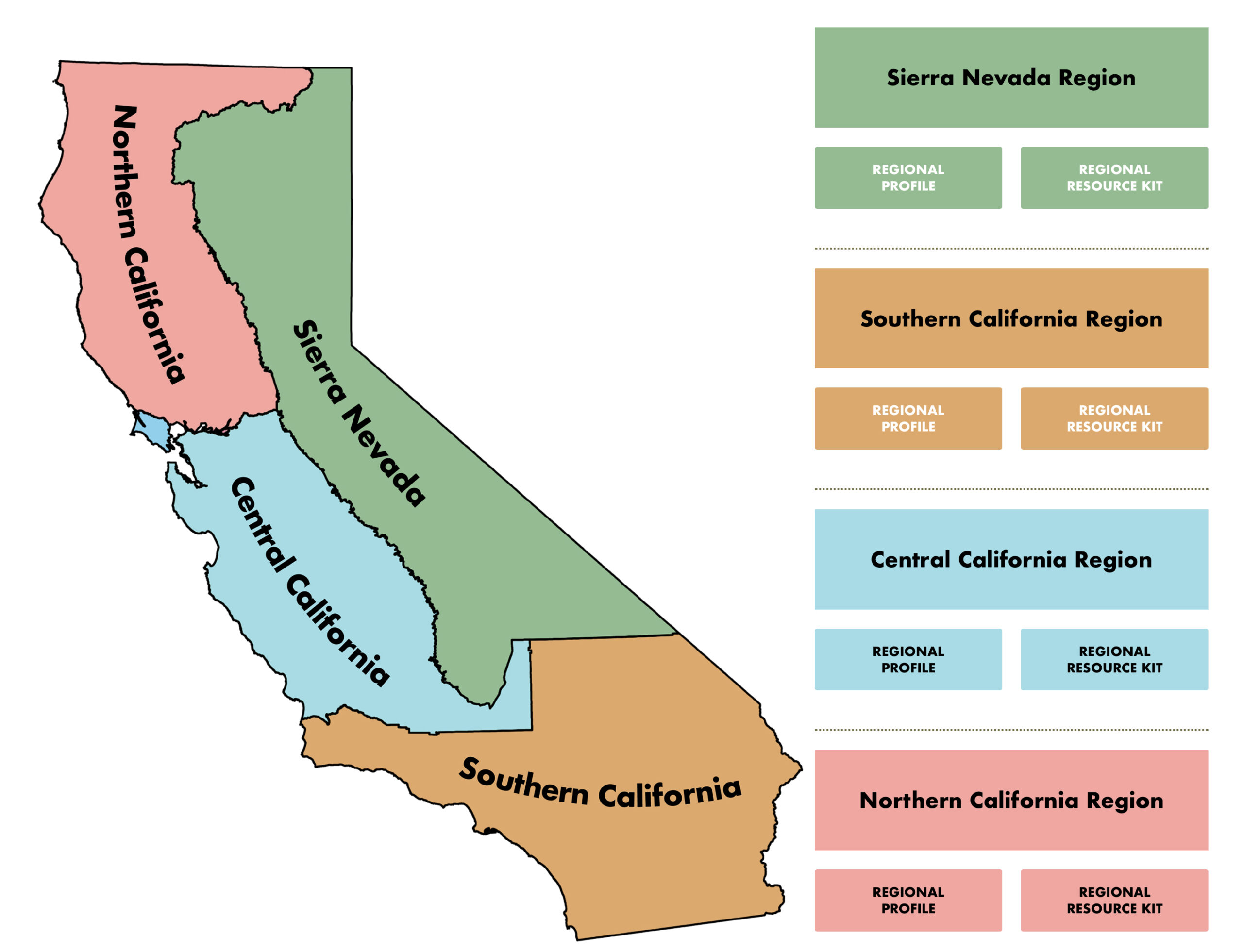
C. Regional Resource Kits
Regional Resource Kits are sets of tools and data created to accelerate the work by regional partners and collaboratives to reduce wildfire hazard and improve the conditions of forested and shrub landscapes. Kits are composed of coordinated data, information, and tools to provide open access to up-to-date, high-quality, and vetted resources. As of December 2023, Resource Kits have been developed for statewide application and one for each of the four Task Force Regions. The kits will be revised based on user feedback and updated as new science and technologies are developed.
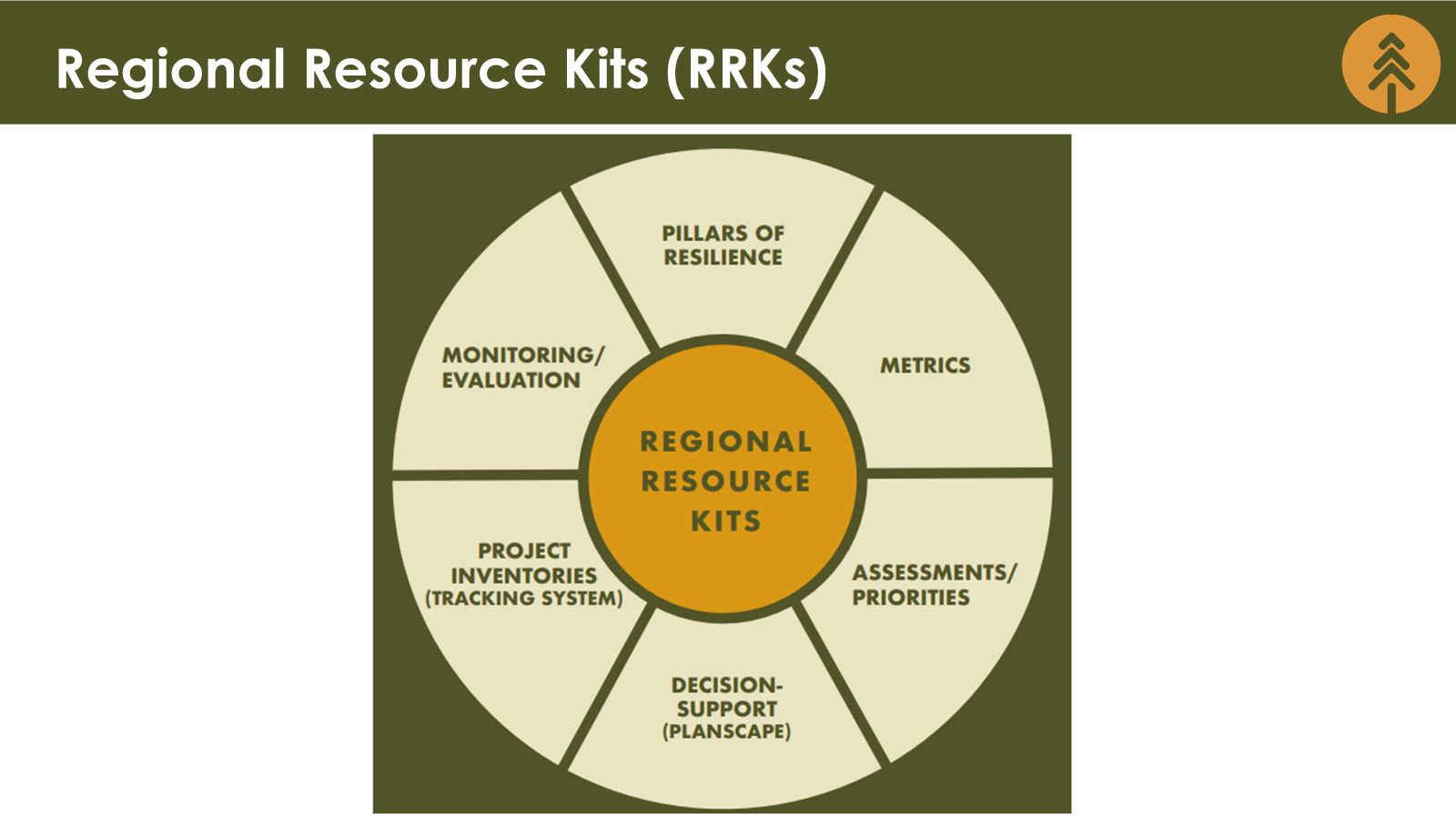
Each Regional Resource Kit provides:
- Pillars of Resilience – The 10 Pillars of Resilience describe desired landscape outcomes that encompass the suite of social and ecological benefits provided by resilient systems across fire-prone landscapes.
- Metrics – Each pillar is supported by a set of statewide or regional data layers to assess current landscape conditions and verify that actions result in meeting resilience objectives.
- Assessments/Priorities – A suite of data and mapping tools that offer spatially explicit assessments of current conditions for key resources.
- Decision-Support – A set of tools to help land managers evaluate large amounts of data to consider potential management options. Such tools are often used to compare current with future or desired conditions or examine tradeoffs among alternative land management actions.
- Planscape – In coordination with the Task Force, CNRA, USFS, University of California, and Google.org have supported the development of Planscape, a free, open-source, web-based tool for regional planners to plan, prioritize, and coordinate resilience treatments across forested and chaparral landscapes. The Task Force is developing mechanisms to continue hosting, maintaining, and supporting the tool for the long-term, and to ensure consistency and integration with other Task Force products.
- Decision Support Guide – an online guide to help land managers better understand the tools available to them to help make the critical decisions required to keep their lands healthy and resilient. The Science Advisory Panel, in collaboration with U.S. Forest Service Region 5 and Pacific Southwest Research Station, created the guide.
- Project Inventories (Interagency Treatment Tracking System & Dashboard) – The Tracking System is a spatial database that integrates wildfire and landscape resilience treatment projects across California from state and federal agencies into a single web-based interactive tool, viewed in the Interagency Dashboard.
- Monitoring/Evaluation – CNRA and the California Air Resources Board (CARB) are teaming up with NASA Ames Research Center to create new statewide, high-resolution datasets that use new types of remote sensing data and treatment data. This effort will monitor changes in California’s forests, shrublands, and grasslands over time and evaluate the effectiveness of management practices. including treatment-wildfire interactions. CARB will maintain this data to help ensure the success of the state’s public health and safety programs, particularly those related to wildfire and climate.
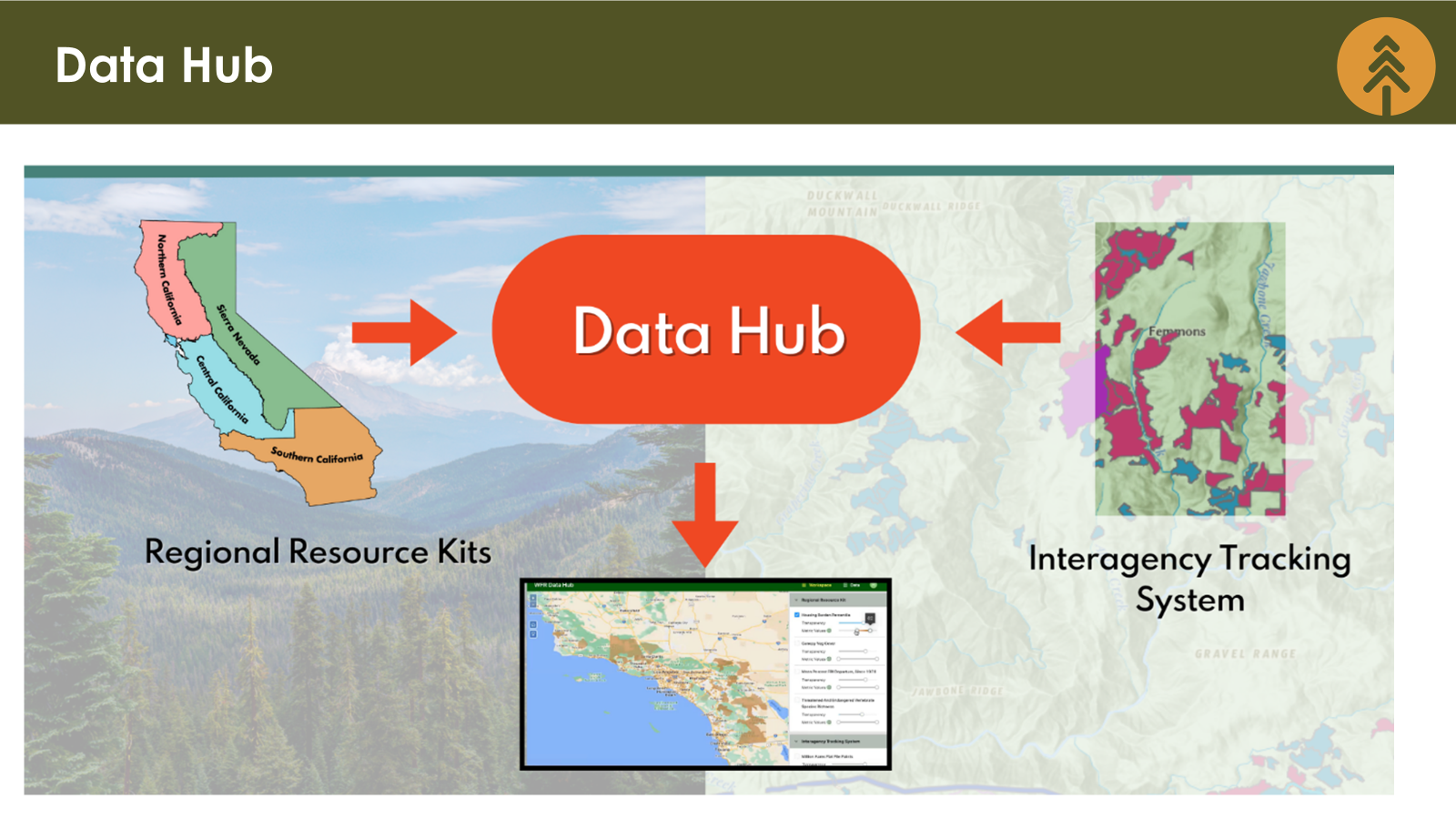
D. Wildfire and Landscape Resilience Data Hub
The data and tools of the Regional Resource Kits will be hosted and delivered by the Wildfire and Landscape Resilience Data Hub (Data Hub). Key Action 4.3 of the Action Plan called for the establishment of a Data Hub to serve as “a multi-institutional information clearinghouse with the goal of supporting, integrating, evaluating, and synthesizing ongoing reporting and monitoring efforts conducted by state and federal agencies, universities, and non-governmental organizations.”
In response, the Task Force and CAL FIRE-FRAP are developing the Data Hub to serve as an integrated resource to catalog and manage data from a multitude of partners (e.g., state, federal, local, regional, and private landowners, etc.), and make this data useful, accessible, and interoperable for planning, tracking, monitoring, evaluating, and sharing information.
As of December 31, 2023, the Task Force and CAL FIRE-FRAP have designed a federated, scalable Data Hub platform including, 1) developing the structure and functionality of the data mediator, 2) performing alpha testing of the system; and 3) integrating into the central database the Task Force’s Interagency Tracking System and Regional Resource Kits.
In 2024 the Task Force expects to 1) publicly share the Data Hub; 2) begin exploring adding additional sources of data; 3) develop a governance structure and guidance document; 4) present a long-term, sustainable solution for the Data Hub.
E. Local Plans & Project Pipelines
The Department of Conservation’s (DOC) Regional Forest and Fire Capacity (RFFC) Program is a key component of the Regional Framework adopted by the Task Force. With support from the RFFC Program, local and regional leaders are developing Regional Priority Plans that identify and prioritize projects at the landscape or watershed-level to address forest health and wildfire risks within their region. Regional plans are guiding the development of a pipeline of projects which will feed combined federal, tribal state, and private regional investment strategies.
F. Regional Investment Strategies
The coordination of regional partners is providing a structure for federal, tribal, state, and private entities to coordinate their own efforts to fund landscape-scale, multi-benefit projects.
In 2023, CAL FIRE committed funding to three collaborative land management partnerships for “Regional Grant Pilots.” The intent of these Pilots is to support regional capacity building, partnerships, and prioritization; bring funding to small projects and organizations that could not otherwise access it; and allow CAL FIRE and other funding partners to learn from these pilots prior to investing in other regional projects.
- North Coast Resource Partnership:
- $10 million from CAL FIRE Forest Health
- $2 million from Department of Conservation-RFFC
- Great Basin Institute: Restoration activities in the Crystal Basin supported by the Healthy El Dorado Partnership
- $7 million from CAL FIRE Forest Health
- $2 million from Sierra Nevada Conservancy
- $1 million from U.S. Forest Service
- RCD of Greater San Diego County:
- $5 million from CAL FIRE Forest Health
- $5 million from CAL FIRE Wildfire Prevention
- $30 million from USFS-National Forest Foundation Master Stewardship Agreement
- $20 million from the Department of Conservation-RFFC
- $10 million from the USFS Fireshed Risk Reduction Strategy
V. 2025 Action Plan Update
SB 456 (2021, Laird) requires the Task Force to complete an update of the Action Plan by January 1, 2026. To provide information to the state, federal, tribal, local, and private partnership on what actions are needed and most effective for increasing pace and scale, the Action Plan will need to integrate the following:
- Joint strategies that incorporate and align state, federal, and tribal plans, mandates, and initiatives.
- A set of modeled treatment scenarios by region with varying locations, amounts, intensities, and types of treatments.
- An evaluation of the costs, benefits, and trade-offs between the modeled scenarios by region.
- Other statewide modeling data.
The Action Plan update will lay out the charge for the next five years and the steps necessary to increase the pace and scale of landscape management and wildfire resilience efforts beyond 2025. The Action Plan Update will include:
- A set of recommendations drawing from treatment scenarios and derived from a common framework of metrics and assessments to align state, federal, and local investments in state and regionally driven forest and wildland health programs across regions.
- An analysis to identify existing policy and organizational frameworks that can support these efforts, as well as identifying policy changes that will be required to meet the one-million-acre treatment target.
- Processes for aligning and integrating Task Force data activities with initiatives and mandates that overlap with the update, including the USFS 10-Year Wildfire Crisis Strategy, California’s 5th Climate Change Assessment, Climate Change Scoping Plan, Natural and Working Lands Climate Smart Strategy, Pathways to 30×30.
VI. State Wildfire and Forest Resilience Budget & Expenditures
A. State Highlights:
The Task Force has developed a Wildfire and Forest Resilience Expenditure Plan that links Action Plan deliverables with the state’s proposed and enacted budget allocations. The Expenditure Plan was last updated to reflect AB179, the Budget Act of 2022, and SB 101, the Budget Act of 2023, which provided more than $1.3 billion to accelerate forest health and wildfire resilience projects throughout the state. With these investments, the Newsom Administration has committed more than $2.7 billion to the Action Plan.
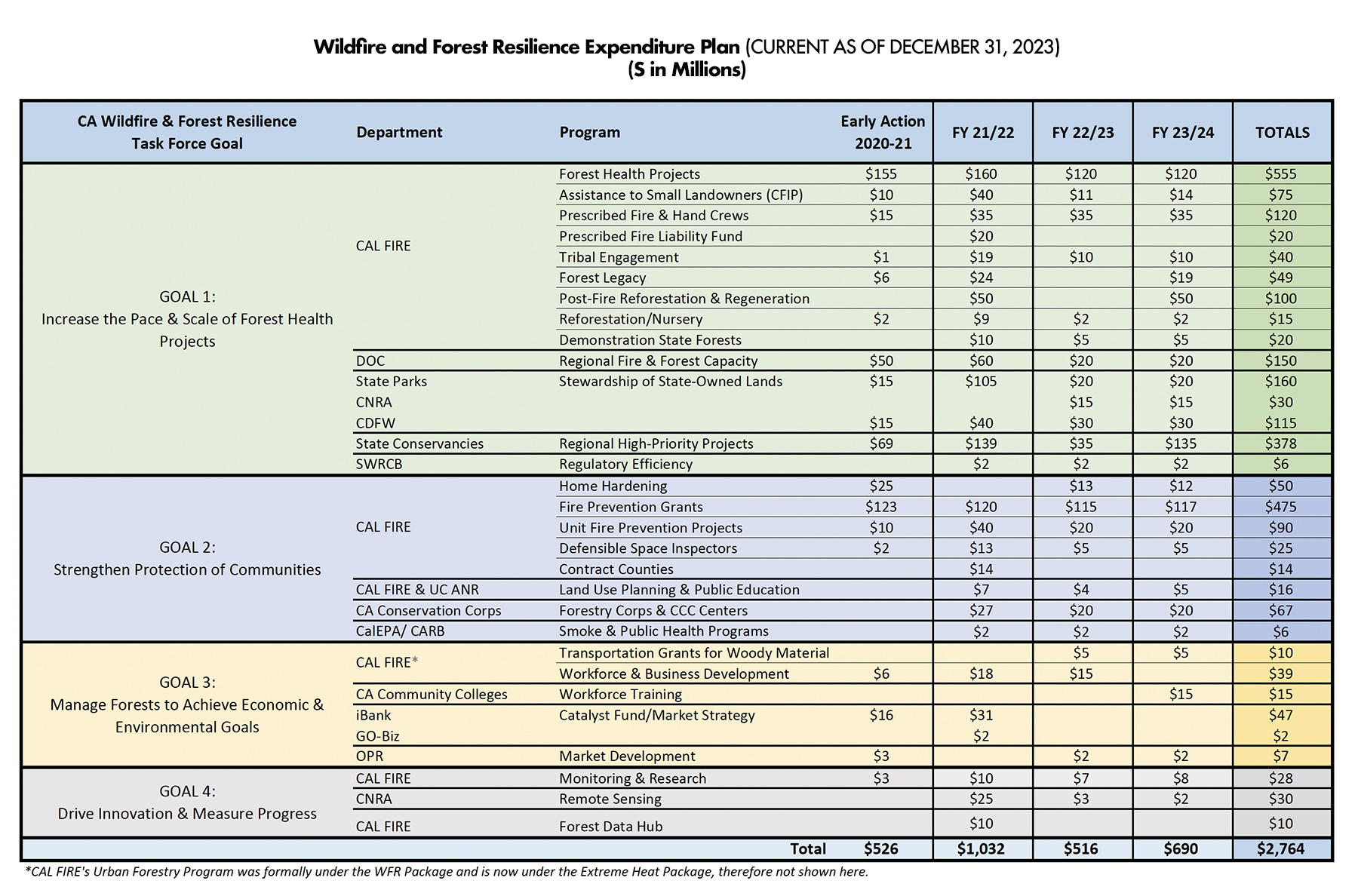
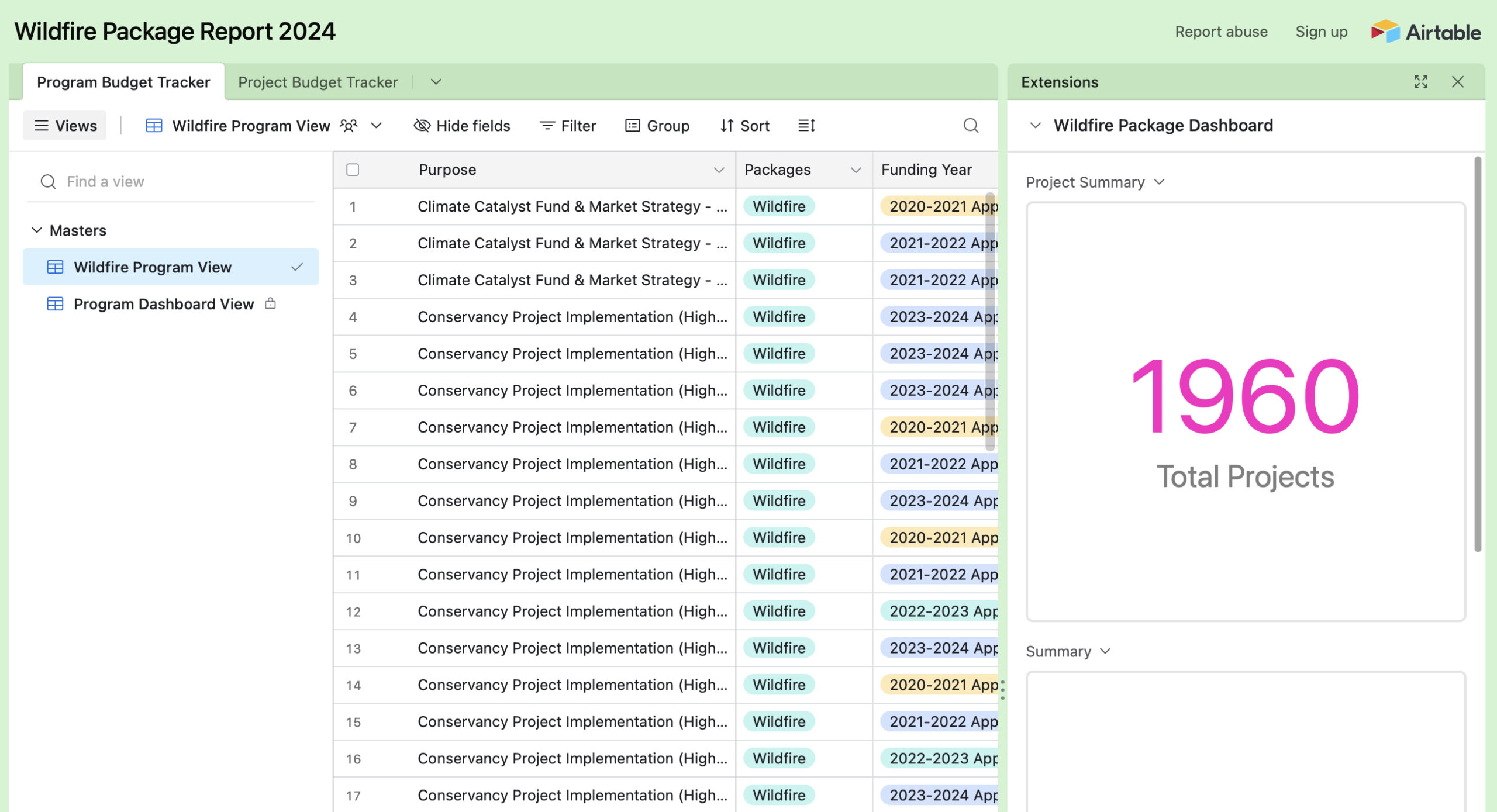
The California Natural Resources Agency compiled a report on California’s Wildfire Resilience Investments through March 1, 2024, a program-by-program description of the 40 programs these investments fund, examples of recent impacts from each of those programs, and an interactive table that shows the status, location and description of each of the nearly 2,000 projects already completed or underway (shown below).
B. Federal Highlights:
U.S. Forest Service
- Wildfire Crisis Strategy: $930 million to expand and continue efforts to reduce wildfire risk across the Western United States in 21 high risk landscapes, seven of which are in California, covering nearly 19 million acres, including:
- Klamath River Basin in California and Oregon – 10 million acres
- Trinity Forest Health & Fire-Resilient Rural Communities – 910,000 acres
- Plumas Community Protection – 285,000 acres (January 19, 2023)
- North Yuba – 313,000 acres
- Stanislaus – 245,000 acres
- Southern California Fireshed Risk Reduction Strategy – 4 million acres
- Sierra & Elko Fronts in Nevada and California – 3.4 million acres
- Joint Chief’s Landscape Restoration Partnership: More than $48.6 million for 14 joint USFS and Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) projects nationwide that mitigate wildfire risk, improve water quality, restore forest ecosystems, and ultimately contribute to USDA’s efforts to combat climate change. An award of $3.3 million funded a phase three project focused on fire resilience in Trinity County. The project addresses high-risk cross-boundary threats by strategically treating forests on both private and national forestlands, and address new threats created by 2020 and 2021 wildfires. (February 21, 2023)
- Community Wildfire Defense Grant program: $197 million in funding for 100 projects across 22 states and seven tribes as part of the. Grants to California counties, cities and tribes totaled over $97M across 22 projects including: $10M in Tuolumne County; nearly $10M in Siskiyou County; $9.9M in Lake County; $7.2 M to the City of Ukiah and Mendocino County; $6.8 in Plumas County; and $6.4M in Butte County. (March 20, 2023)
- Wood Products Infrastructure Assistance: 14 California projects received funding to help strengthen wood products economy, forest sector jobs, and sustainable forest management. (April 6, 2023)
- Community Wood Grants and Wood Innovations Grants: California received nearly $3.5 million to invest in 12 Wood Innovations grants as part of USFS’ $54 million nationwide investment. The funded projects will expand modern wood use — as construction material in commercial buildings, as an energy source, and as manufacturing and processing for wood products used in framing homes and more. (June 9, 2023)
- Urban and Community Forestry Grants: Over $1 billion to plant and maintain trees, combat extreme heat and climate change, and improve access to nature in cities, towns, and suburbs. This includes 43 funded projects with funds totaling over $100 million across cities in California. (September 14, 2023)
Natural Resources Conservation Service
- NRCS California: Over $20 million investment in climate-smart agriculture practices and forest resiliency in California from the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), including $6.8 million for the Environmental Quality Incentives Program; $5.2 million for the Conservation Stewardship Program; and $7.6 million for the Conservation Technical Assistance Program. The IRA represents the single largest investment in climate and clean energy solutions in American history. It is expected to provide continued high level of funding for forestry in California. (February 17, 2023)
Department of the Interior
- More than $417 million for 47 projects dedicated to recreation improvement, wildlife habitat conservation, hazardous fuels reduction, wildfire prevention, and other purposes throughout Nevada and on the California side of the Lake Tahoe Basin. (March 16, 2023)
- $185 million from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law to support wildland fire management nationwide in fiscal year 2023 and to assist land managers in planning for wildfire management activities in fiscal year 2024. (July 12, 2023)
- $12.2 million from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law to advance wildfire resilience work and support fuels management projects on 27,669 acres in California. (November 30, 2023)
VII. Continued Communications
The Task Force uses multiple communication channels to ensure timely and transparent communications to interested parties. These channels include:
- Bi-Monthly Meetings: The Task Force met bi-monthly in 2022 and 2023 and will meet quarterly in 2024 (in-person and livestreamed options), with twice-yearly convenings hosted in each of the four regions of the state. The meetings are recorded and archived.
- Task Force Website: The Task Force hosts a full-service website with the latest news and updates; meeting agendas and recordings of past meetings; Task Force organization and contacts; Airtable updates; Working group assignments; and press releases and publications.
- Monthly Update to the Governor: The Task Force assembles a monthly newsletter comprised of briefs of the latest state and federal updates; Task Force news; pending legislation; and science and press publications. The “Governor’s Monthly Update” is delivered via e-Newsletter to an electronic mailing list of over 3,000 subscribers.
- Social Media: Regular posts on Task Force and partner accomplishments are delivered across the following outlets:
- Twitter: @CAwildfireTF
- LinkedIn: CA Wildfire & Forest Resilience Task Force
- Instagram: wildfiretaskforce
- Facebook: CA Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force
- Videos: The Task Force hosts videos on YouTube (@cawildfireforestresilience6079) of archived Task Force meetings, Work Group presentations and partner interviews.