State Conservancies Award Nearly $14 Million of Climate Bond Funds for Wildfire Resilience Projects

State Conservancies Award Nearly $14 Million of Climate Bond Funds for Wildfire Resilience Projects
In April of 2025, Governor Newsom signed Assembly Bill 100 which allocated over $170 million in accelerated, or “early action” Climate Bond funding to conservancies for urgent forest and vegetation management across California. The California State Coastal Conservancy (Coastal Conservancy) and the Sierra Nevada Conservancy (SNC) have moved quickly to ensure these funds are being distributed to enable progress on-the-ground.
November 20,2025 – Coastal Conservancy Awards Over $11 Million for Wildfire Resilience: The Board of the State Coastal Conservancy awarded over $11 million for ten projects that aim to reduce the risk and impact of catastrophic wildfires along the coast. Five of these projects received $9.4 million in accelerated funding from the Climate Bond (Prop 4).
- Esselen Tribe of Monterey County: $1,250,000 to plan and implement a series of cultural fire trainings that include live fire cultural burning operations on 50 to 500 acres of land.
- La Jolla Band of Luiseño Indians: $2,900,000 to implement critical fuel reduction treatments and cultural burning on 516 acres along the Highway 76 corridor and to provide community fire preparedness training.
- Mendocino County Fire Safe Council: $803,000 to continue their free community chipping program, implement volunteer workdays, and develop a sustainability plan, over three years.
- University of California San Diego: $1,400,000 to remove Eucalyptus trees and restore the native chaparral ecosystem on a 30-acre site to improve wildfire resiliency and to serve as a biochar demonstration project.
- Sempervirens Fund: $3,050,000 to undertake the Big Basin Redwood Wildfire Resilience Project, consisting of vegetation fuels reduction and habitat enhancement on 215 acres in the old-growth coast redwood area of Big Basin Redwood State Park.
Additionally, five projects were awarded $1,665,000 in accelerated Climate Bond funding from the Department of Conservation’s Regional Forest and Fire Capacity Program.
December 12, 2025 – Sierra Nevada Conservancy Awards $4.6 Million in Wildfire and Forest Resilience Grants to Help Protect Communities: SNC’s Board approved three separate grants totaling nearly $4.6 million to fund projects that will reduce fuels and create fuel breaks in efforts to restore forest health and protect nearby communities from wildfire. The three grants from SNC’s Wildfire and Forest Resilience Directed Grant Program will fund projects in Butte, Mono, and Madera counties.
California Unveils First-ever Statewide LiDAR Maps
California Unveils First-ever Statewide LiDAR Maps
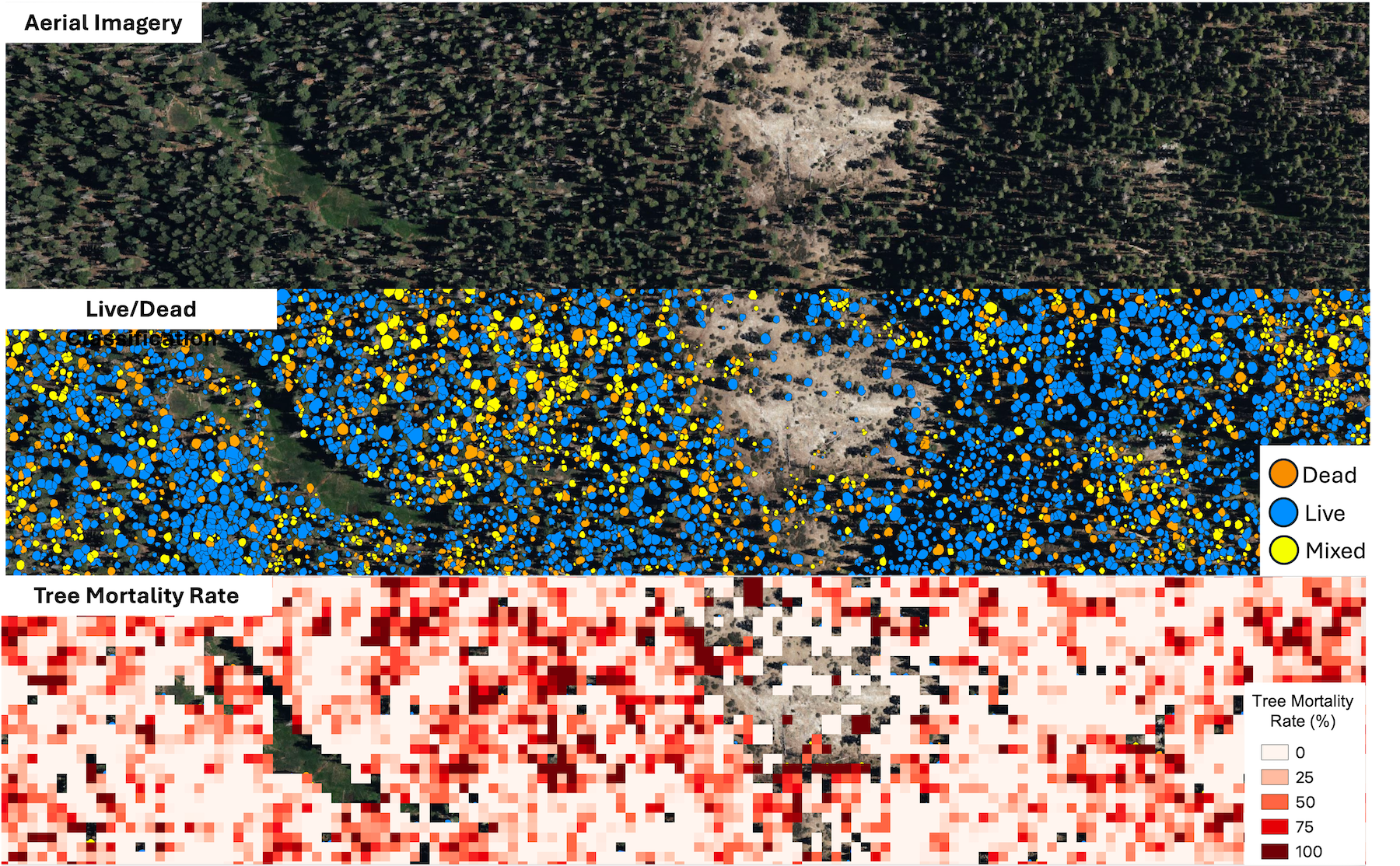
December 12, 2025 – The California Natural Resources Agency (CNRA), in partnership with the California Air Resources Board (CARB), NASA Ames Research Center, and the Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force announced the public release of consistent, statewide datasets on forest and vegetation conditions built from LiDAR, the gold standard for forest and vegetation information. This release is powered by the Wildfire, Ecosystem Resilience, and Risk Assessment Initiative (WERK) which has processed more than 100 million acres of LiDAR data across California. That total includes 40 million acres collected through CNRA’s use of $30M dedicated by the State Legislature for wildland remote sensing. For the first time, California has a single wall-to-wall picture of forest and vegetation conditions that is the highest resolution available and consistent across the entire state. Agencies, tribes, researchers, land managers, and community partners can begin incorporating the released products into their own tools, models, and planning processes immediately.
LiDAR (light detection and ranging) creates detailed three-dimensional maps of the landscape. Using LiDAR, the WERK initiative provides information on where trees and shrubs are, how tall and dense they are, where ladder fuels can carry fire into the canopy, and how much carbon is stored in vegetation. The statewide release includes 10-meter and 30-meter resolutions datasets that cover all of California. In addition, 1-meter datasets are already available in select areas, with statewide access to ultra-high resolution data launching in early 2026.
The WERK datasets are being hosted in partnership with the Wildfire Science & Technology Commons at the San Diego Supercomputer Center, supported by the National Science Foundation. These products will also be incorporated into the Task Force’s California Landscape Metrics beginning with the next data refresh.
CAL FIRE Awards Over $62 Million in Wildfire Prevention Grants

CAL FIRE Awards Over $62 Million in Wildfire Prevention Grants
December 12, 2025 – CAL FIRE announced it will award nearly $62.6 million in funding for 84 local wildfire prevention projects across the state, including 41 projects in low-income and disadvantaged communities. CAL FIRE’s Wildfire Prevention Grants enable local organizations like fire safe councils to implement activities that reduce wildfire risk to communities. Funded activities include hazardous fuel reduction, wildfire prevention planning, and wildfire prevention education. These projects reach all corners of the state, including:
- Siskiyou County: The Shasta Valley Resource Conservation District will implement wildfire prevention efforts on the McCloud Fuels Management and Forest Stewardship Project, which proposes 375 acres of treatment including 200 acres of mastication and thinning and 175 acres of ridgeline shaded fuel break.
- Riverside County: the Twenty-Nine Palms Band of Mission Indians will reduce hazardous fuels (saltcedar) on 223 acres of tribal lands. The project will reduce dust and wildfire fuel loads by removing saltcedar using root plowing and chipping.
- Los Angeles County: The San Gabriel Valley Council of Governments is one of many organizations receiving funding towards wildfire prevention efforts. Their project will work towards developing a Regional Wildfire Protection Plan that will help to protect over 31 cities and communities, 22 of which are identified as “Communities at Risk.”
These projects all meet the goals and objectives of California’s Wildfire and Forest Resilience Action Plan, as well as the Strategic Fire Plan for California. Over the last six years, CAL FIRE has awarded more than $566 million in its Wildfire Prevention Grants Program to over 575 projects across the state. A full list of the 2025/2026 Wildfire Prevention Grant recipients is available here.
Watershed Research and Training Center and Sierra Business Council Release Wildfire Resilience Workforce & Career Development Roadmap

Watershed Research and Training Center and Sierra Business Council Release Wildfire Resilience Workforce & Career Development Roadmap
November 25, 2025 – The Watershed Research and Training Center and Sierra Business Council released Advancing Wildfire Resilience Workforce & Career Development, a nonprofit-led roadmap recommending how California can grow and sustain the skilled workforce needed to protect communities and restore healthy landscapes in the face of wildfire. Developed in coordination with the California Wildfire & Forest Resilience Task Force, this roadmap outlines how the state can strengthen its wildfire resilience efforts by investing in the people and organizations driving this critical work. Key recommendations in the roadmap include:
• Building education, training, and professional development pipelines.
• Supporting high-quality, well-paying jobs with clear career pathways.
• Pairing wildfire resilience investments with workforce capacity investments statewide, including urban, rural, and Tribal communities.
• Removing barriers to recruit, train, and retain a robust wildfire resilience workforce.
By integrating solutions to two of California’s most pressing challenges—wildfire risk and economic opportunity—this roadmap charts a path toward both community safety and statewide prosperity.
Governor Newsom Signs Executive Order to Expand Beneficial Fire Use

Governor Newsom Signs Executive Order to Expand Beneficial Fire Use
October 29, 2025 – Governor Newsom signed an executive order directing state agencies to reduce red tape and expand tools to safely deploy beneficial fire projects. The order directs a suite of actions to fast-track critical work in the coming months with a key focus on directing state agencies to provide immediate on-the-ground support to local governments and fire practitioners to maximize use of beneficial fire, helping ensure that California does not miss the critical fall weather window to conduct prescribed and cultural burns. The order supports collaborative efforts to update beneficial fire permitting, address air quality concerns associated with smoke and enable resource conservation districts and other entities to carry out beneficial fire projects.
The executive order helps strengthen and build on California’s wildfire prevention strategy by:
- Accelerating funding and projects: Distributes funding to resource conservation districts and other eligible government agencies in advance of beneficial fire work, as well as creates more simplified grant funding processes.
- Expanding local participation: Removes policies and regulatory roadblocks that would make it more difficult for local agencies to engage in this work, including suspending the state law that prohibits resource conservation districts and volunteer fire departments from participating in the Prescribed Fire Liability Claims Fund Pilot Program.
- Working with tribal communities: Directs state agencies to continue prioritizing tribal consultation, access, collaboration, and co-management—so we can work together to expand and support cultural burning and other forms of tribal stewardship.
- Increasing education and data: Directs the California Air Resources Board (CARB) to create new modeling and related technologies, such as the Prescribed Fire Information Reporting System (PFIRS) and make this technology available to support air districts’ efforts to promote fast, efficient and low-cost permitting, and expands training opportunities for beneficial fire practitioners.
- Mitigating air quality risks: Increases collaboration and creates new best practices that provide beneficial fire practitioners consistent permitting and smoke management plan guidance while protecting public health and communicating potential smoke impacts to the public and create guidance for local communities.
Building on nation-leading progress
The executive order builds on unprecedented progress already made by state, federal, tribal, local, and nonprofit partners to increase the pace and scale of beneficial fire implementation across the state. Key advancements include:
- The Task Force issued California’s Strategic Plan for Expanding the Use of Beneficial Fire (2022), a comprehensive roadmap to coordinate the efforts of state, federal, and tribal partners to treat up to 400,000 acres with beneficial fire annually by 2025.
- Prescribed fire treatments in California nearly doubled between 2021 and 2023. Federal, state, and local agencies completed 260,000 acres of prescribed fire treatments in 2023.
- In May, CAL FIRE, for the first time ever, met and exceeded its 50,000-acre goal for beneficial fire as outlined as a goal within the California Strategic Plan for Expanding the Use of Beneficial Fire. This was accomplished even with the Park Fire in late 2024 and the January 2025 fires in Los Angeles.
- As of June, CARB, in close coordination with the California Air Pollution Control Officers Association, has held over 20 prescribed fire training sessions for stakeholders to discuss smoke management, public information, and tools and technology related to prescribed fire.
- In 2021, CARB released California Smoke Spotter — a critical tool to inform the public of air quality impacts from wildfire and prescribed fire smoke.
- The Governor and Legislature established a first-in-the-nation Prescribed Fire Liability Claims Fund in 2022 backed with $20 million in state funding, to accelerate beneficial fire on private lands by covering losses in the rare instance that a prescribed or cultural burn escapes control.
- In September 2024, Governor Newsom signed SB 310, which reduces barriers for California Native American tribes to conduct cultural burns in their ancestral territories. The Karuk Tribe and the California Natural Resources Agency (CNRA) entered into the landmark SB 310 Cultural Fire agreement in February 2025. Out of this effort, the Tribe and CNRA have developed a template agreement for other tribes to utilize educational materials to support government-to-government collaboration in advancing cultural fire.
- In September 2024, Governor Newsom signed SB 1101, which streamlines CAL FIRE’s contracting and procurement process to support beneficial fire.
- In August 2023, the Governor’s Wildfire and Task Force launched an Interagency Treatment Dashboard that provides transparency on the location of completed beneficial fire projects.
- CAL FIRE’s Prescribed Fire Monitoring Program released the first version of a manual outlining field monitoring protocols in 2023 to assist land managers with unit selection, data collection, tools and technologies, data storage, and analysis procedures.
Governor Newsom Signs Executive Order to Address Economic Consequences of the State’s Climate and Wildfire Crisis

Governor Newsom Signs Executive Order to Address Economic Consequences of the State’s Climate and Wildfire Crisis
September 30, 2025 – Governor Gavin Newsom signed an executive order that calls for multiple state agencies and departments to collaborate on research and recommendations to develop long-term durable tools to mitigate and fairly allocate the costs of recovering from natural catastrophes, further stabilize the insurance market and utility sector, make insurance more affordable and accessible, protect ratepayers, ensure compensation for wildfire survivors, and more. The Order will expedite the state’s work to undertake the analysis called for in SB 254.
What’s included in SB 254?
SB 254 will create the next generation of the state’s Wildfire Fund to support wildfire survivors and protect ratepayers from excessive utility liability costs. One major component of SB 254 directs the state’s wildfire fund administrator to prepare a report by April 2026 analyzing new approaches to responding to catastrophes, including wildfires. This executive order expedites the state’s work to undertake that analysis, reflecting the Governor’s urgency to protect Californians from the costs of catastrophic wildfire, and other climate threats and natural disasters.
Updates to the Wildfire Fund:
The California Earthquake Authority (CEA), as the Wildfire Fund Administrator, will evaluate and prepare a report on innovative and durable reforms to California’s energy utility and insurance markets in the face of the state’s growing exposure to natural catastrophes. CEA will collaborate with several state agencies on the study and has issued a call for stakeholder contributions to the study. Those with an interest in California’s natural catastrophe resiliency are encouraged to participate and share their expertise.
CNRA and Partners Install First Ever Redwood Forest Observatory
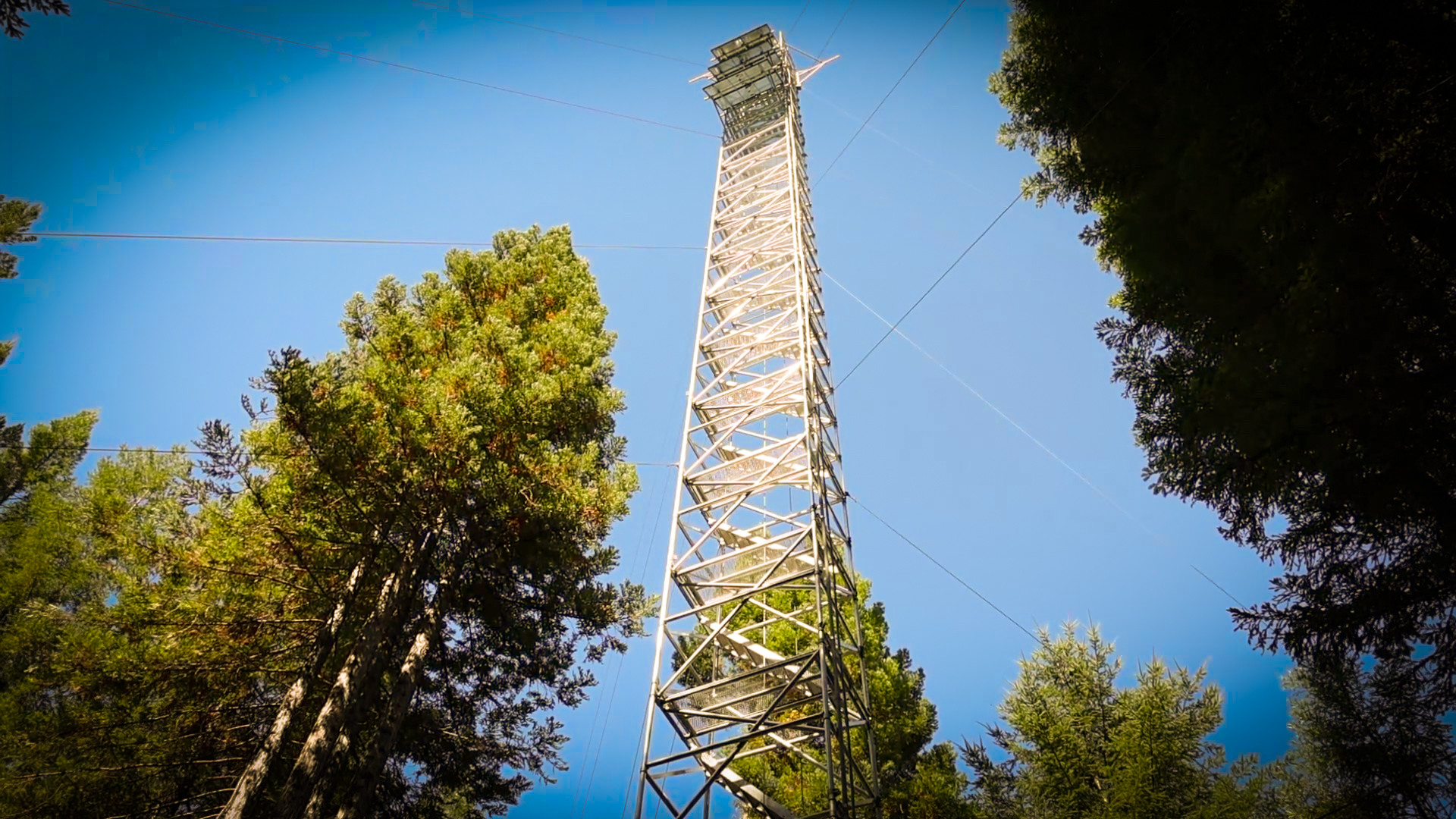

CNRA and Partners Install First Ever Redwood Forest Observatory
The California Natural Resources Agency (CNRA), in partnership with UC Davis, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, the California Air Resources Board, and CAL FIRE, installed the first ever redwood forest observatory consisting of two research towers that will provide critical forest health information on California’s coast redwood forests. The recently installed flux towers are located in Jackson Demonstration State Forest, where they are measuring the inflow and outflow of carbon dioxide, water vapor, and energy between the redwoods and the surrounding environment. Instruments on these towers provide real time understanding of how redwoods respond to changing environmental conditions, wildfire, and management to help land managers protect this iconic forest ecosystem undergoing rapid change. Within the next year, aggregated measurements produced by these towers will be processed for public use.
What is a Flux Tower?
A flux tower is a tall structure that extends above the forest canopy, equipped with sensors at various heights to measure the exchange of gases and energy between the forest and the atmosphere using the eddy covariance technique.
These towers will provide:
- Direct, continuous measurements of redwood forests’ carbon sequestration and their response to climate, management, or natural disturbance, such as wildfire.
- Data on how the redwood forests respond to weather dynamics, such as fog, cloudiness, and summer drought, providing critical information on forest health.
- An important link between satellite data and computer models to enable evaluation of the health and resilience across California’s coast redwood forests.
- Data with the AmeriFlux research network, along with hundreds of research sites across the Americas. These networks help assess the responses and feedback of American terrestrial ecosystems to environmental changes, including those caused by climate, land use, and extreme events.
Senate Advances Bipartisan Fix Our Forests Act

Senate Advances Bipartisan Fix Our Forests Act
October 21, 2025 – The U.S. Senate advanced the Fix Our Forests Act through the Senate Committee on Agriculture, Nutrition, and Forestry, setting the pivotal fire and forestry legislation up for a vote by the full Senate. The bipartisan legislation would help combat catastrophic wildfires, restore forest ecosystems, and make federal forest management more efficient. The Fix Our Forests Act would:
• Establish new and updated cross-jurisdictional programs to reduce wildfire risks across large, high-priority areas.
• Streamline and expand tools for forest health projects (e.g., stewardship contracting, Good Neighbor Agreements) and provide faster processes for certain hazardous fuels treatments.
• Create a single interagency program to help communities in the wildland-urban interface build and retrofit with wildfire-resistant measures, while simplifying and consolidating grant applications.
• Expand research and demonstration initiatives — including biochar projects and the Community Wildfire Defense Research Program — to test and deploy cutting-edge wildfire prevention, detection, and mitigation technologies.
• Strengthen coordination efforts across agencies through a new Wildfire Intelligence Center which would streamline the federal response and create a whole-of-government approach to combating wildfires.
• Create fire safe electrical corridors by allowing electric utilities with permits or easements on National Forest System or BLM land to cut and remove vegetation near power lines without requiring a separate timber sale.
• Improve reforestation, seedling supply, and nursery capacity; as well as clarify policies to reduce wildfire-related litigation and expedite forest health treatments.
CAL FIRE and the Community Wildfire Planning Center Awarded for Training Program

CAL FIRE and the Community Wildfire Planning Center Awarded for Training Program
October 22 – The American Planning Association (APA) awarded CAL FIRE and the Community Wildfire Planning Center with the 2025 National Planning Award for Resiliency & Sustainability in recognition of their Land Use Planning for Wildfires in California training program. Launched in 2023, the training program offers free, full-day, in-person sessions designed for land use planners, fire marshals, fire chiefs, fire mitigation specialists, building officials, and other professionals from both government agencies and the private sector. To date, nearly 700 attendees participated in one of 24 trainings held across the State. Trainings have helped attendees:
• Increase understanding of the most up-to-date state requirements for planning in fire hazard areas.
• Expand knowledge of wildfire vulnerabilities in the built environment.
• Share information on best practices and resources.
• Interact with peers to exchange perspectives on fire mitigation and planning.
U.S. Forest Service Invests Nearly $32 Million to Protect California Communities from Wildfire

U.S. Forest Service Invests Nearly $32 Million to Reduce Wildfire Risk in California
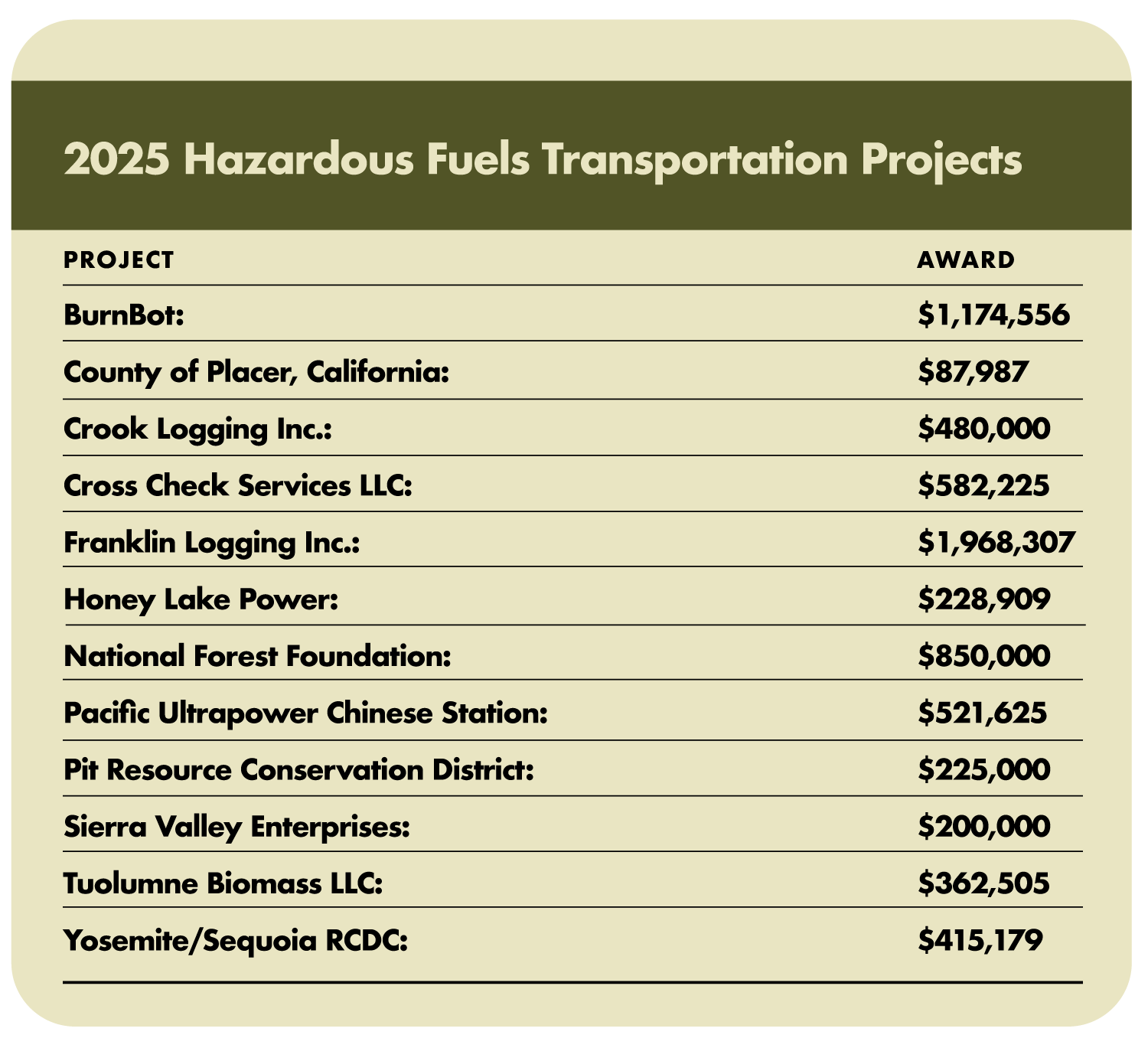
Over $7 Million to Increase Timber Production and Reduce Wildfire Risk:
September 16, 2025 – The U.S. Forest Service announced it is investing $7.1 million for 18 projects in California. These projects are on or adjacent to 8 National Forests and will remove more than 275,000 tons of biomass that would otherwise remain in the forests. These investments into California are part of a national investment of $23 million to help 35 grant recipients remove and transport an estimated 1.1 million tons of low-value trees and woody debris from national forests to processing facilities. The grants are delivered through the agency’s Hazardous Fuels Transportation Assistance Program, which is designed to help businesses, nonprofits, and state, local, and tribal governments make use of trees, downed vegetation, and other hazardous fuels that would otherwise go to waste or fuel catastrophic wildfires. The trees and woody debris, often too low in value to cover transportation costs, are transformed from a wildfire hazard to valuable products and a source of energy.
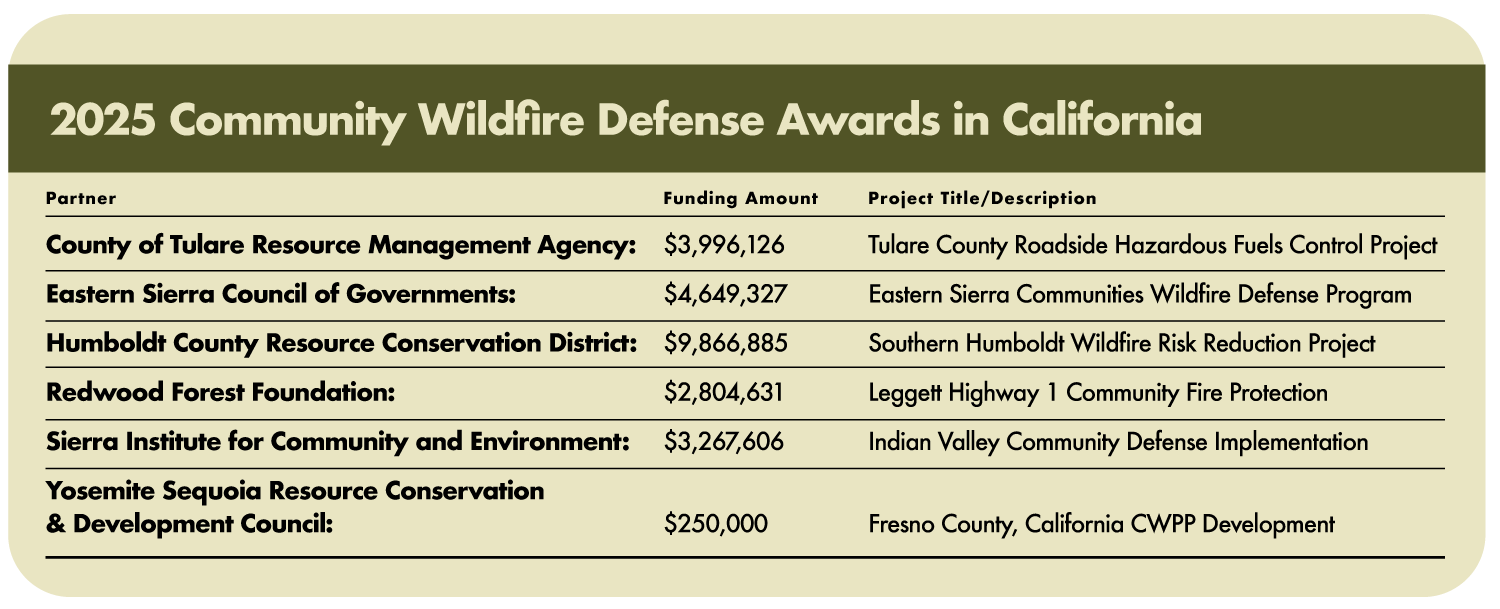
Nearly $25 Million to Protect Communities from Wildfire:
September 23,2025 – The U.S. Forest Service announced it is investing $200 million in 58 projects through its Community Wildfire Defense Grant Program. Nearly $25 million will be allocated to 6 projects that will protect communities across California. These projects are intended to help at-risk communities plan for and reduce wildfire risk, protecting homes, businesses, and infrastructure. See details on each of California’s funded projects here.