U.S. EPA Awards 14.7 million to the Tule River Tribe for Biochar Project

U.S. EPA Awards 14.7 million to the Tule River Tribe for Biochar Project
February 18, 2026 – The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has awarded a $14.7 million grant to a biochar project that will enable the Tule River Tribe of California to tap into carbon credit revenue. Under the project, the Tule River Economic Development Corp. (TREDC) will utilize the EPA grant to construct a biochar production plant in California’s Central Valley that will also have the capacity to generate renewable electricity. According to TREDC estimates, the plant will be able to process up to 31,500 tons of woody residue annually, producing approximately 4,500 tons of biochar and roughly 4,000 megawatt-hours of renewable power each year. Its operations are also projected to be able to remove up to 10,600 metric tons of carbon dioxide annually and provide jobs for tribal citizens.
Santa Monica Mountains Conservancy Awards Over $3.6 Million of Climate Bond Funds for Local Wildfire Prevention
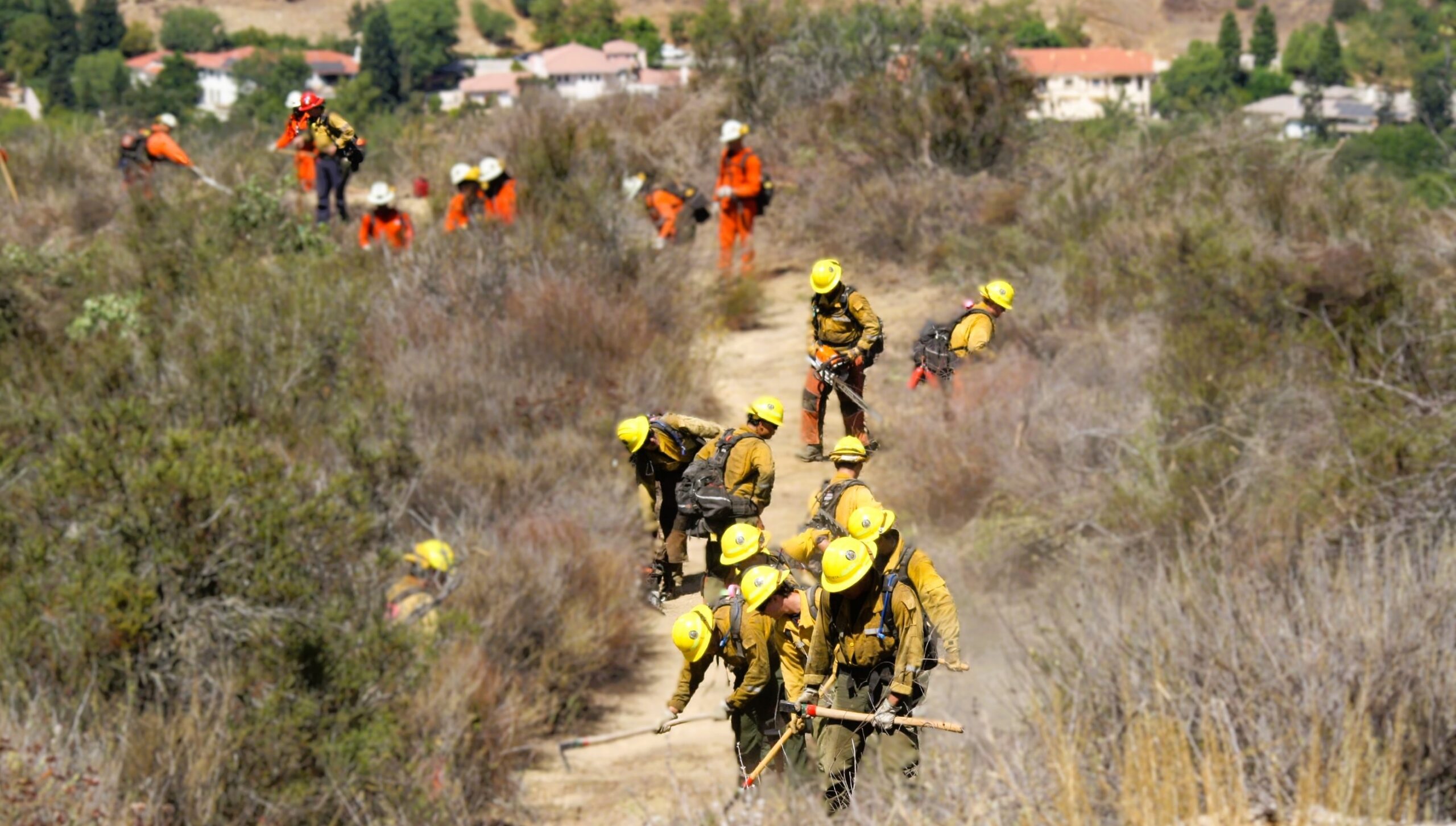

Santa Monica Mountains Conservancy Awards Over $3.6 Million of Climate Bond Funds for Local Wildfire Prevention
February 23, 2026 – The Santa Monica Mountains Conservancy (SMMC) Board approved three grants, funded by Prop 4 (Climate Bond), to support efforts by the Mountains Recreation and Conservation Authority (MRCA) to reduce wildfire risk in the Los Angeles area. MRCA received $2,065,500 to support reduction of flashy non-native fuel, support defensible space, and remove hazard trees; $590,000 for workforce development, to train and deploy fire-ready crews for vegetation management and wildfire readiness and suppression; and $344,500 for structure hardening and renovations for crew accommodations to support surges in staffing needs for Red Flag and fire events. In addition to the grants to MRCA, SMMC also granted $649,322 to Ventura County Fire Protection District in January for targeted fuel reduction, including fuel breaks, prescribed grazing, and roadside clearing.
U.S. Department of Interior Launches U.S. Wildland Fire Service
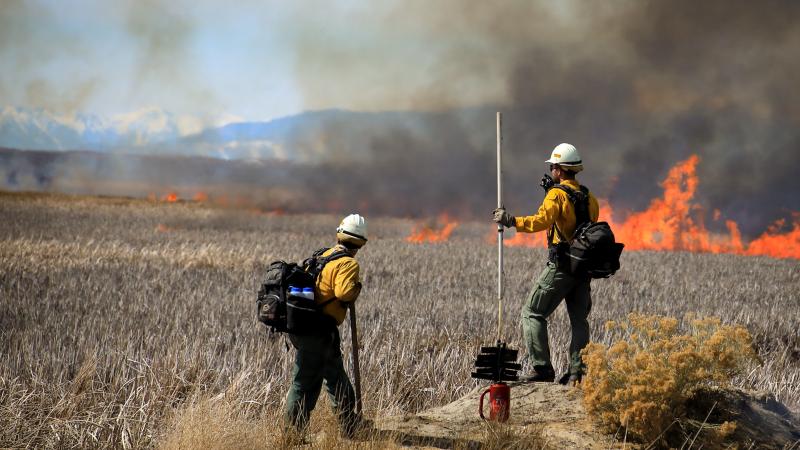

U.S. Department of Interior Launches U.S. Wildland Fire Service
January 2026 – The U.S. Department of the Interior (DOI) established the new U.S. Wildland Fire Service which consolidates wildland fire management across the Bureau of Indian Affairs, Bureau of Land Management, National Park Service, Office of Aviation Services, Office of Wildland Fire, and U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service to streamline wildfire prevention, response, and recovery efforts across public lands administered by DOI. The U.S. Wildland Fire Service works to reduce wildfire risk through proactive fuels management; create fire-resilient landscapes; advance wildland fire science and technology; promote fire-adapted communities; and respond to wildfires in collaboration with the U.S. Forest Service and Tribal, state and local partners.
The new service was created following Executive Order 14308, Empowering Commonsense Wildfire Prevention and Response, which directs federal agencies to streamline and modernize wildland fire management nationwide and the DOI Secretary’s Order 3443, Elevating and Unifying DOI’s Wildland Fire Management Program, which directs the establishment of U.S. Wildland Fire Service within the Interior Department. The service will provide wildland fire management on over 500 million acres of public and Tribal lands across the nation, employ 5,780 federal wildland fire personnel annually, and supports approximately 900 tribal wildland fire personnel.
CAL FIRE Launches Forest Health Education Campaign
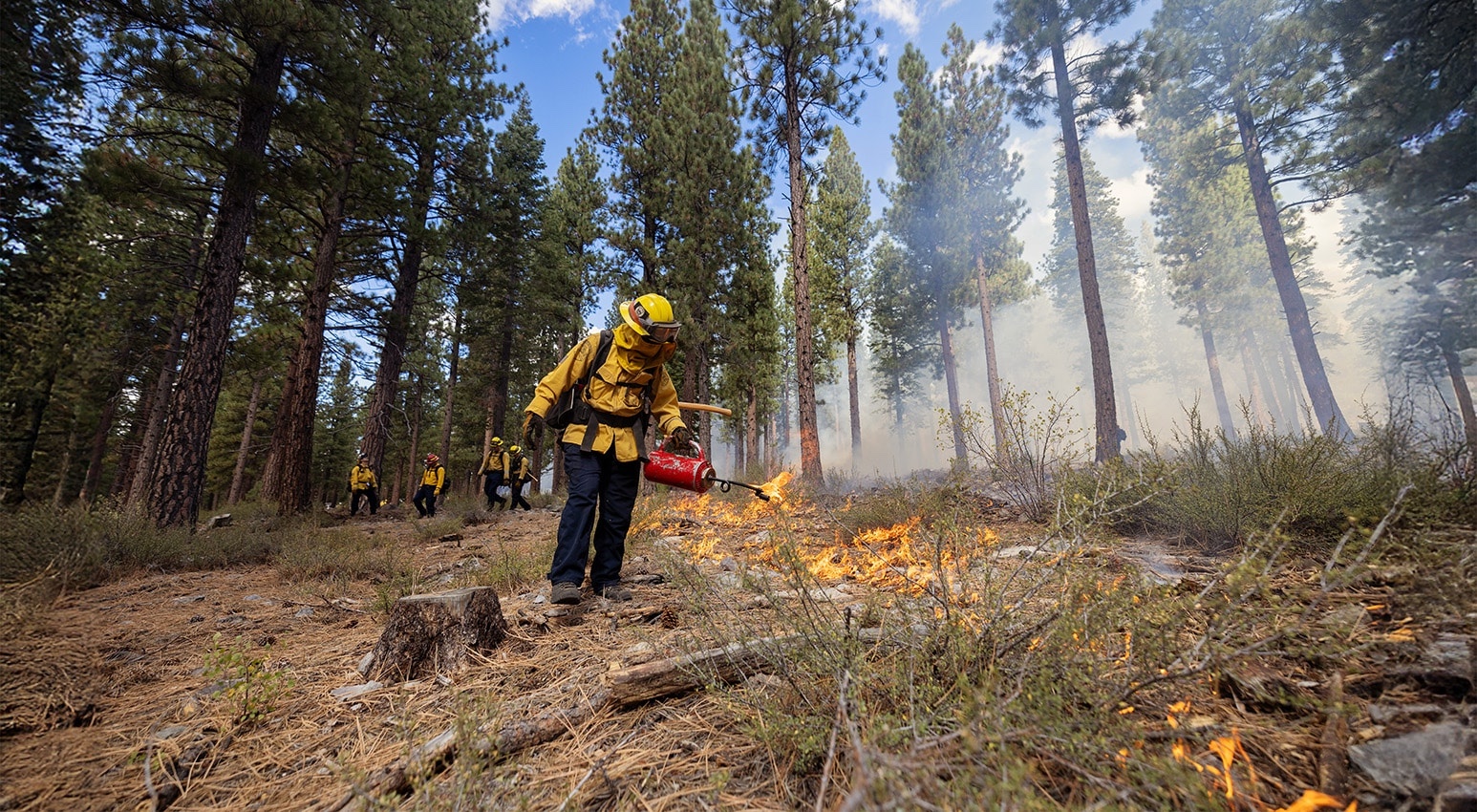

CAL FIRE Launches Forest Health Education Campaign
February 17, 2026 – CAL FIRE launched a new 2026 forest health media and education campaign. The campaign is aimed at helping Californians better understand the role healthy forests play in mitigating the growing wildfire threat and highlights the actions we can take together to reduce risk and protect lives, communities, and natural resources. A key focus of the campaign is highlighting proactive forest management, including beneficial fire as well as the important role individuals play at home and in their communities to prepare for wildfire through home hardening and by creating and maintaining defensible space. To support wildfire resilience messaging and public awareness, the campaign includes a new toolkit that contains easily customizable graphics and copy for use on social media, banners, and billboards.
Governor’s January Budget Invests $457 Million in Wildfire and Forest Resilience
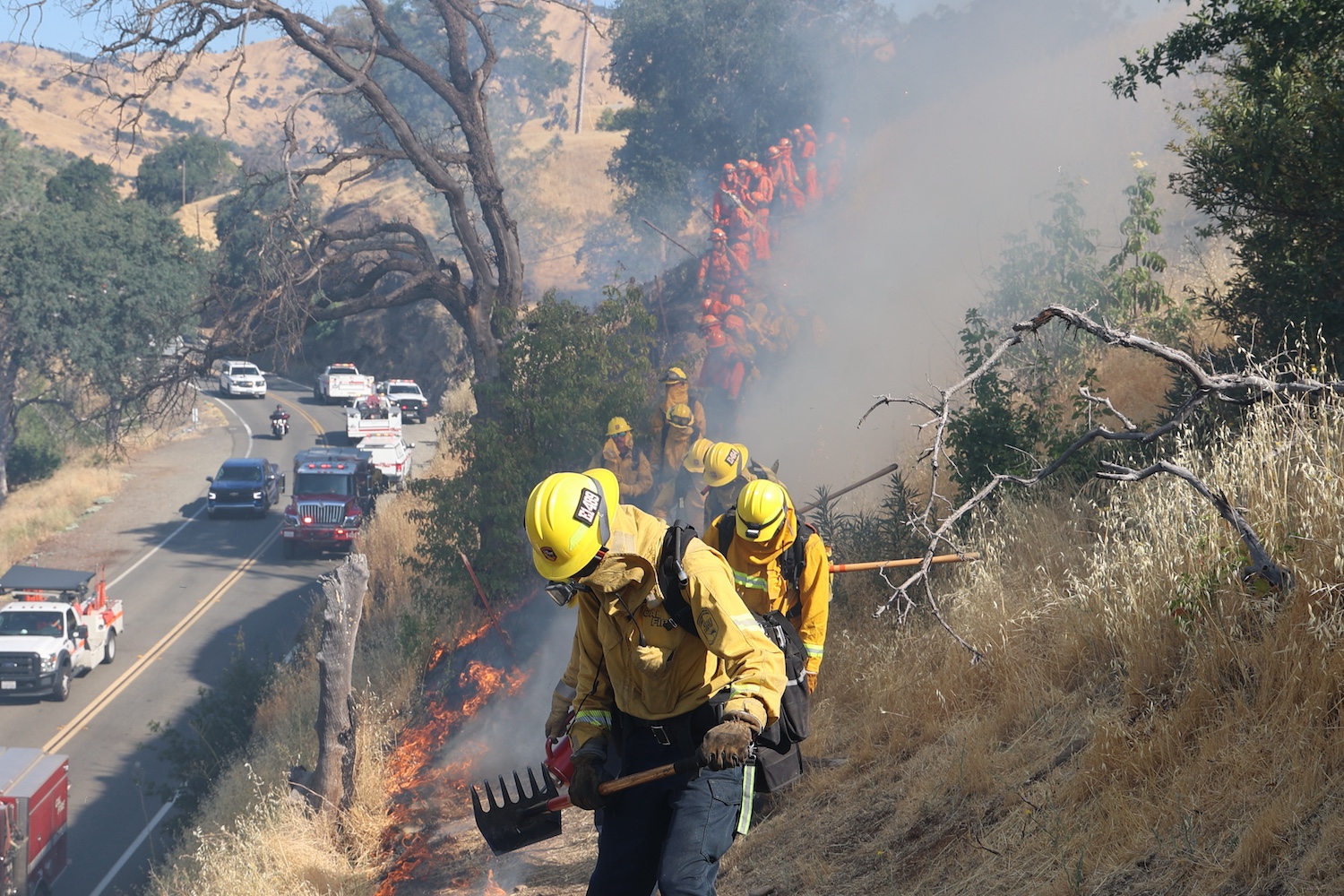

Governor’s January Budget Invests $457 Million in Wildfire and Forest Resilience
January 9, 2026 – The Governor’s proposed 2026–27 January Budget allocates $457 million to advance wildfire and forest resilience statewide, including $142 million from the Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund (GGRF) and $315 million from Climate Bond funding. Due to auction proceeds from the November 2025 Cap-and-Invest auction coming in lower than anticipated, the proposal adjusts the GGRF continuous appropriation to $142 million, with funding prioritized to sustain key capacity, including grant administration staffing, 10 dedicated fuels crews for prescribed fire and fuel reduction, and continued grant support for healthy forests and fire prevention projects. Climate Bond investments will be distributed across CAL FIRE, the Department of Conservation, California State Parks, the California Conservation Corps, and state conservancies, supporting on-the-ground projects that reduce wildfire risk and strengthen community and landscape resilience.
Six Months After the LA Fires, California Continues Unprecedented Recovery Campaign

Six Months After the LA Fires, California Continues Unprecedented Recovery Campaign
July 7, 2025 – On the six month anniversary of the Eaton and Palisades fires, Governor Newsom announced the substantial completion of the public debris removal program from more than 10,000 fire damaged parcels. The near-completion of the public debris removal program comes months ahead of schedule. The LA Fires cleanup is the second largest in state history after the Camp Fire and was jointly managed by the Governor’s Office of Emergency Services (Cal OES) and United States Army Corps of Engineers, in partnership with Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), as well Los Angeles County and City of Los Angeles. Of the 12,048 total properties destroyed in the twin fires, 9,873 opted to participate in the cost-free public cleanup program.
Following cleanup, the Governor signed Executive Order N-29-25 to accelerate rebuilding homes and schools impacted by the fires by suspending local permitting laws and building codes. To further spur rebuilding the Governor and the California Department of Housing and Community Development announced the release of $101 million to help rapidly rebuild critically needed, affordable multifamily rental housing in the fire-devastated LA region.
CAL FIRE Releases Vegetation Burn Severity Online Viewer
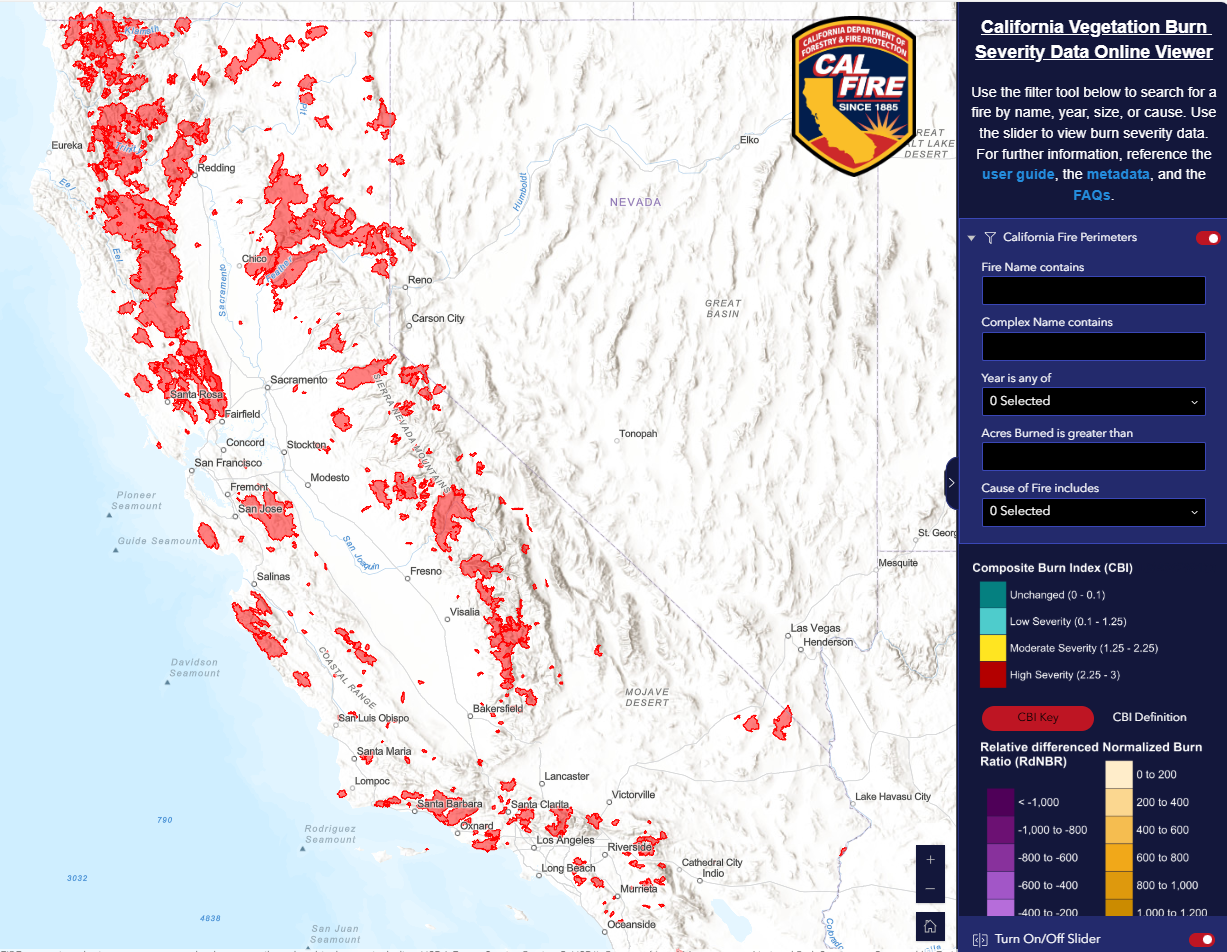
CAL FIRE Releases Vegetation Burn Severity Online Viewer
July 15, 2025 – CAL FIRE’s Fire and Resource Assessment Program (FRAP) released the California Vegetation Burn Severity Online Viewer, a public geospatial tool that displays burn severity data for wildfires across all land ownerships that burned at least 1,000 acres in California from 2015 to 2023. In accordance with Senate Bill 1101, FRAP developed this viewer to enhance public understanding of post-fire conditions and ecological impacts. It offers insight into the severity of impacts to vegetation across both forested and non-forested landscapes. The viewer will support post-fire recovery planning, inform habitat management and conservation efforts, enhance safety through insights for fire suppression planning, and improve preparedness by helping prescribed fire practitioners plan treatments based on past burn severity and fuel changes. Users can view fire perimeters, severity maps, and proportional area statistics for each fire. The viewer will be updated annually to include new fires under 1,000 acres.
California Allocates $9.5 Million for Wildfire County Coordinator Program

California Invests $9.5 Million for Wildfire County Coordinator Program
July 31, 2025 – With the support of Governor Newsom and the California State Legislature, the 2025-26 budget will provide $9.5 million for the Wildfire County Coordinator Program. Delivered in partnership between the California Fire Safe Council and CAL FIRE, the program establishes critical local capacity in 47 California counties with dedicated coordinators to secure funding, implement mitigation projects, engage vulnerable populations, and build resilience in high-risk communities. Coordinators serve as the crucial link between state strategy and local execution—ensuring California communities are better prepared, better connected, and more resilient to wildfire. The program will continue:
- Operationalizing California’s Wildfire and Forest Resilience Action Plan at the county level;
- Accelerating home hardening, defensible space implementation, and public education;
- Standardizing data collection to track local and statewide wildfire resilience progress; and
- Improving public safety, community insurability, and wildfire preparedness in California’s highest-risk regions.
Impact of the Wildfire County Coordinator Program
Investments in community capacity through the program have already produced substantial mitigation and resiliency benefits:
- Secured over $85M in funding for local wildfire mitigation projects;
- Coordinated with over 10,000 organizations to increase collaboration, break down silos, and leverage resources for community mitigation;
- Hosted over 3,800 events for community engagement and education;
- Educated and empowered over 800,000 residents to take action for wildfire resilience; and
- Established more than 100 new FireWise Communities and Fire Safe Councils.
Testimonials from the Wildfire County Coordinators
“The Program has allowed Del Norte County Fire Safe Council to protect many underserved residents and coordinate with other wildfire mitigation groups to maximize impact. Our County Coordinator has brought nearly $4 million in federal funding to Del Norte County, created defensible space around 372 homes, and completed 1,500 home assessments.”
– Aaron Babcock, Del Norte County
“A small investment in capacity can lead to sustainable, long-term improvements for any organization. Because of the County Coordinator Grant, Plumas Fire Safe Council had the capacity to obtain a $6.8 million dollar grant dedicated to hazardous fuels reduction and assessment.”
– Liam Gallaher, Plumas County
“The County Coordinator Grant has supported collaboration in our county by allowing us to create a collaborative meeting of 14 fire prevention agencies in the county to better inform the public and improve our ability to leverage funds and labor.”
– Jon Cottington, Madera County
“We’ve been able to significantly expand our youth education impact by implementing three new school programs and getting back into the classroom with students for the first time since the 2018 Camp Fire.”
– Lauren de Terra, Butte County
“The program has given us the time and opportunity to strengthen our outreach countywide while implementing critical fuel reduction programs. We’ve also been able translate educational materials into Spanish, expanding our outreach to underserved populations.”
– Marika Ramsen, Sonoma County
“We’ve reduced redundancy, supported capacity and collaboration for other Fire Safe Councils, and boosted community engagement through Firewise USA. We also learn from other County Coordinators & implement those lessons learned.”
– Stephen Watson, Ventura County
USFS Invests Nearly $8 Million in Wood Innovation Grants in California

USFS Invests Nearly $8 Million in Wood Innovation Grants in California
July 17, 2025 – The U.S. Forest Service announced awarding $80 million in Wood Innovations and Wood Product Infrastructure Grants to spur wood products manufacturing, expand active forest management, and accelerate energy innovation. Of these investments, nearly $8 million will go to 16 projects in California. A list of California awardees is below:
Wood Product Infrastructure Assistance Grant Program:
- Alpenglow Timber, LLC – $906,492: Establishes sawmill operations to support reduced wildfire risk and active forest management on National Forests and tribal forestlands in California and Nevada.
- California Hotwood, Inc. – $232,000: Upgrades firewood processing capacity to support reduced wildfire risk and active forest management on National Forests in California.
- Fall River Resource Conservation District – $252,642: Upgrades and modernization of biomass power facility operations to support reduced wildfire risk and active forest management on National Forests in California.
- Franklin Logging, Inc. – $907,568: Upgrades to lumber drying operations at sawmill to support reduced wildfire risk and active forest management on National Forests in California.
- Green Diamond Resource Company – $337,500: Establishes a stationary chipping facility to utilize small diameter and low value species in support of wildfire risk reduction and active forest management on National Forests in California.
- Lignum Support, LLC – $1,000,000: Upgrades and expansion of forest residues chipping operations for biomass energy to expand the utilization of forest residues and reduce wildfire risk and support active forest management on National Forests in California.
- Pacific Ultrapower Chinese Station – $960,000: Improves operational efficiencies at biomass power plant to support reduced wildfire risk and active forest management on National Forests in California.
- Tuolumne Biomass, LLC – $999,131: Upgrades small log processing operation to expand markets for small diameter and lower value species and support reduced wildfire risk and active forest management on National Forests in California.
Wood Innovations Grant Program:
- American Wood Fibers, Inc. – $300,000: Installs wood pellet mill to increase low-value wood utilization while supporting active forest management in California.
- DTE Materials Inc. – $300,000: Advances the production of wood concrete aggregates to improve utilization of low-value biomass and support active forest management.
- Enfilade Partners – $300,000: Designs and engineers a mass timber affordable housing project to accelerate the adoption of domestic mass timber thereby increasing active forest management and markets for small-diameter timber.
- Falk Forestry, Inc – $299,664: Establishes sawmill and firewood production to increase timber utilization and active forest management in Northern California.
- Fall River Resource Conservation District – $150,000: Establishes biochar production capabilities to support active forest management and wildfire risk reduction across national forests in California.
- Happy Camp Community Action, Inc. – $300,000: Advances the development of a new wood composite product to improve utilization of low-value biomass and support active forest management.
- Loamist, Co. – $300,000: Identifies locations for new low-value biomass markets to support active forest management and wildfire risk reduction in California.
- Sierra Institute for Community and Environment – $300,000: Installs mass timber manufacturing equipment thereby increasing active forest management across western forests.
First Set of Projects Fast-tracked as Part of Governor’s Emergency Proclamation on Wildfire

CNRA and CalEPA Identify First Set of Fast-tracked Projects as Part of Governor’s Emergency Proclamation on Wildfire
New Streamlined Process:
Governor Newsom issued an Emergency Proclamation (Proclamation) on March 1, 2025, to confront the severe ongoing risk of catastrophic wildfires that threatens public safety across California. The Proclamation authorizes the Secretaries of the California Natural Resources Agency (CNRA) and the California Environmental Protection Agency (CalEPA) to determine which projects are eligible for suspension of certain State of California statutory and regulatory requirements to expedite critical fuels reduction projects, while at the same time protecting public resources and the environment. The Task Force has established a website that includes eligibility criteria, FAQs, and a link to the application to request a determination of eligibility for suspension of relevant State of California statutory and regulatory requirements. The Secretaries also hosted a virtual briefing on the Proclamation and the process.
First Set of Approved Projects:
Just one week after applications opened, CNRA and CalEPA identified a 450-acre collaborative wildfire resilience project in Humboldt County as the first project to be determined eligible for streamlining. Three projects totaling 882 acres have been approved to date, spanning from the northern California coast to Sierra Nevada Mountains and all the way down to San Diego. Each of these projects involve tribes and other partners, natural resource managers and fire districts. Here is an overview of the first set of approved projects.
- The Prosper Ridge Community Wildfire Resilience Project in Humboldt County is the first approved project under the Governor’s emergency proclamation on wildfire. This collaborative state, federal, and tribal project will treat nearly 450 acres with a combination of mechanical thinning, manual treatments, and prescribed fire.
- The Sycuan Wildfire Resiliency Project covers over 240 acres in San Diego County and aims to protect the Sycuan Reservation from wildfire by reducing fire hazard, ensuring defensible space, and providing safe egress with the use of 300 grazing goats.
- Vedanta Hazardous Fuels Reduction Project will reduce wildfire risk, improve forest health and enhance landscape resilience within the WUI, reducing risk of crown fires spans across 190 acres near Lake Tahoe.
These projects are focused on removing flammable dead or dying trees, creating strategic fuel breaks, creating safe egress along roadways, manual and mechanical removal of ladder fuels and beneficial fire use. Approved project location maps and documentation will be made available on the Task Force website.
