Interagency Treatment Dashboard Shows Progress Toward Resilience

FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
October 10, 2024
California Unveils First-of-Their-Kind Dashboards Mapping Out Fire-Prevention Work to Protect Communities
New tools created by CAL FIRE and Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force simplify data, boost transparency, and help inform wildfire planning and response – adding to the suite of tools the state has created
(South Lake Tahoe, CA) – The Governor’s Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force and the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (CAL FIRE) unveiled several new tools today to help California track and communicate the state’s significant progress in improving wildfire and landscape resilience.
Key takeaways from the Task Force’s Sierra Nevada Regional Meeting in South Lake Tahoe include:
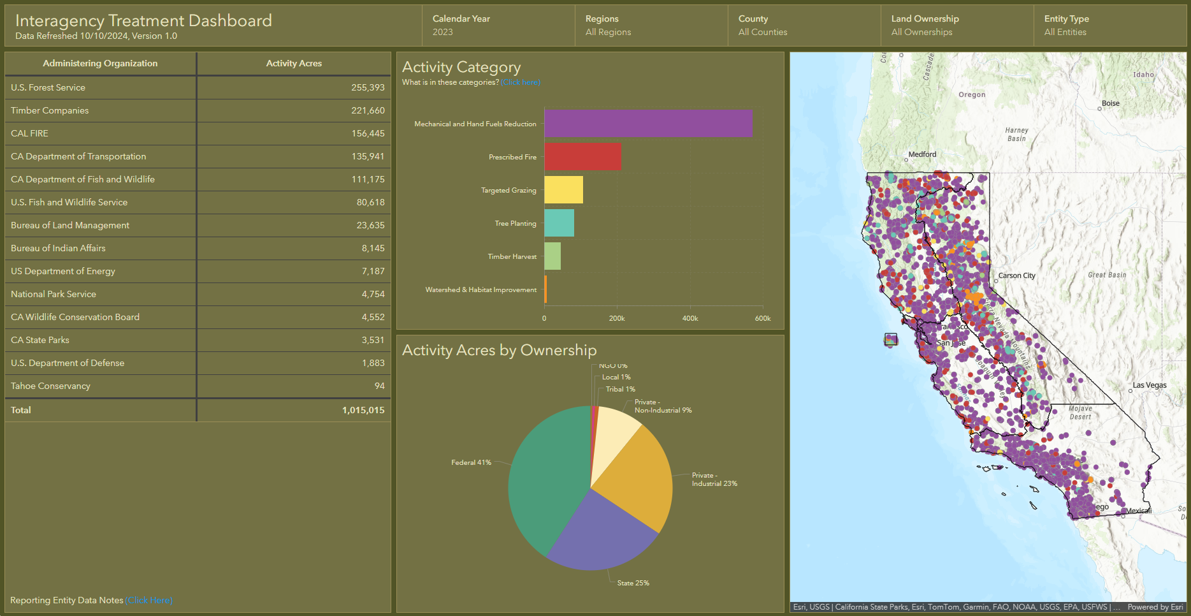
• Interagency Treatment Dashboard updated to show 2021, 2022 and 2023 data.
• Over one million acres of treatments were conducted on about 700,000 footprint acres in 2023.
• Prescribed fire treatments more than doubled between 2021 and 2023.
• CAL FIRE Fuel Treatment Effectiveness Dashboard is showing the impact of treatments impacted by recent wildfires.
“Thousands of wildfire resilience projects have been completed across California to protect our communities and landscapes from catastrophic wildfire in recent years, and more are underway,” said Wade Crowfoot, Secretary of the California Natural Resources Agency and co-chair of the Task Force. “Thanks to historic investments from our state and federal leaders, dozens of local agencies and hundreds of organizations are delivering these projects. Now for the first time, we have a dashboard that tracks all these diverse projects in one place and on one map. This enables us to measure our overall progress toward building wildfire resilience across the state and provides regional leaders valuable information to plan future projects.”
Interagency Treatment Dashboard
The updated version of the Interagency Treatment Dashboard shows wildfire resilience work (or “treatments”) for three calendar years (2021, 2022 and 2023). The data, which was sourced from federal, state, local, tribal, and private entities, is now available in a single hub that allows Californians to easily see where treatments (such as prescribed fire, mechanical thinning, and tree planting) have been completed. This information is used to inform firefighting efforts, ensure transparency to the public, and track progress toward statewide goals.
The Task Force released a Beta version of the Dashboard last year with 2022 data. This updated version now includes data for 2021, revised data for 2022, and new data for 2023.
Over 1 million acres worth of treatment work on 700,000 acres of land
The Dashboard shows significant progress on multiple fronts to bolster wildfire resilience in California. In 2023, more than one million acres of treatments were conducted on about 700,000 acres, with many acres receiving multiple treatments such as thinning, prescribed fire, or other practices to improve forest health and community resilience. The Task Force is tracking both “activity acres” – which reflect the level of effort conducted through various state, federal, and private programs – and “footprint acres” – which show the total geographic area treated in a calendar year.
The 2023 data shows a significant increase in acres treated since 2021. The increase is largely due to a significant expansion of prescribed fire treatments, which more than doubled since 2021. These efforts have put the state on a solid path toward meeting its joint commitment with the U.S. Forest Service to complete treatments on more than a million acres by the end of 2025.
The Task Force is committed to increasing the pace and scale of statewide actions to address California’s wildfire crisis. The Dashboard is part of a larger strategy to connect the various statewide entities committed to this monumental task.
Fuel Treatment Effectiveness Dashboard
CAL FIRE also launched a Fuel Treatment Effectiveness Dashboard, which shows how wildfire prevention projects are helping protect communities and landscapes when wildfire strikes. “Utilizing technology, we can now track in real time when wildfires hit areas where fuel treatments have been conducted. We can then go into an area and see how those treatments affected fire behavior, evacuation routes, firefighting efforts and more,” said CAL FIRE Chief/Director Joe Tyler. “This new dashboard is a tool for the public to see how fuels treatments had a positive impact on the firefight and how this work is making a difference.”
“No other state in the country is tackling wildfire resilience at this scale or with this level of innovation,” added U.S. Forest Service Deputy Regional Forester Kara Chadwick, who co-chaired today’s meeting. “From groundbreaking prescribed fire projects to comprehensive data tracking systems, we’re setting the standard for what it means to protect our landscapes and communities.”
The meeting is supplemented by field tours on October 8 and 11, to showcase wildfire resilience projects in the Tahoe Basin. Tour highlights include recovery efforts following the 2021 Caldor Fire, long-term prescribed burn projects in Sugar Pine Point State Park, meadow restoration at Máyala Wát undertaken by the Washoe Tribe of Nevada and California, and the first new industrial-scale sawmill built in Sierra Nevada in several decades.
“Today’s meeting is a major milestone in our efforts to better document and share our collective progress,” said Task Force Director Patrick Wright. “We will continue to build on our collective momentum to make California more resilient to wildfire.”
The next Task Force meeting will take place in Sacramento on December 13 and will provide a synthesis of the latest scientific findings that are informing California’s approach to address wildfire risks in a changing climate. These findings will be incorporated into the Task Force’s 2025 Action Plan Update.
Sky Biblin, Communications Coordinator
Governor’s Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force
916-502-6527
120,000 Acres Added to California National Monuments

120,000 Acres Added to California National Monuments
May 2, 2024: On May 2, President Biden signed proclamations expanding the San Gabriel Mountains and Berryessa Snow Mountain National Monuments. Together, these actions will protect nearly 120,000 acres of lands in California of scientific, cultural, ecological, and historical importance. This will expand federal wildfire management programs and response to these newly added lands.
105,919 acres of U.S. Forest Service lands will be added to San Gabriel Mountains National Monument. The proclamation directs the U.S. Forest Service to manage the area according to the same terms, conditions, and management as the original national monument designation and calls for development of a management plan for the expansion area that incorporates Indigenous Knowledge and community input.
13,696 acres will be added to Berryessa Snow Mountain National Monument. The proclamation directs the Bureau of Land Management to manage the area according to the same terms, conditions, and management as the original national monument designation and directs the Secretary of the Interior to explore co-stewardship of the area with Tribal Nations.
Giant Sequoia Lands Coalition Exceeds 2023 Goals and Plants 542,000 Trees

Giant Sequoia Lands Coalition Exceeds 2023 Goals and Plants 542,000 Trees
May 2024: The Giant Sequoia Lands Coalition has exceeded its goals in 2023, its second year of large-scale collaboration. The Coalition, made up of 20 partner entities, treated nearly 9,900 acres in 28 giant sequoia groves in 2023. This restoration work brings the total giant sequoia grove acres treated since the extreme 2020-21 wildfires to 14,143 out of 26,000.
The Coalition also planted over 294,000 native tree seedlings in severely burned areas, bringing the total to over 542,000. Other Coalition accomplishments include initiating and hosting research studies by academic, government, and nonprofit organizations, reviving cultural practices, and expanding co-stewardship agreements with tribes and nonprofits.
California Launches Online Tool to Track Wildfire Resilience Projects



FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
August 29, 2023
California Launches Online Tool to Track Wildfire Resilience Projects
New beta statewide tracking system brings local, state, and federal wildfire resiliency projects into one place to reflect significant progress.
(Sacramento, CA) – Today, the Governor’s Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force (Task Force) launched the beta version of a first-of-its-kind Interagency Treatment Dashboard that displays the size and location of state and federal forest and landscape resilience projects in California.
The dashboard offers a one-stop-shop to access data, provide transparency, and align the efforts of more than a dozen agencies to build resilient landscapes and communities in California. It reports treatment activities such as prescribed fire, targeted grazing, uneven-aged timber harvest, mechanical and hand fuels reduction, and tree planting. Users can sort treatments by region, county, land ownership and more.
“Thanks to historic funding from our Legislature and Governor Newsom, over 1,000 wildfire resilience projects are in motion across the state to protect communities and our diverse landscapes from catastrophic wildfire,” said California Secretary for Natural Resources Wade Crowfoot, co-chair of the Task Force. “Now we can track our progress like never before through this public Interagency Dashboard. It identifies where projects are happening, what kind of work is happening in a given location, and how much overall resilience work is being done. It’s one more step forward in building a comprehensive, durable approach to increasing our wildfire resilience in years to come.”
“This dashboard delivers a new tool for collaboration among agencies and communities,” said U.S. Forest Service Regional Forester Jennifer Eberlien, who co-chairs the Task Force with Secretary Crowfoot. “Having access to treatment information in this format will allow us to coordinate landscape scale activities aimed at restoring and enhancing ecosystem resilience.”
The dashboard compiles data from a broad range of organizations and government departments—many of which have different reporting requirements guiding how they capture information. While individual reporting tools and data will sometimes differ from this statewide snapshot, the dashboard brings these different reporting approaches together as a single and streamlined reporting tool. Key differences are addressed in the dashboard website FAQs .
“It takes everyone to create a more wildfire resilient California and this dashboard reflects the strides being made to get us there,” said CAL FIRE Director and Fire Chief Joe Tyler. “This dashboard shows how far we’ve come, the significant efforts underway, and our firm commitment to future work. As our many partners share data and outcomes to a central place, the mission of protecting communities and natural resources will remain the common thread driving our work. This new tool will also provide first responders a snapshot of where treatment has occurred to help inform fire suppression efforts.”
The dashboard is an important step to increase the pace and scale of statewide actions addressing California’s wildfire crisis and is a key deliverable of the Governor’s Wildfire and Forest Resilience Action Plan , issued by the Task Force in January 2021.
The beta version of the dashboard will continue to be refined to include additional data, including projects by local and tribal entities, along with revisions based on public feedback. An official launch is expected in spring 2024 with more complete data on projects implemented in 2022.
Contact Information:
Sky Biblin, Communications Coordinator
Governor’s Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force
916-502-6527
Albert Lundeen, Director of Media Relations
California Natural Resources Agency
albert.lundeen@resources.ca.gov
916-606-3990
D’Artanyan Ratley, Public Affairs Specialist
USDA Forest Service
California’s Joint Strategy for Sustainable Outdoor Recreation & Wildfire Resilience

California’s Joint Strategy for Sustainable Outdoor Recreation & Wildfire Resilience
This Joint Strategy, developed by the Task Force Sustainable & Accessible Recreation Key Working Group, provides a roadmap for improved access to sustainable outdoor recreation, with a focus on areas where wildfires are impacting those opportunities throughout California.
RESOURCES
The 2021 Caldor Fire: One Year Later Video Series

The 2021 Caldor Fire: One Year Later Video Series
October 21, 2022, marks exactly one year since the Caldor Fire was completely contained.
Over the last year and with months of research and collaboration, the Eldorado National Forest released a four-part series examining the Caldor Fire. This series reviews the suppression efforts that took place, the fire behavior challenging firefighters, the road to rehabilitation and restoration, and what is being done now to lower the future risk of fire to communities.
RESOURCES
Episode 1: Initial response and experiences of firefighters who not only worked but also lived in the area
Episode 2: How fire behavior and fuel conditions made for a challenging fire fight
Episode 3: What restoration and rehabilitation work has occurred and its importance
Episode 4: What is being done to reduce extreme wildfire behavior
Biden Signs Inflation Reduction Act Affecting Health, Climate and the Economy

Biden Signs Inflation Reduction Act Affecting Health, Climate and the Economy
Biden Signs Inflation Reduction Act Affecting Health, Climate and the Economy. On August 16, President Biden signed a landmark climate change and health care bill into law. The Act includes the most substantial federal investment in history to fight climate change — some $375 billion over the decade, and significant investments in wildfire and forest resilience including:
Wildfire Resilience and Ecosystem Restoration
- $1.8 billion for hazardous fuels reduction projects on National Forest System land within the wildland-urban interface.
- $200 million for vegetation management projects on National Forest System land.
- $250 million for conservation, ecosystem, and habitat restoration projects on National Park Service and Bureau of Land Management lands.
Climate-Smart Forestry for Non-Federal Forest Landowners
- $450 million for grants to support climate mitigation, forest resilience, and carbon sequestration and storage practices.
Urban and Community Forests
- $1.5 billion for competitive grants to cities, tribal nations, nonprofits, and other eligible entities.
Forest Conservation
- $700 million for competitive grants through the Forest Legacy Program.
Forest Products and Innovation
- $100 million for grants under the Wood Innovation Grant Program.
RESOURCES
Wildfire Resilience Work Helps Save Yosemite Sequoias
Wildfire Resilience Work
Helps Save Yosemite Sequoias
photo credit: New York Times
Fuels Reduction Partnerships Pay Off In Controlling The Washburn Fire
Some of the world’s most iconic trees in one of the world’s most famous forests are safe today thanks in part to resilience treatments funded through CAL FIRE’s Forest Health grant program.
“This project has meant the difference for the community and the grove. I suspect that if Wawona Road was in the state that it was prior to the project, it could be a very different outcome for the Mariposa grove and the community.”
– Garett Dickman, National Park Service Vegetation Ecologist
photo credit: New York Times
Protecting the ancient, majestic giant sequoias in the largest and most popular of Yosemite’s sequoias clusters was an immediate concern for land managers when the Washburn Fire broke out near Mariposa Grove. Fortunately, a partnership that includes the Mariposa County Resource Conservation District, National Park Service and local private landowners had done the important fuels reduction work that reduced the fire’s severity and helped firefighters protect the invaluable trees.
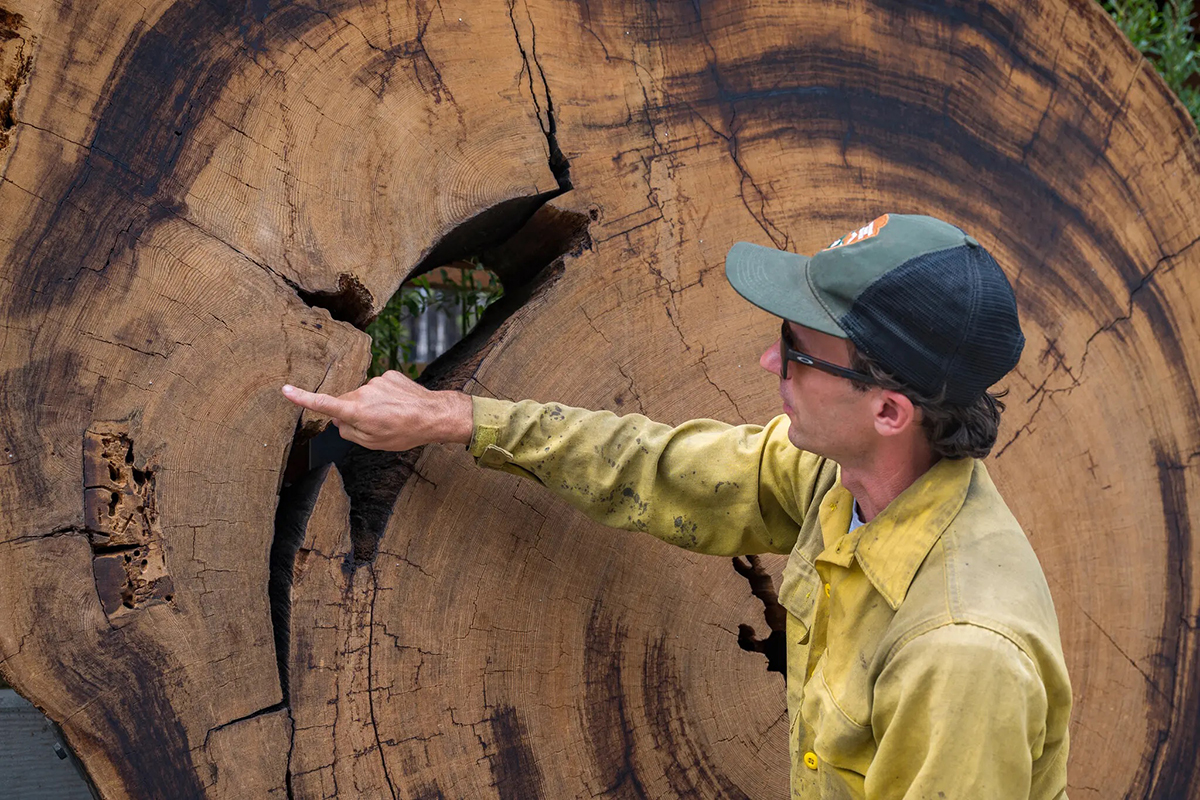

Garrett Dickman, a Vegetation Ecologist at Yosemite National Park was on the fire and observed its behavior. Referring to biomass removal treatments along a key road in the park, he said, “Firefighters [were] able to hold the road with minimal prep,” and the fuels reduction was “…proving critical in our ability to protect the community of Wawona.” Dickman pointed out that flame heights were a few inches to a just a few feet in treated areas, compared to flames that were tens to hundreds of feet long elsewhere.
photo credit: New York Times
CAL FIRE Forest Health provides funding to local and regional organizations that coordinate multiple treatment objectives, within landscape scale projects. Objectives include fuel reduction, prescribed fire, reforestation, biomass utilization and pest management. Land may be owned by tribes, private individuals, private companies, and local, state, or federal governments. The Washburn Fire is a good example of the critical impact these projects have in slowing the spread of wildfire, promoting forest health and, in this case, protecting some California’s most iconic natural treasures.
RESOURCES
CalRec Vision Whitepaper

CalRec Vision Whitepaper
Over several months in 2020, MLTPA convened and facilitated an advisory committee of federal, state, and regional participants, which met and produced the CALREC Vision white paper. This white paper sufficiently inspired the California Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force to task MLTPA with the establishment, convening, and facilitation of the Key Working Group to deliver Key Actions 3.13 and 3.14 from California’s Wildfire & Forest Resilience Action Plan.
Congress' plan to save California’s giant sequoias from worsening wildfires

Congress' plan to save California’s giant sequoias from worsening wildfires
Over the past two years, nearly a fifth of all giant sequoias, once considered virtually immune to wildfire, burned so badly they died. Fire experts fear more lethal blazes are imminent.
In a rare show of bipartisanship, California’s Democratic Rep. Scott Peters of San Diego and Republican House Minority Leader Kevin McCarthy of Bakersfield plan to introduce the Save our Sequoias Act, a bill that would provide money and support to restore and help fireproof the venerable giants.


