Forest Stewardship and Post-fire Forest Resilience Projects 2022 Annual Report

Forest Stewardship and Post-fire Forest Resilience Projects 2022 Annual Report
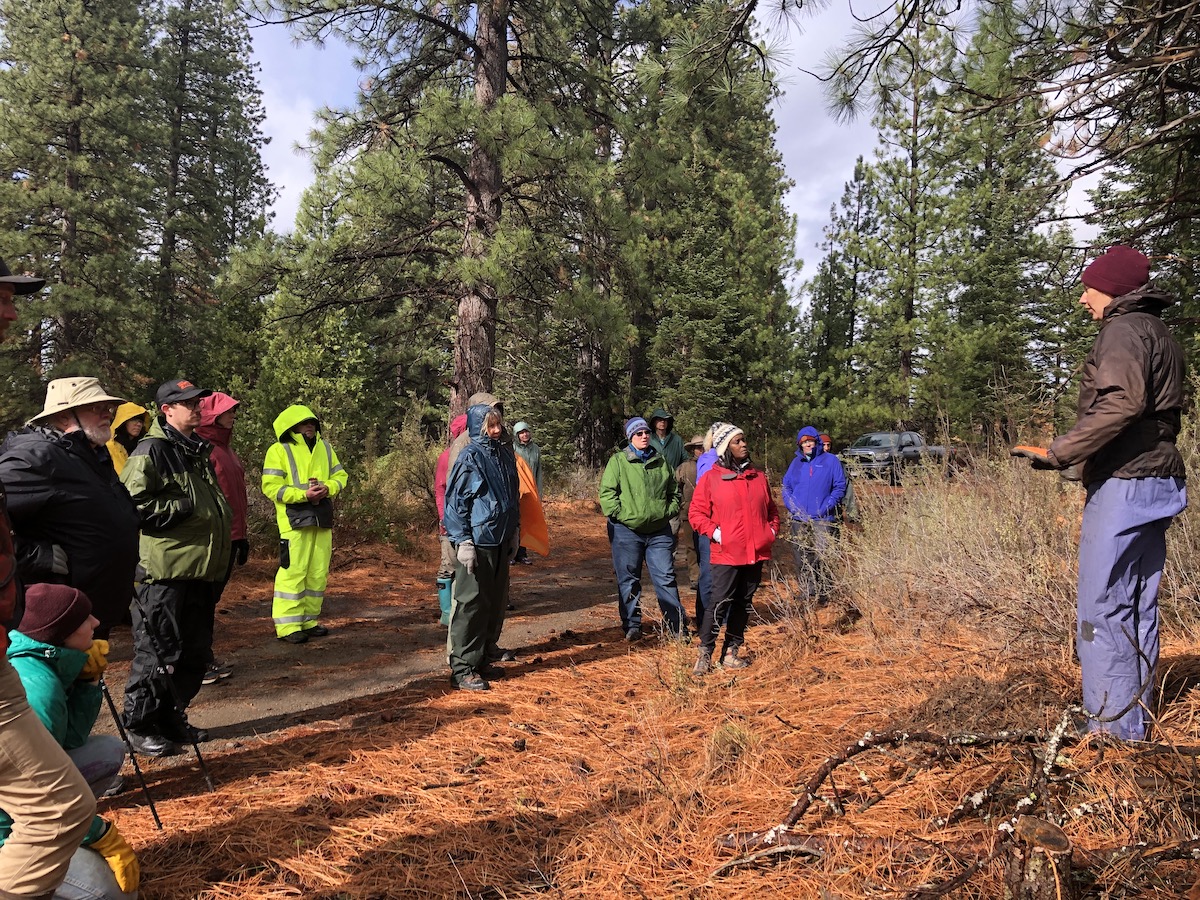
Launched in 2019 in response to a recommendation by Governor Brown’s Forest Management Task Force the UC ANR Forest Stewardship Education Initiative established the Forest Stewardship and Post-Fire Resilience Programs. These programs involve forest landowners in managing and protecting their forests through the development of a forest management plan. Since 2020, 368 people have completed one of the 19 workshop series offered across the state. The 2022 Annual Report summarizes the impact of the programs.
Regional Resource Kits and Profiles Are Now Available

Regional Resource Kits and Profiles Are Now Available
The Task Force’s Science Advisory Panel has completed Regional Resource Kits and Regional Profiles for both the Sierra Nevada and Southern California regions. These invaluable tools are now available here on the Task Force website.
Regional Resource Kits offer critical tools and data to guide regional partners and collaboratives in their efforts to reduce wildfire hazard and improve the conditions of forested and shrub landscapes.
Likewise, Regional Profiles bring together the best available scientific information and a wide range of input from stakeholders throughout the region.
The Science Team will now focus on collecting data and tools for the Central Coast in preparation for the May 2023 Task Force meeting.
SNC to Pilot Wildfire Resilience Landscape Investment Strategy

SNC to Pilot Wildfire Resilience Landscape Investment Strategy
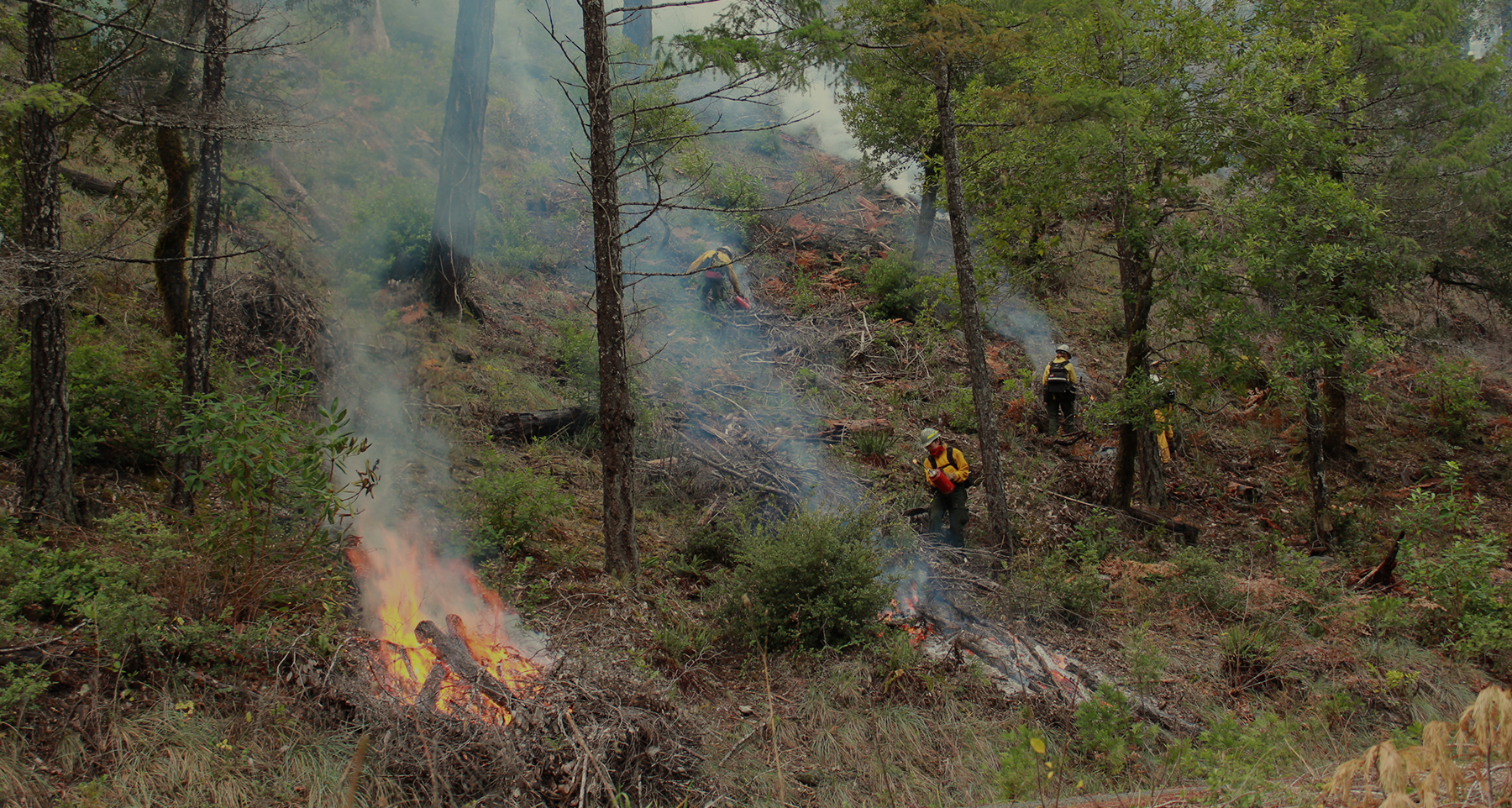
Made possible by increased state and federal funding and cooperation, the the Landscape Grant Pilot Program will give land managers a new tool that seeks to meet the wildfire crisis where it is occurring—at the landscape level. The program will seek to align funding from multiple entities to provide one or two large landscape grants that support strategic portfolios of projects across large landscapes over a 5- to 10-year timeframe. The program will help SNC implement its Sierra Nevada Landscape Investment Strategy
RESOURCES
Fighting the Goldspotted Oak Borer Instructional Video

Fighting the Goldspotted Oak Borer Instructional Video
Oak Grove, a small San Diego backcountry community, is a success story in stopping an invasive, tree-killing pest from attacking California’s beautiful native oaks. The Goldspotted Oak Borer (GSOB) is a deadly invasive pest that that is threatening California’s oak trees. In this video, UC wildlife biologist Dr. Tom Scoot and arborist Bret Hutchinson summarize proven techniques for identifying and treating GSOB.
RESOURCES
San Diego RCD Fire Safe Council
Village News, 8/27/22: Learn how to protect California oak trees from a deadly, invasive pest
Wildfire-Safety Work Completed in South Fork Mokelumne Watershed
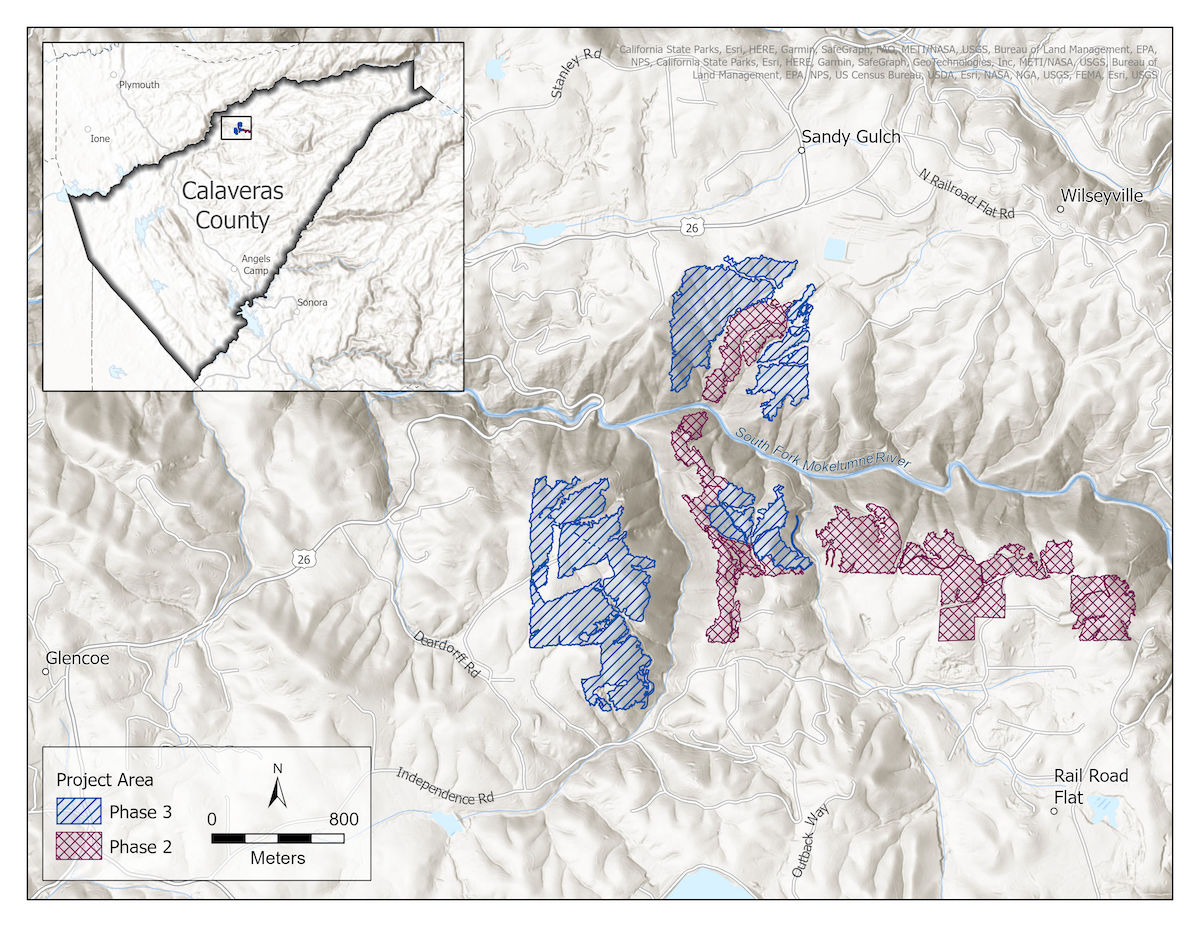
Wildfire-Safety Work Completed in South Fork Mokelumne Watershed
One year after the 2015 Butte Fire destroyed nearly 500 residences nearby, CAL FIRE identified the South Fork Mokelumne River watershed as a top priority for fuels reduction in order to protect communities from future wildfires. With the recent completion of the South Fork Mokelumne River Watershed Restoration Project Phase 3, many of those wildfire worries have, fortunately, been doused.
Funded by the Sierra Nevada Conservancy (SNC) in 2019, Phase 3 removed small-diameter trees and ladder fuels on 285 acres of dense, pine-plantation forests managed by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM), completing the project’s goal of restoring roughly 500 acres of forest. Considering the project area borders many neighborhoods and is surrounded by nearby towns, such as Glencoe, Sandy Gulch, Rail Road Flat, and Wilseyville, this strategic work should greatly reduce the threat of wildfire for thousands of Calaveras County residents.
Jackson Demonstration Forest: A Great Recreation Choice
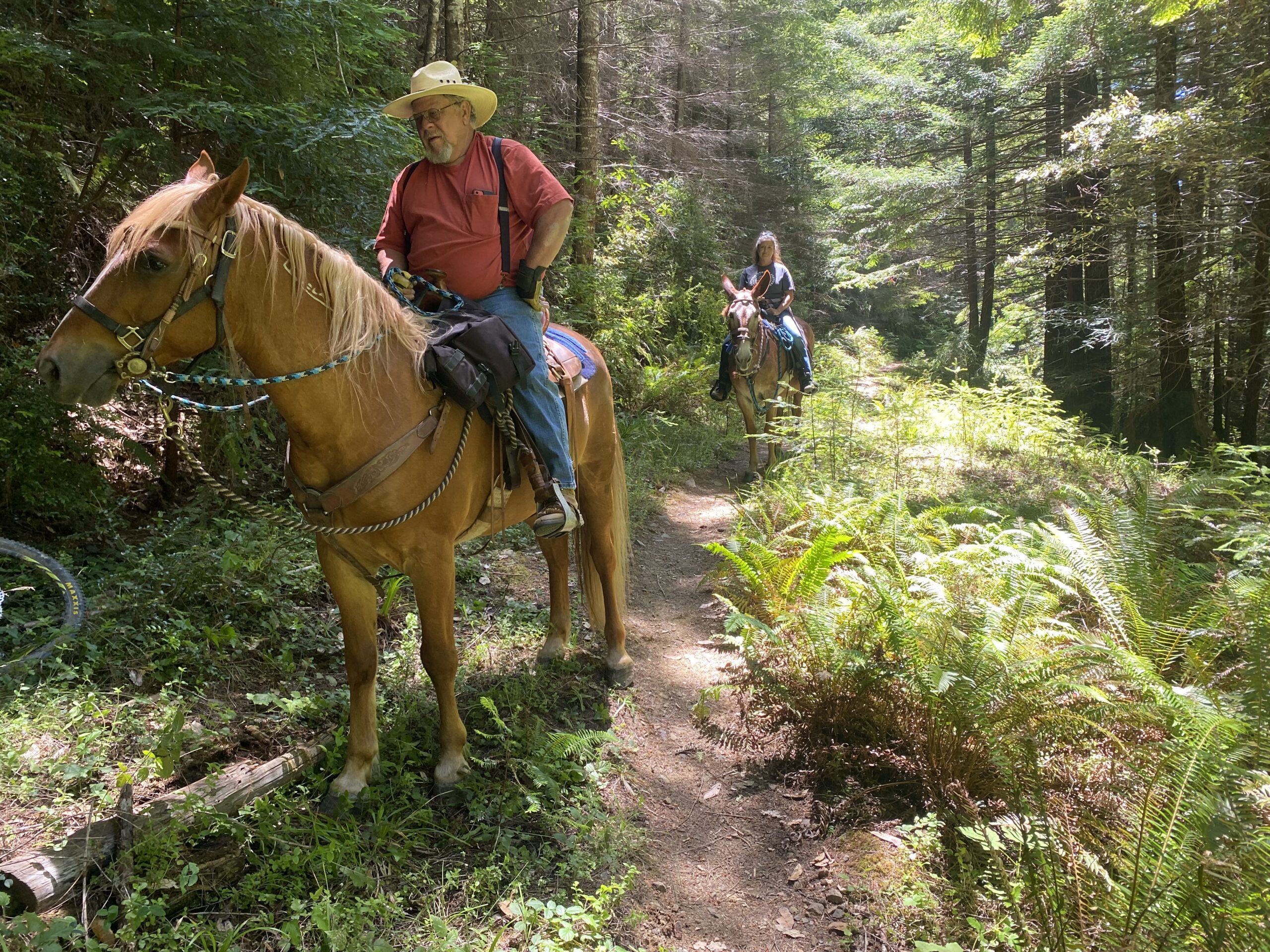

Jackson Demonstration Forest: A Great Recreation Choice
California’s demonstration state forests serve as a living laboratory for how to care for and manage California’s forest lands for multiple benefits—wood products and timber production, recreation, watershed protection, and habitat restoration—given a changing climate and increasingly severe and intense wildfire seasons. The forests provide unique research and demonstration opportunities where environmental scientists, foresters, and other researchers can study the effects of various forest management and restoration techniques that help inform management practices for government, nonprofit and private forestland owners.
Common activities on state forests include experimental timber harvesting techniques that test the Forest Practice Rules, watershed restoration, mushroom collecting, hunting, firewood gathering, cone collecting for seed, a variety of university research projects, horseback riding, camping, mountain biking, and hiking.
Jackson is the largest of CAL FIRE’s ten demonstration state forests. The area has a long history of logging which began in under private ownership 1862 then evolved into sustainable harvesting after the State’s purchase of the property in 1947. Today, more forest growth occurs each year than is harvested. The most common tree on the forest is coast redwood, but visitors will also find Douglas-fir, grand fir, hemlock, bishop pine, tanoak, alder, madrone and bay myrtle.
RESOURCES
U.S. Economic Development Administration Awards $21.5 Million for CA Workforce Training

U.S. Economic Development Administration Awards $21.5 Million for CA Workforce Training in Forest Health and Fire Safety
Through its proposed CA Resilient Careers in Forestry program, the Foundation for California Community Colleges (FCCC) will partner with employers, educational institutions, and local community-based organizations to build a state-wide infrastructure for training in forest health and fire safety. The 32 winning projects were selected from a pool of 509 applicants.
RESOURCES
U.S. Department of Commerce Announces Winners of American Rescue Plan $500 M Good Jobs Challenge to Expand Employment Opportunities
LA Times Op-Ed: Why Forest Managers Need To Team Up With Indigenous Fire Practitioners

LA Times Op-Ed: Why Forest Managers Need To Team Up With Indigenous Fire Practitioners
Los Angeles Times, July 31, 2022, By Don Hankins, Scott Stephens and Sara A. Clark
The forests of the Western United States are facing an unprecedented crisis, besieged by wildfires and climate change. There is a precedent for part of the solution, though: intentional burns such as those set by Indigenous peoples.
RESOURCES
Grant Guidelines Released for the 2022 Regional Forest & Fire Capacity Program

Grant Guidelines released for the 2022 Regional Forest & Fire Capacity Program
RFFC grants support regional leadership to build local capacity and fund projects that create fire-adapted communities and landscapes by providing ecosystem health, community wildfire preparedness, and fire resilience. The grants funded with these Guidelines utilize the $110 million of General Fund monies appropriated to the DOC for the RFFC Program.
Administration Announces $1 Billion in Community Wildfire Defense Grants

Biden-Harris Administration Announces $1 Billion in Community Wildfire Defense Grants from Bipartisan Infrastructure Law
On July 26, Agriculture Secretary Tom Vilsack launched a new $1 billion Community Wildfire Defense Grant Program. Under this new, five-year, competitive program funded by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law individual grants of up to $250,000 will be awarded to create and update community wildfire protection plans or conduct outreach and education, and grants of up to $10 million will be awarded for associated infrastructure and resilience projects. Applications will be available soon. Local and Tribal governments are encouraged to conduct planning exercises to assist their communities with wildfire preparedness, response and adaptation efforts.
